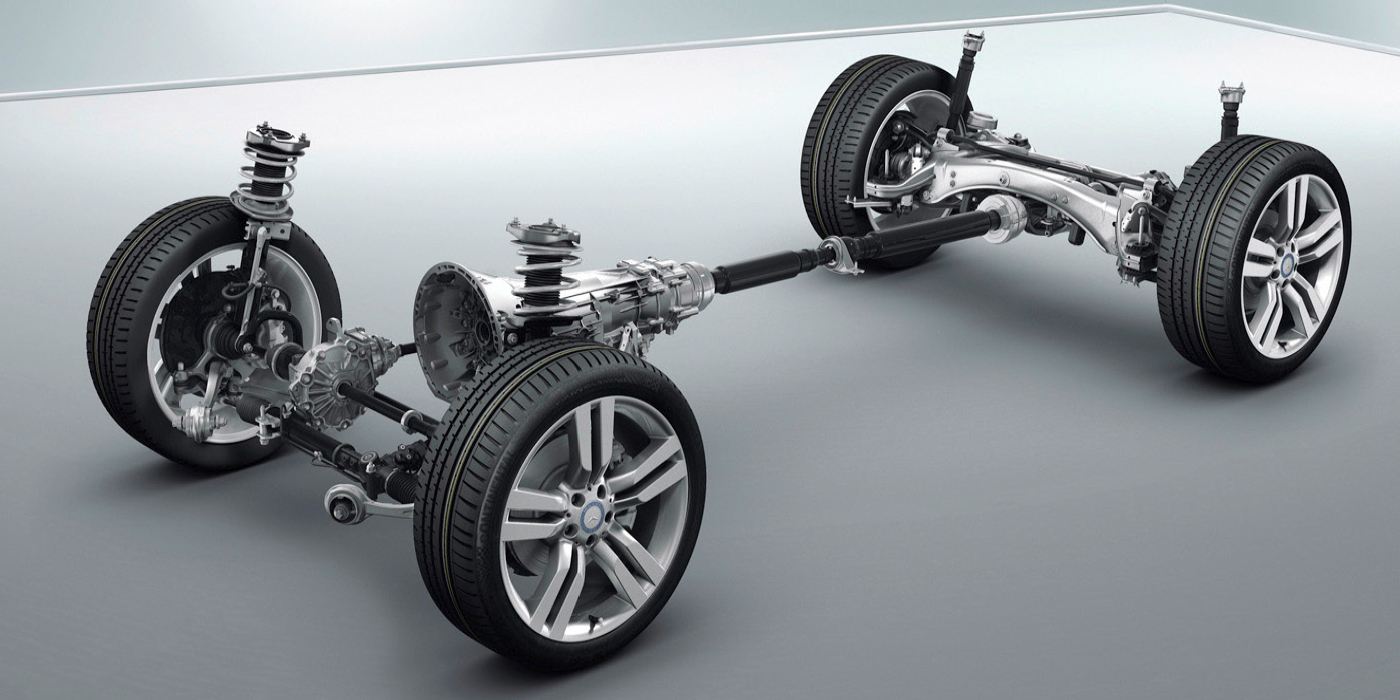
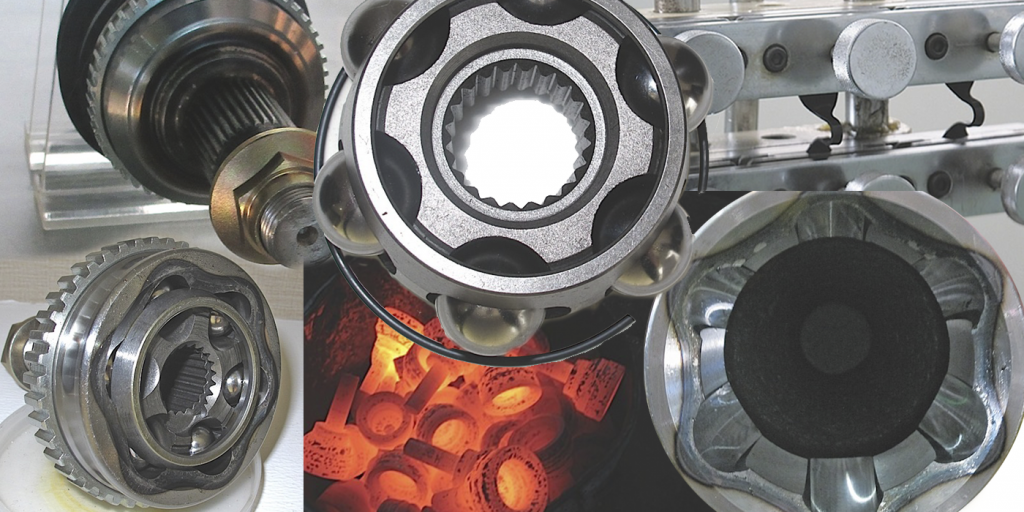
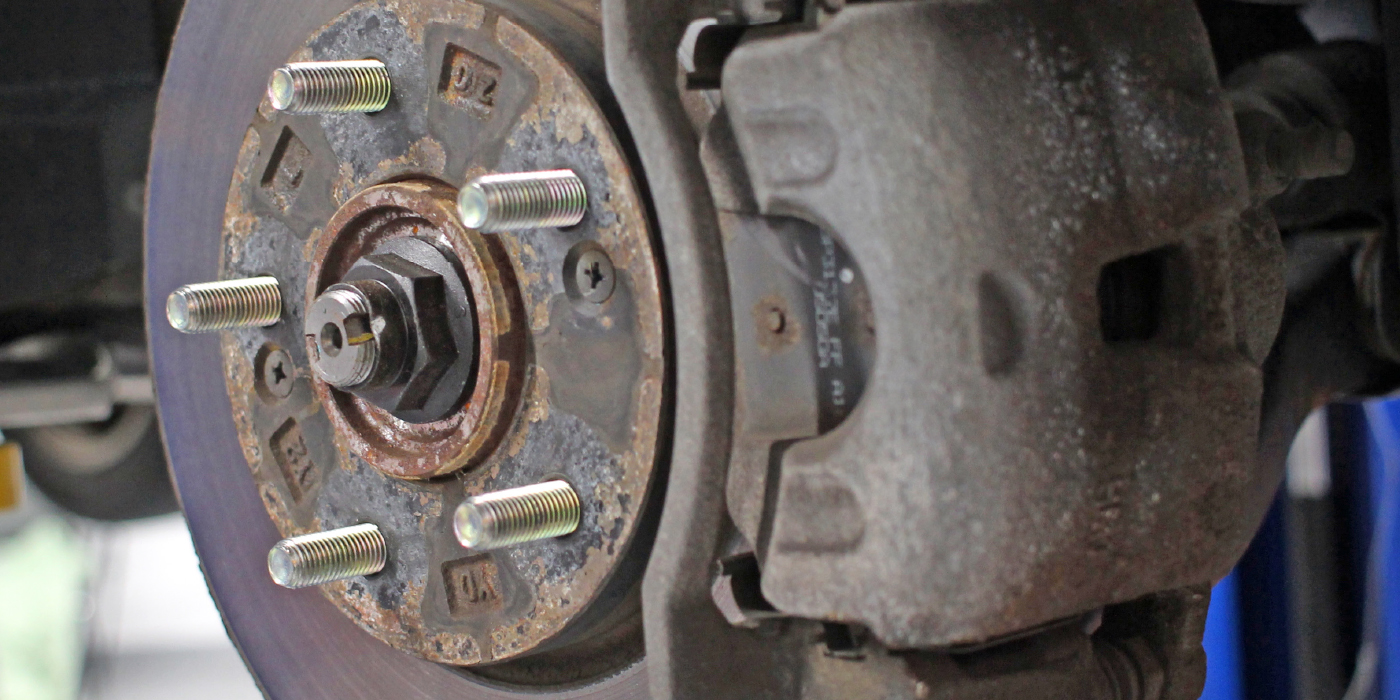
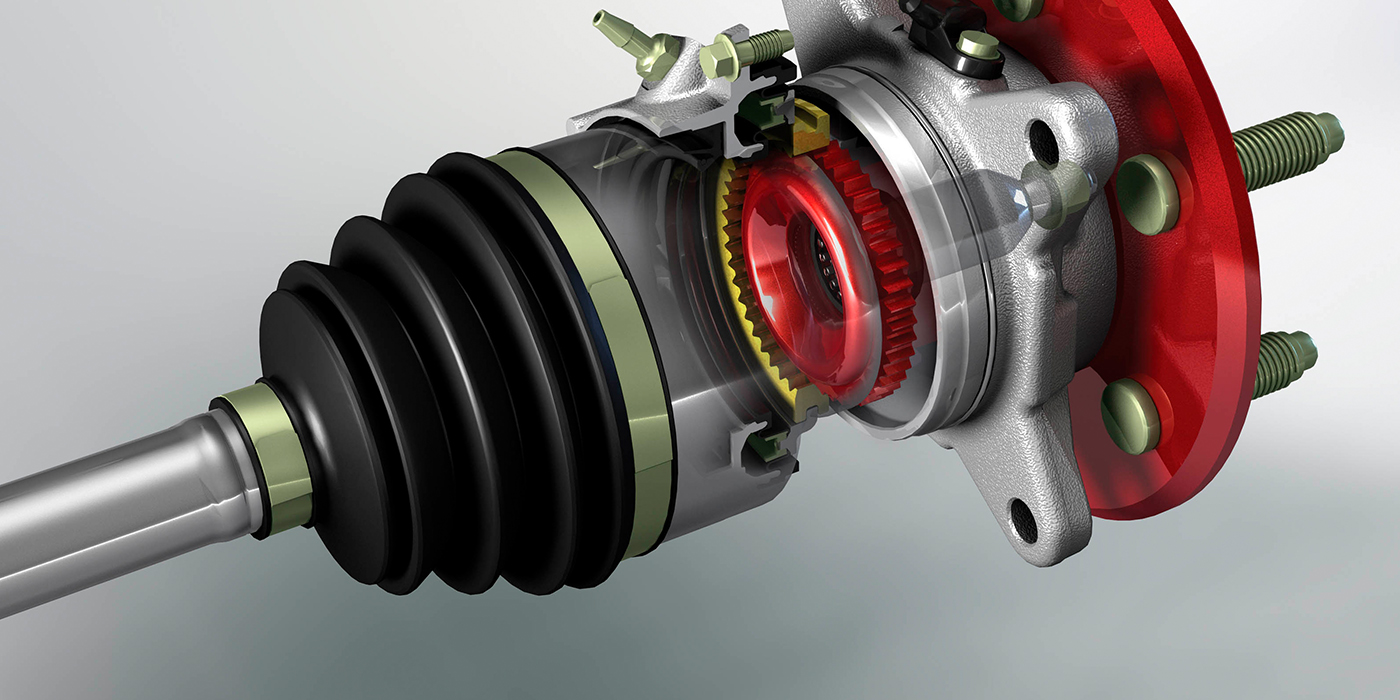
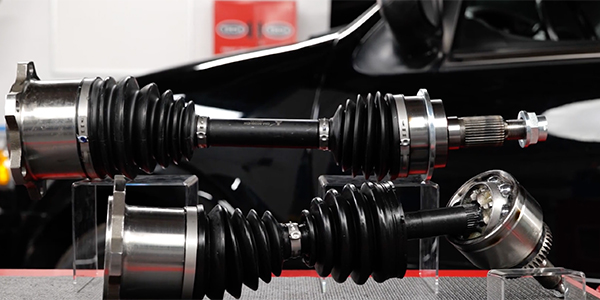
CV joint housings are typically forged from iron billets. After the joint is machined, induction heat treating is used to harden wear surfaces. Wear in a Rzeppa CV joint typically occurs on the cage, gear and cup. This wear is typically caused by a loss of lubrication due to a boot failure, or debris in the joint. Once heat treated surfaces are damaged, they typically cannot be restored.
