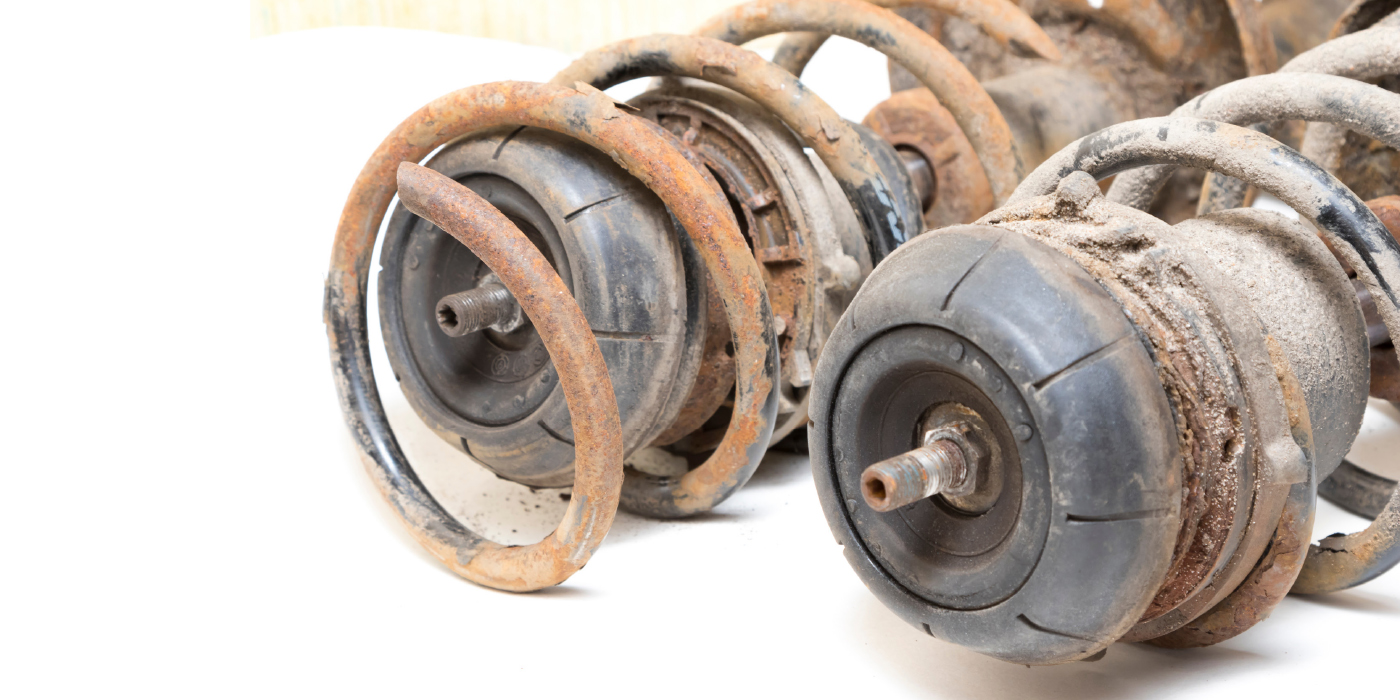
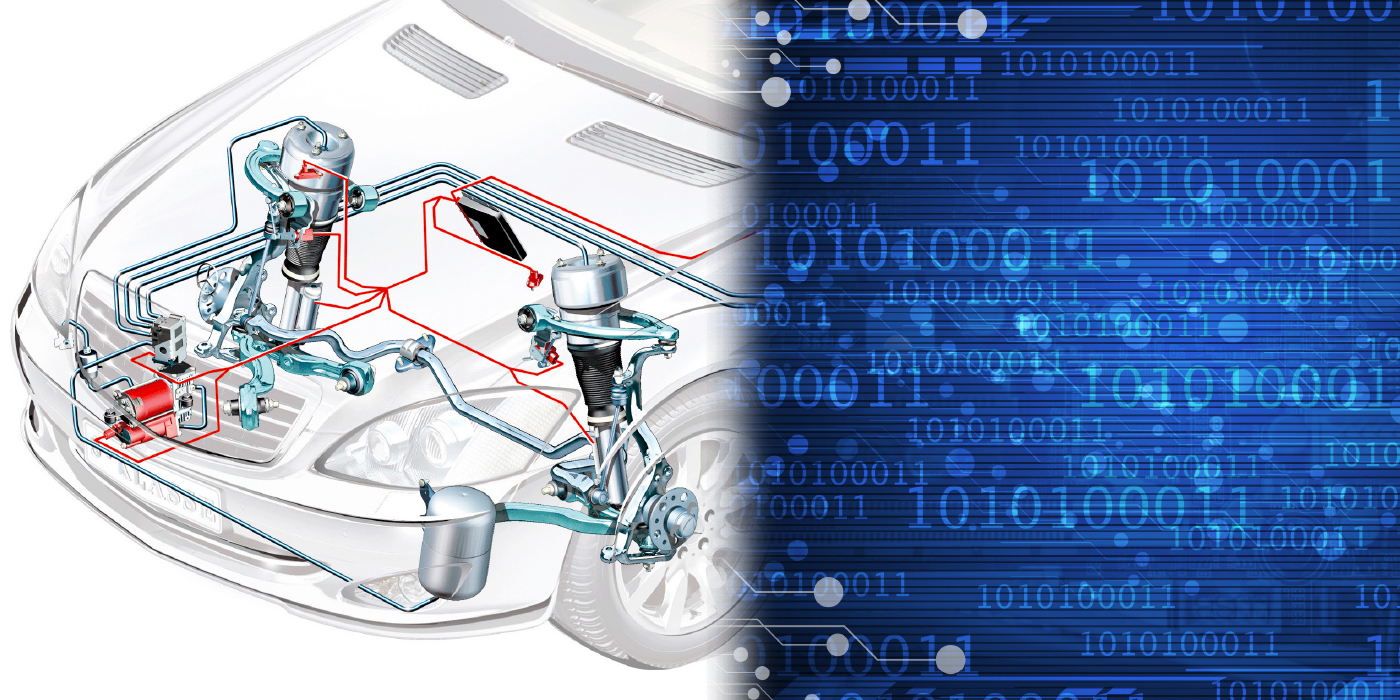
The Ford Expedition air suspension does more than just lift and raise the vehicle. The system levels the vehicle under loads and when a trailer is attached. The system uses only two air bags on the rear axle.
Before starting any work, you need to disable the system through the message center. The message center is located on the instrument cluster and displays important information through a constant monitoring of vehicle systems. Select display features on the message center for a display of status preceded by a brief chime. The system will also notify the driver of potential vehicle problems with a display of system warnings followed by a long indicator chime. The message center is used to disable and enable the vehicle air suspension system. The system will default to ON when the ignition key is cycled.
• Turn the ignition to the ON position, close all doors and clear warnings.
• Select the SETUP control function on the message center.
• Select the AIR SUSPENSION function to display the current status of the air suspension system.
• Press the RESET control to turn the air suspension OFF or ON.
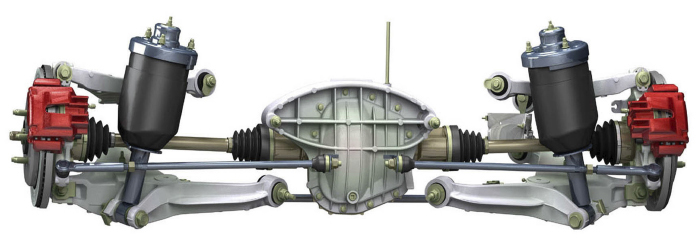
