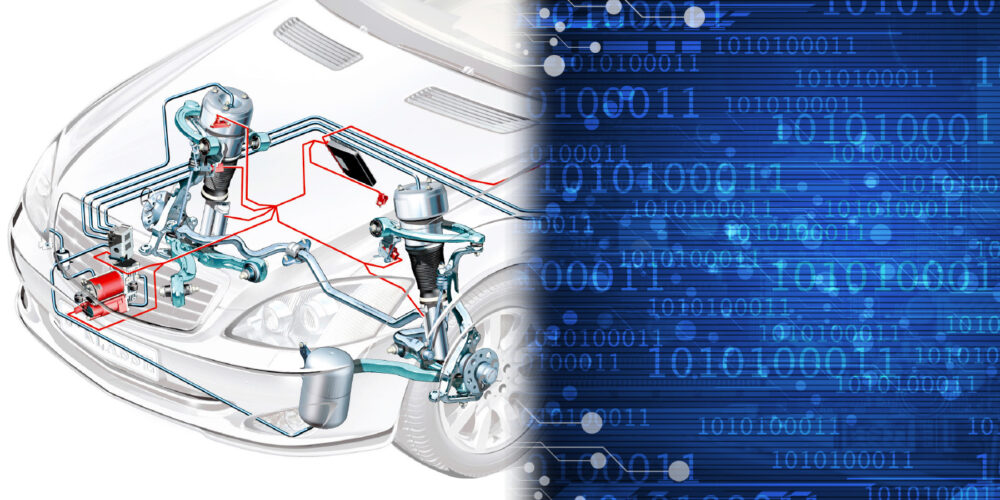
Air ride systems can control vehicle ride height, passenger comfort and improve handling. How they operate and work with the rest of the systems on the vehicle is part of their control system’s embedded logic. There are three main edicts written in this programming: preserve the compressor; keep the vehicle level; and keep the vehicle safe.
Save the Compressor, Save the System, Save the Driver
If a system has a leak, the compressor will have to work harder to keep the vehicle at the same ride height, and gets hotter the longer it has to work. Excess heat can cause premature wear of the piston rings, and, if the leak goes unchecked, it can cause the compressor to fail completely. When the pump fails, oil and metal debris can enter into the valves, reservoirs and bladders.
The computer module controlling the pump keeps track of how long the compressor has run and how long the correction should take. If a correction to ride height takes too long, the system knows that the compressor could overheat, so it can set a code and then disable the pump before it’s damaged.
Almost every air ride vehicle has a self-diagnostic process that occurs during startup. On some vehicles, if the self-check detects a problem, it will disable the system or put it in a fail-safe mode and alert the driver. It will also set a soft or pending “C” (chassis) code.
The check does a bias voltage check – a quick voltage signal applied to the circuit that needs to come back at a specific range. If a solenoid has a damaged coil, the decreased or increased resistance will cause a code. Some systems will do a quick actuation of the suspension to see if the solenoids and valves are functioning. The module will also look at the pressure in the reservoir or compressor run time to verify system integrity.
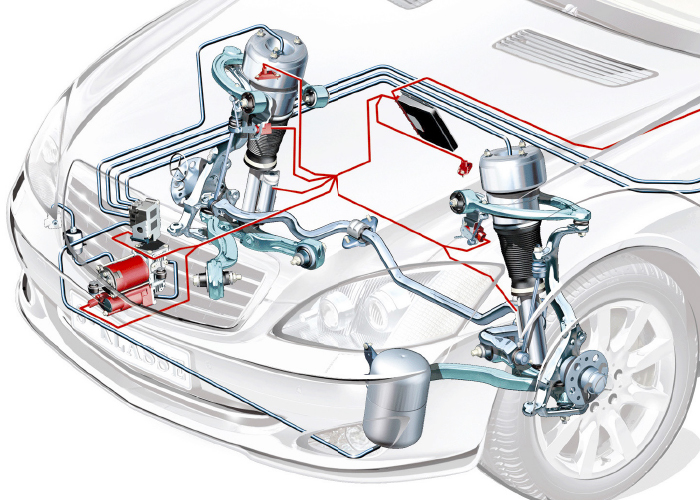
Vehicle Leveling Logic
When the air ride system detects a substantial change in position due to a load, its preprogrammed logic makes the right correction by taking into account vehicle key position, amount of movement and other information.
If the key is off, some systems may wait 10 seconds before making a correction, while some may wait until the vehicle is started. Most systems will limit compressor run-time with the key off to preserve the battery. If the vehicle is running, corrections to the ride height are smaller and more targeted at tuning vehicle attitude.
Keep the Vehicle Safe
Most intelligent air ride systems use information from the ABS and electronic stability control (ESC) system, like vehicle speed, yaw and driver inputs. If there is a problem with the air ride system, the vehicle knows the lack of body control will impact stability.
Late-model air ride systems are incorporated on the serial data bus. They can use different inputs from other systems to determine the correct position of the suspension, which can include vehicle speed, engine load and other PIDs. Likewise, the air ride module shares data with the other modules on the serial data bus. A simple failure of a door switch can prevent the system from working on some vehicles.
Rather than letting the vehicle rest on the bump stops with the compressor running non-stop, the air ride system will disable or set the suspension at a safe pressure. The vehicle will then alert the driver with a warning on the instrument panel. Some air ride systems even limit the speed of the vehicle until the problem is resolved.
Information is Key
The key to understanding the embedded logic of air ride systems is using service information, which for most vehicles is included in the “system description and operation” section. Some OEMs include tests in the service information that can pinpoint faults.
Some OEMs also have released new calibrations and programs that can be “reflashed” onto the control module. They can help to eliminate excessive key-off power drains and improve the logic of the air ride system.