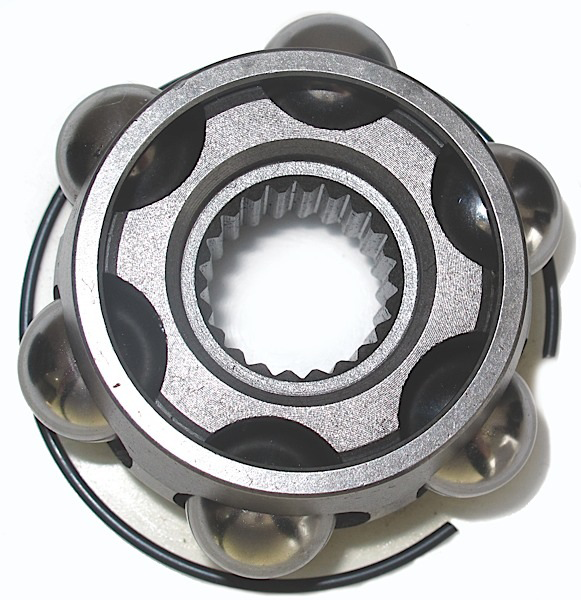
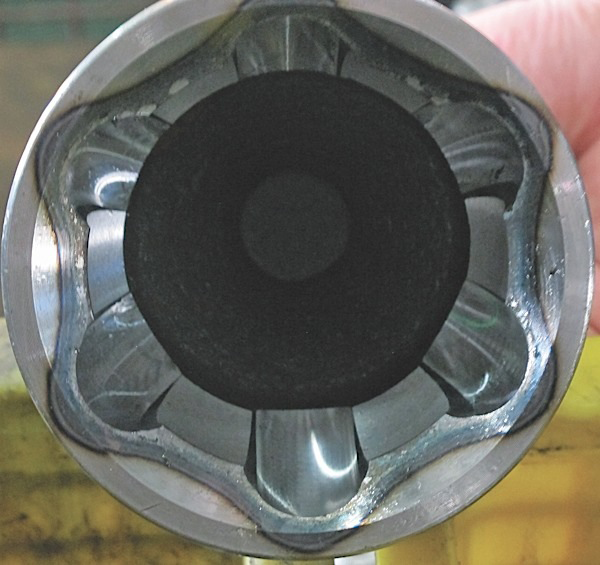


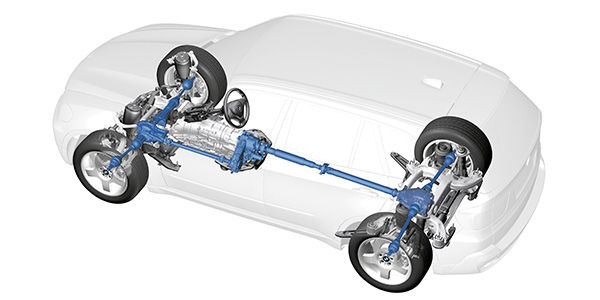
Rzeppa CV joint can be found on the majority of vehicles on the road. A typical Rzeppa joint allows 45°– 48° of articulation
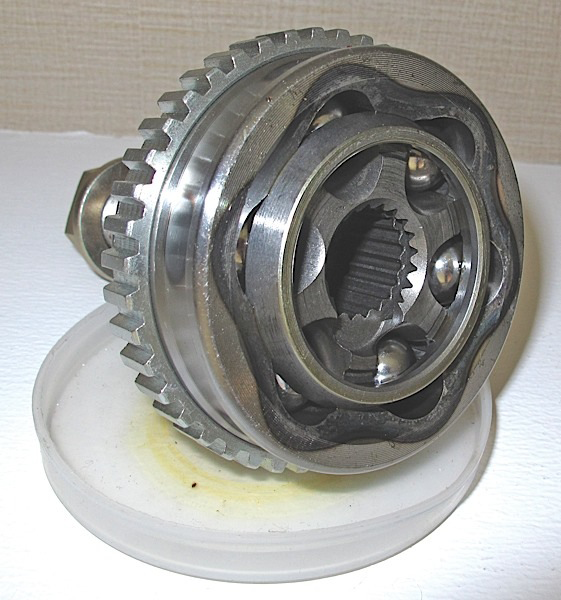

Tone rings are often pressed onto a CV joint. Make sure the number of teeth or windows match the original axle. New
axles should always get a new axle nut.
