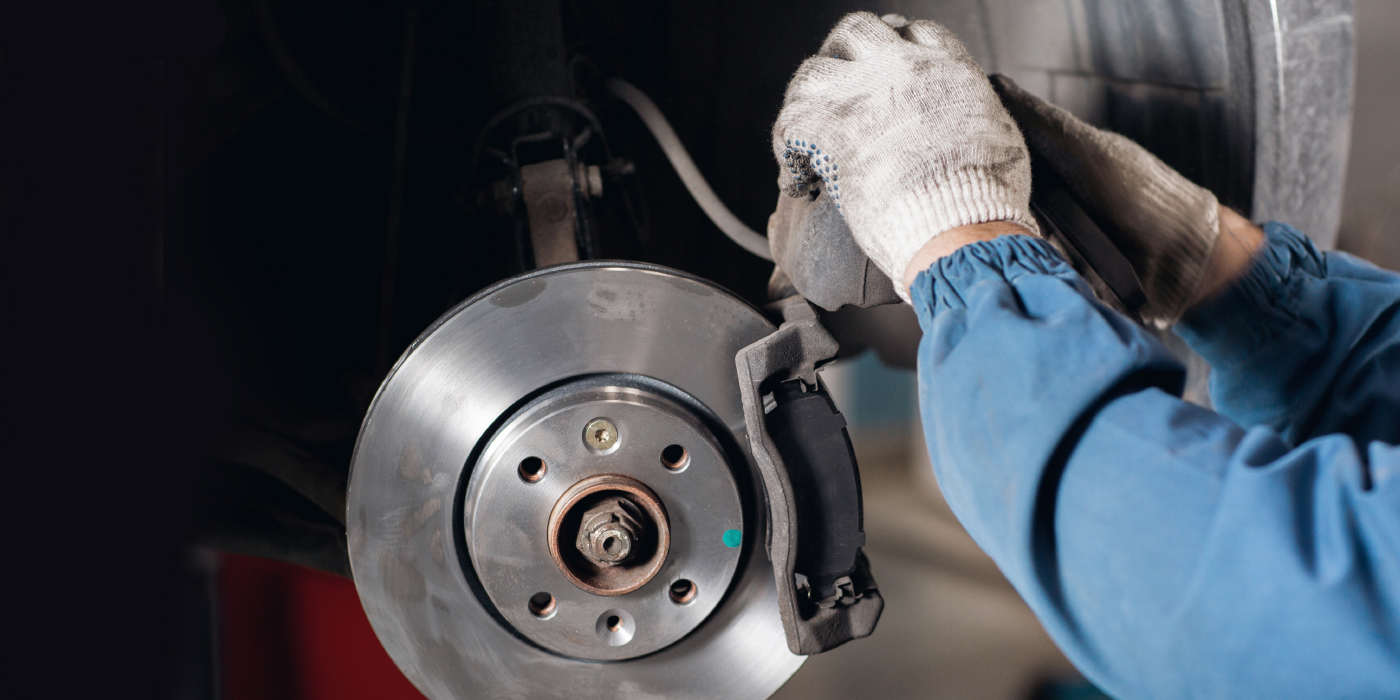
The third-generation Hyundai Elantra is the vehicle that put the Korean automaker on the map. With a roomy interior and a reliable drivetrain, the Elantra sold well to a wide demographic of import and domestic buyers. Under the car, the brake system, for the most part, is generic.
The third-generation Hyundai Elantra is the vehicle that put the Korean automaker on the map. With a roomy interior and a reliable drivetrain, the Elantra sold well to a wide demographic of import and domestic buyers. Under the car, the brake system, for the most part, is generic.
For the 25th installment of BRAKE JOB, we will be performing a complete brake job on a 2002 Hyundai Elantra with almost 200,000 miles on the clock and has seen some tough winters in the rust belt. The car even had the front sub-frame replaced two years ago under warranty.
For all of the shops in non-rust belt states, you are about to be amazed and surprised what a little snow and salt can do to a vehicle.
TSB and Recalls
There are no TSBs of relevance for the 2000-2006 Elantra. In 2003, Hyundai recalled some 2000-2003 Elantras for corrosion on the rear brake lines that pass behind the front suspension crossmember. The contact causes the outer coating on the brake lines to wear away. Without the coating, the lines corrode. The fix for dealers was to reposition the rear brake lines so they do not contact the mounting brackets. The repair involves installing brake line clips to control the location of the rear brake tubes, and apply anti-corrosion material to the lines.
