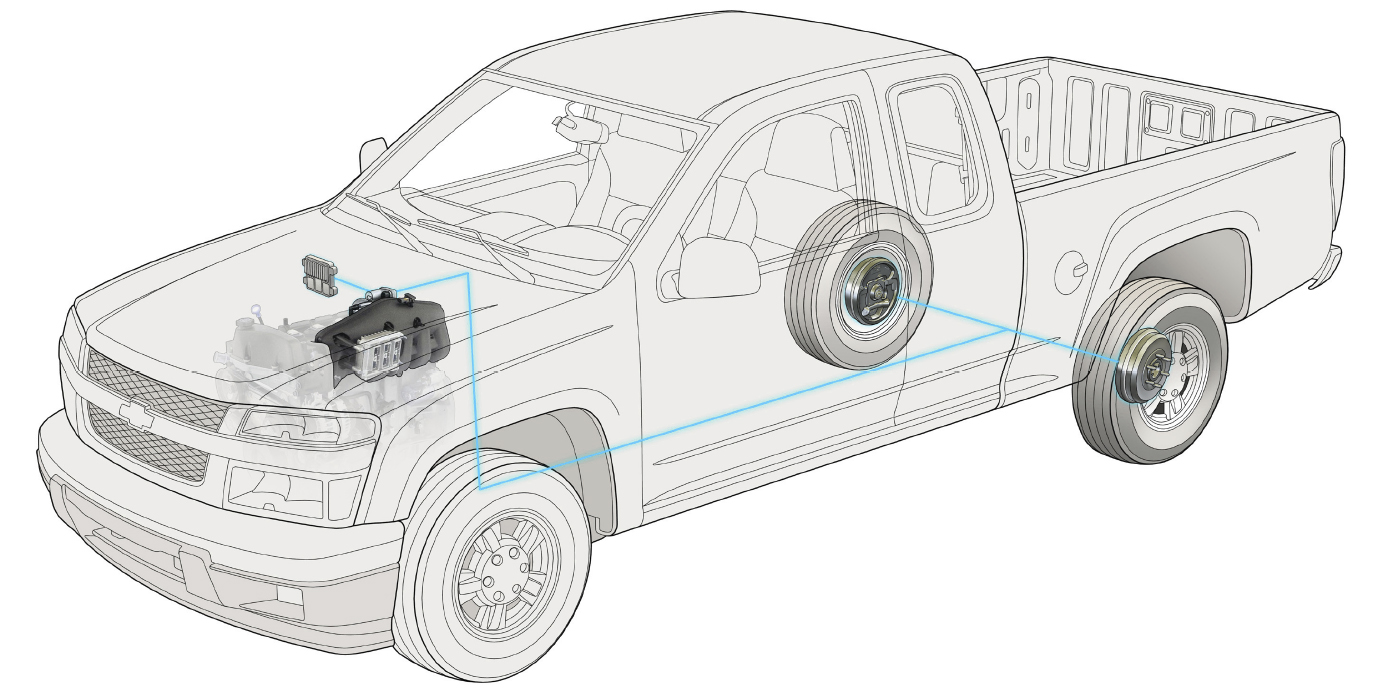
The BMW 1-Series might be the least expensive BMW, but it shares a lot of the procedures that are common when it comes to servicing brakes on larger BMWs.
BMW can be one of the most confusing cars to order parts for because with some parts people like to talk in chassis or platform numbers instead of year, make and model. The BMW 1-Series is no different. To BMW drivers and parts pros, the first-generation of the 1-Series goes by the designations of E81, E82, E87 and E88. For that production series, those codes indicate the number of doors and if it is a hatchback or convertible.
Service Calculator
When an inner brake pad reaches 5mm of material, it triggers the wear sensor. The sensor causes a warning in the Condition Based Services menu explaining the brakes will need to be serviced within a recommended mileage. If the car is still equipped with a functioning TeleServices system, it will set the mileage so it falls with other services like an oil change. This can “bundle” these together, so the customer does not have to make multiple trips to the dealer. The service messages typically will indicate that service is due or recommended, but the recommended mileage will usually never exceed 2,500 miles. If you are performing any service work or replacing the brake pads, you need to reset the reminder using a scan tool or by going in through the driver information center.