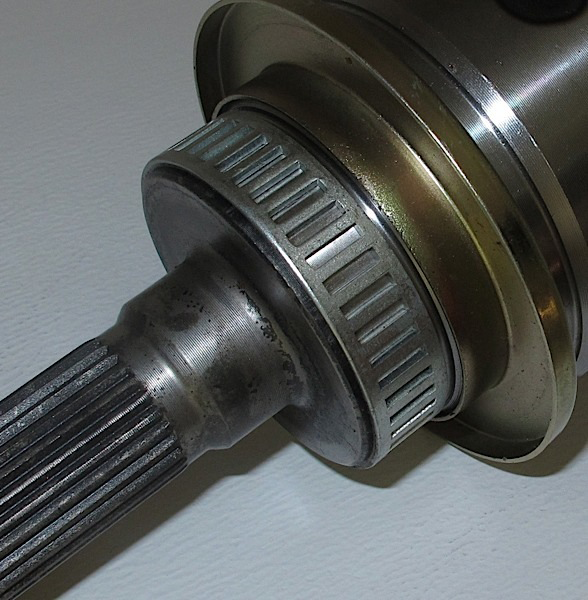
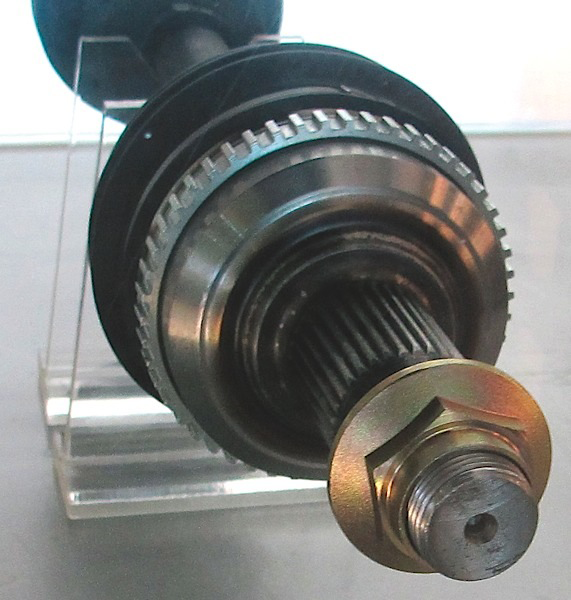


Grease is often packed by hand at the factory. If there is too much grease, the grease will be pushed out of the boot. If you are servicing a joint, use only the recommended amount of grease or only what comes in the kit.
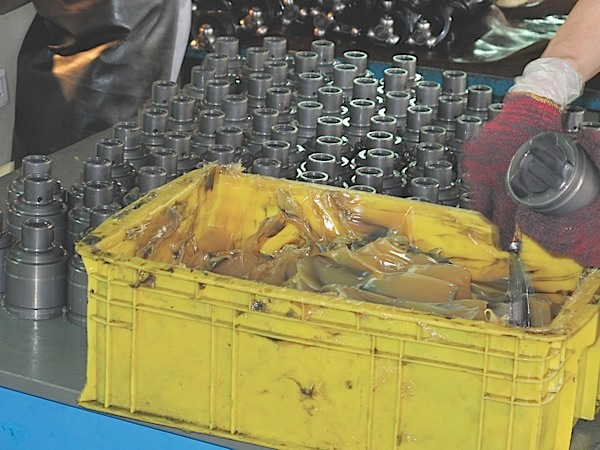

The materials used to make the boot are not just plastic or rubber. They’re designed to last millions of cycles in a wide range of temperatures.