INSPECTION
The initial inspection revealed the front rotors were below specifications and had uneven pad wear on the right front inboard pad.

The rear drums were also out of specification and a leaking wheel cylinder had contaminated the brake shoes. Hyundai recommends replacement of the wheel cylinders if any brake fluid is found in the dust boots.
Runout measurements of the rotors and hubs revealed little or zero runout.
FRONT BRAKES
 The caliper guide pins have insulator sleeves on the ends. These are designed to prevent vibration from being transferred to the caliper bracket. Over time, the ridges on the guide pin become compressed and it is possible to transfer vibration and noise to the vehicle. Some hardware kits include the insulator sleeves. It is always a good idea to replace these every time the pads are replaced.
The caliper guide pins have insulator sleeves on the ends. These are designed to prevent vibration from being transferred to the caliper bracket. Over time, the ridges on the guide pin become compressed and it is possible to transfer vibration and noise to the vehicle. Some hardware kits include the insulator sleeves. It is always a good idea to replace these every time the pads are replaced.
 The boot for this caliper guide pin had a 4mm gash. From heat expansion and contraction and the movement of the caliper centering over the rotor, the gash pumped in enough water and salt to corrode the pin and bore of the bracket.
The boot for this caliper guide pin had a 4mm gash. From heat expansion and contraction and the movement of the caliper centering over the rotor, the gash pumped in enough water and salt to corrode the pin and bore of the bracket.
 This is an example of a good idea gone bad. The previous technician put a coating of what looks to be anti-seize or brake lubricant on the piston or inboard pad. Over time, the grease has broken down and migrated on to the piston’s boot. This has attracted dust and dirt that has damaged the boot.
This is an example of a good idea gone bad. The previous technician put a coating of what looks to be anti-seize or brake lubricant on the piston or inboard pad. Over time, the grease has broken down and migrated on to the piston’s boot. This has attracted dust and dirt that has damaged the boot.
 A moly-based brake lubricant should be applied to only the fingers of the caliper.
A moly-based brake lubricant should be applied to only the fingers of the caliper.
 Lubricant should be applied to the abutment clip on the caliper bracket. Less is more! For some vehicles, it is only necessary to put a moly-based lubricant on the ears of the pad that make contact with the abutment clip. Dust and debris stick to lubricants and can cause problems down the road.
Lubricant should be applied to the abutment clip on the caliper bracket. Less is more! For some vehicles, it is only necessary to put a moly-based lubricant on the ears of the pad that make contact with the abutment clip. Dust and debris stick to lubricants and can cause problems down the road.

Make sure the hub is clean and free of all debris. Even a small piece of rust the thickness of two pieces of paper can cause .001” of runout.
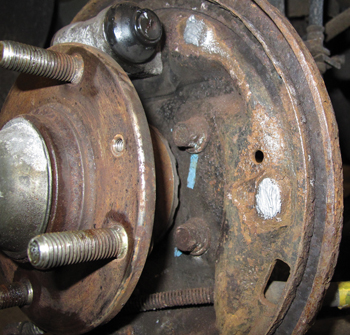 Rear Brakes
Rear Brakes
After the shoes are removed, clean up the lands the shoes ride on. If the lands are grooved from the shoes, replace the backing plate. Place a small amount of moly-lube on the lands. Do not use too much. Excess lubricant attracts dust and debris that can cause the shoes to stick.
 Inspect the teeth on the self-adjusters. Rounded, broken or worn teeth can cause the adjuster to malfunction. Clean and lubricate the adjusters. A little bit of lubricant can go a long way.
Inspect the teeth on the self-adjusters. Rounded, broken or worn teeth can cause the adjuster to malfunction. Clean and lubricate the adjusters. A little bit of lubricant can go a long way.
 When a drum is off the vehicle, assemble the shoes and hardware in the drum. The adjuster can be set so only a small adjustment has to be made on the vehicle.
When a drum is off the vehicle, assemble the shoes and hardware in the drum. The adjuster can be set so only a small adjustment has to be made on the vehicle.
 Be aware, most rear brake hardware kits might have two different length shoe anchors. If the shoe seems too loose or too tight, check the parts bag for an alternative part.
Be aware, most rear brake hardware kits might have two different length shoe anchors. If the shoe seems too loose or too tight, check the parts bag for an alternative part.