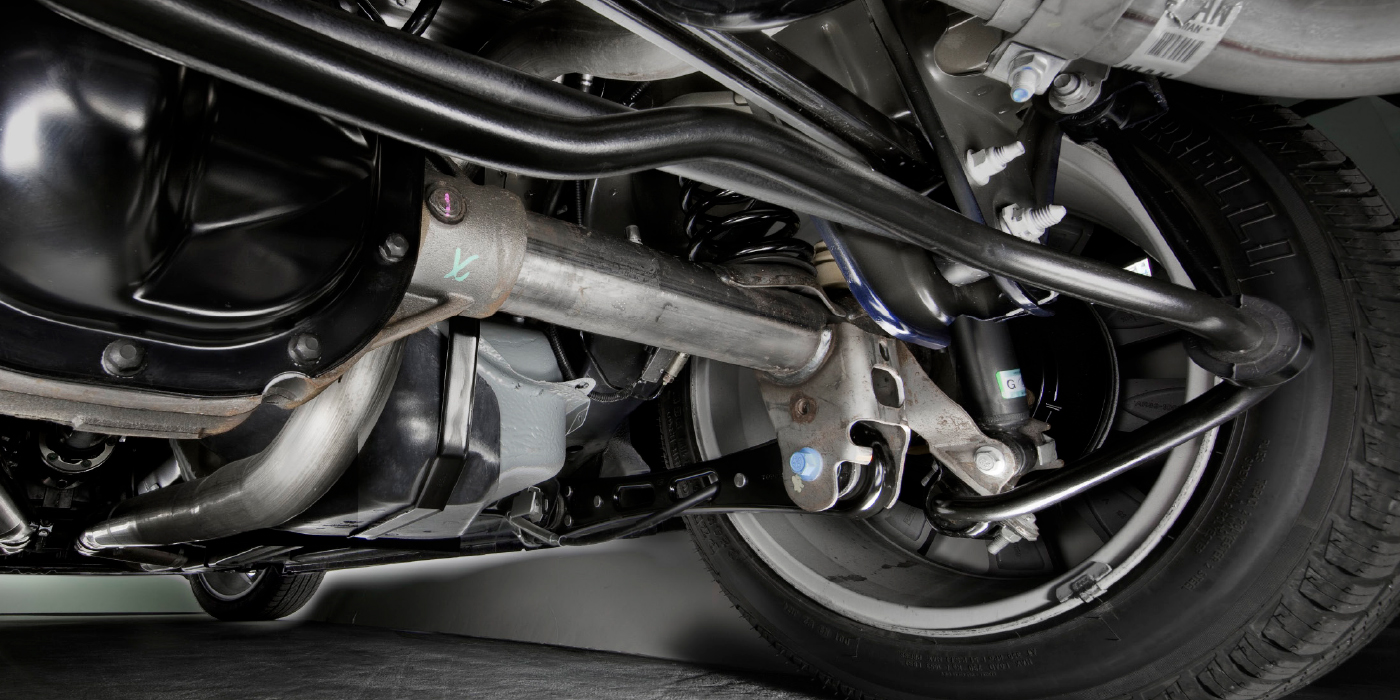
The air bag and shock absorber can be separated. Make sure you know the orientation of the upper mount and air spring before you take the assembly apart. To deflate the spring, remove the air line from the solenoid, remove the retaining clip and rotate the solenoid counter-clockwise. The O-rings on the shaft and upper mount should always be replaced and lubricated with a silicone-based spray lubricant. These help to seal the unit from outside debris.
Operation
The system uses two ride height sensors mounted to the rear axle. The voltage output decreases (goes from high to low) as the suspension system raises the vehicle. The output voltage is between 0.5 and 4.5 volts. These signals are sent to the Vehicle Dynamics Module (VDM).
Testing these sensors can be done with a meter, scope or scan tool. With a meter, it is possible to observe changes in the voltage or resistance.
The air bags have solenoids mounted to the side that allow the bladder to either fill or compress. There is no air reservoir on this system.
When the key is in the ON position, the load leveling feature automatically makes adjustments to the vehicle height so that the vehicle is always at target height and constant front-to-rear vehicle attitudes are maintained when loads change.
When the key is in the OFF position, the system will remain active for 40 minutes after the ignition is turned off, allowing the system to deflate (vent) at any time, while allowing the system to inflate only once at the end of 40 minutes.
The system also looks at vehicle speed, system voltage and even the ambient temperature to decide if an action should be taken. Also, problems with door switches and the power running boards can inhibit the air suspension from making a correction.
The system will set C- or chassis codes if the system notices abnormal behavior. These codes typically start as C17XX. Criteria for these codes typically involve a ride height sensor detecting a change in suspension height if the compressor or solenoids are activated.
Calibration
Scan tools are essential for working on some systems. Some enhanced scan tools can observe PIDs for the air ride system like valve operation, modes and vehicle position.
The Expedition’s ride height and trim can be calibrated with a scan tool. Not calibrating the ride height can result in suspension and tire damage. To do this the vehicle must be on a level surface. The ride height is measured and the scan tool can vent or fill the correct bag.