Front Brakes
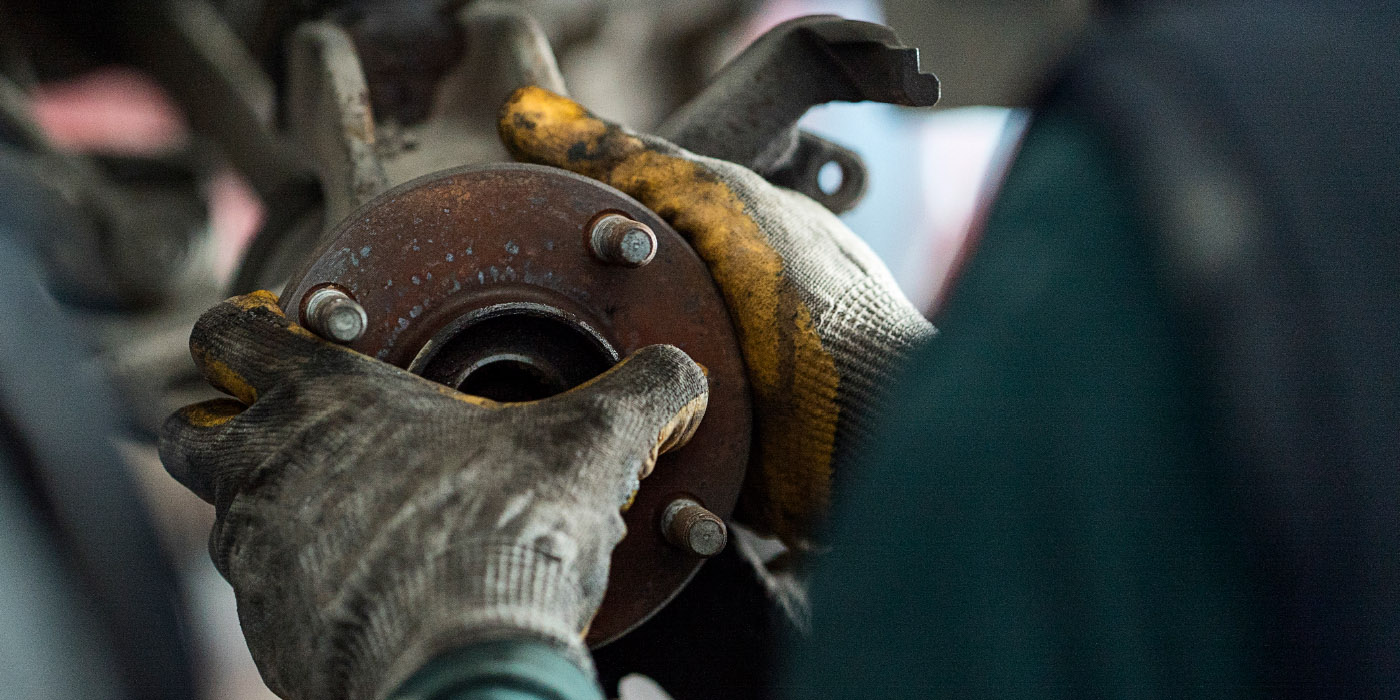
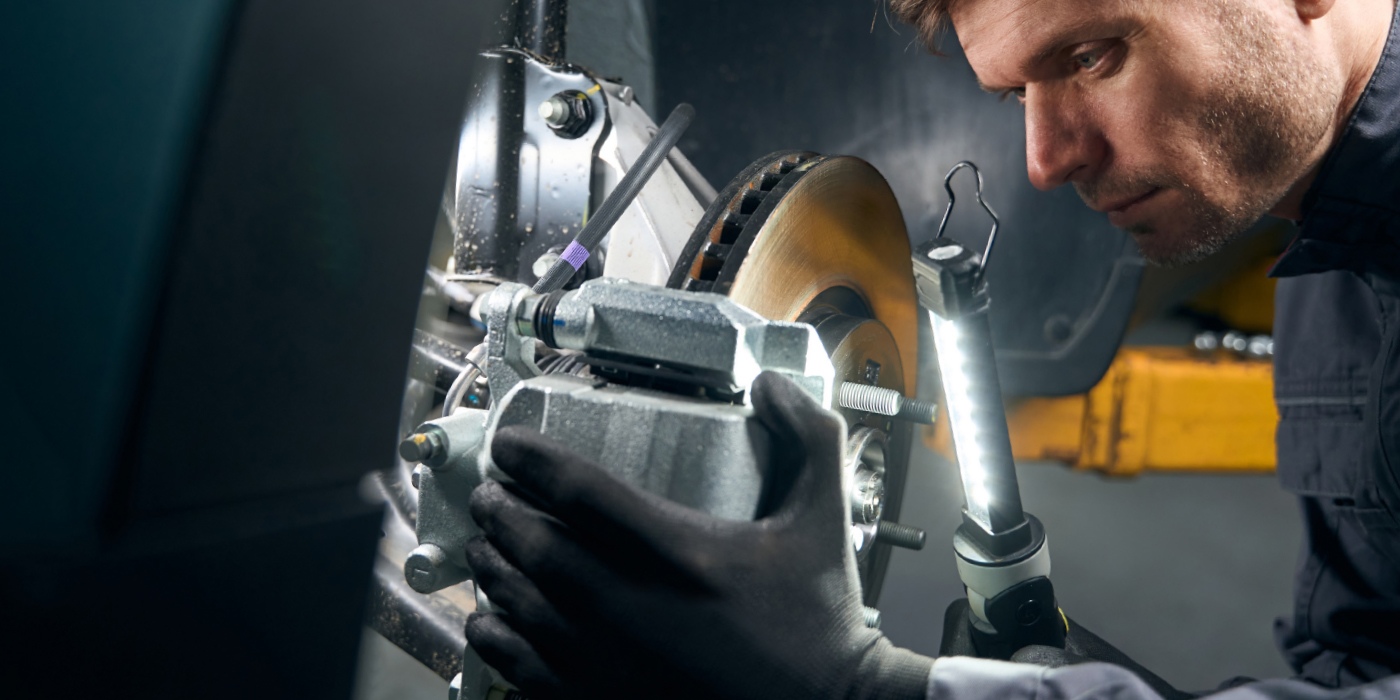
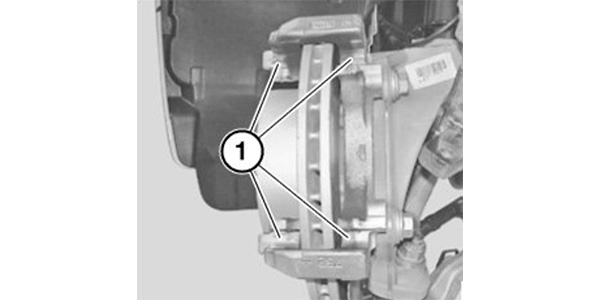
The 1-Series has two front brake options. The first is a single-piston floating caliper. BMW does not recommend cleaning the caliper bracket pad guides with a wire brush or bench grinder (see Figure 1). Instead, the recommended procedure is to clean them with a solvent and apply a thin layer of brake paste or high-temperature brake lubricant. This method is recommended because the bracket is plated with an anti-corrosion layer that can be removed. In the BMW service information, they suggest that the anti-rattle clip needs to be replaced if it is older than four years.
The optional Brembo brakes have six pistons, and the pads are mounted to guide pins. The pads need to be properly seated on the guide pins. The pins should not be lubricated. When installing the pads, make sure not to damage the boots on the pistons.
New brake pad sensors should be installed every time the pads are replaced. Water can enter into the brake pad’s wear sensor connector and change the resistance in the circuit. The change in resistance caused by the oxidation of the connector pins causes a warning in the instrument cluster to illuminate. The customer may report that the problem is intermittent, with the light going out once the connector has dried out during the next ignition cycle. The connector can be cleaned with electrical contact cleaner and sealed with dielectric grease. This tends to occur on vehicles with removable wear sensors that are not replaced along with the brake pads.
