TSB NUMBER: 05-002/19
Models:
2012-2013 Mazda3 (SKYACTIV A/T)
2014-2018 Mazda3 (SKYACTIV A/T)
2013-2016 CX-5 (SKYACTIV A/T)
2017-2019 CX-5 (SKYACTIV A/T except for 2.5T engine) with VINs lower than JM3KF515940 (produced before November 1, 2018) 2014-2017 Mazda6 (SKYACTIV A/T) 2018 Mazda6 (SKYACTIV A/T except for 2.5T engine) with VINs lower than JM1GL330038 (produced before November 1, 2018) 2016-2019 CX-3 (SKYACTIV A/T) with VINs lower than JM1DK427352 (produced before October 31, 2018)
Concern:
Some customers may complain of a whining noise from the automatic transaxle when driving at 10 mph and above. The noise depends on the vehicle’s speed (the more speed, the more noise). The noise also occurs with all types of driving (acceleration, deceleration and steady speed).
The whine does not depend on rpm, gear or ATF temperature.
Cause:
The whining noise is caused by a damaged bearing in the transaxle due to improper configuration of the transaxle case. A modification has now been implemented on automatic transaxles with the following serial numbers:
• 7TN0820364 and higher (CX-3) / 8TN1090104 and higher (except CX-3)
• 8TR1008883 and higher
• 8TD1003276 and higher
• 8T50331192 and higher (CX-3) / 8T50329705 and higher (except CX-3).
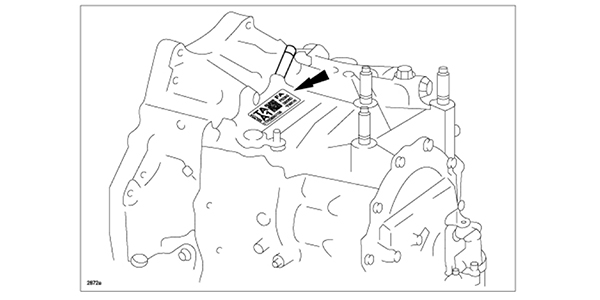
NOTE: The serial number can be found on top of the transaxle case near the manual shaft lever (see Figure 1).
Repair Procedure:
- Verify customer concern.
- Replace the 6AT assembly with a new one according to MGSS online instructions.
- Verify repair and align the vehicle.