Rear Brakes
The rear brakes closely resemble the front brakes. Do not damage the plated surfaces on the caliper, only clean with solvent and lubricate.
The optional Brembo package uses a two-piston caliper. The pads are held in the caliper with retaining pins and an expanding spring.
Parking Brake
If new parking brake shoes are installed or it takes more than 10 clicks to set the parking brake, inspection and adjustment of the system are necessary.
1. Pull up the boot on the lever.
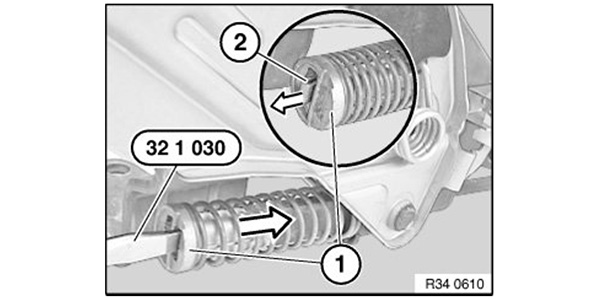
2. Pull up on the lever and with a small flathead press the stop (1) of adjusting spring back to such an extent that retaining hook (2) engages in stop (1) (see Figure 2).
3. Unscrew one wheel stud on both rear wheels.
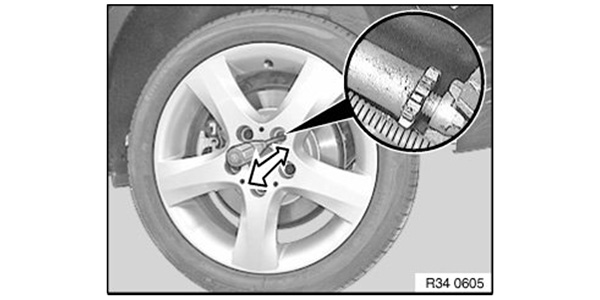
4. Turn the wheel until adjustment screw is visible in the tapped hole (see Figure 3).
5. Turn the adjusting screw with a screwdriver until the wheel cannot be turned anymore by hand.
6. Release the adjusting screw eight to nine notches.
An adjustment with fewer than eight notches may lead to the brake shoes being damaged. Reducing the number of notches on the duo-servo brake to shorten lever travel is not permitted.