Application:
Ford Rack and Pinions: 22-217, 218, 220, 231, 232, 234, 235, 239, 241, 242, 243, 244, 246, 253, 264, 268, 271, 272, 276, 283, 294
Problem:
Correctly transferring and installing pressure port check valve.
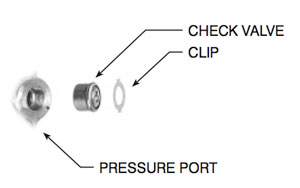
Solution:
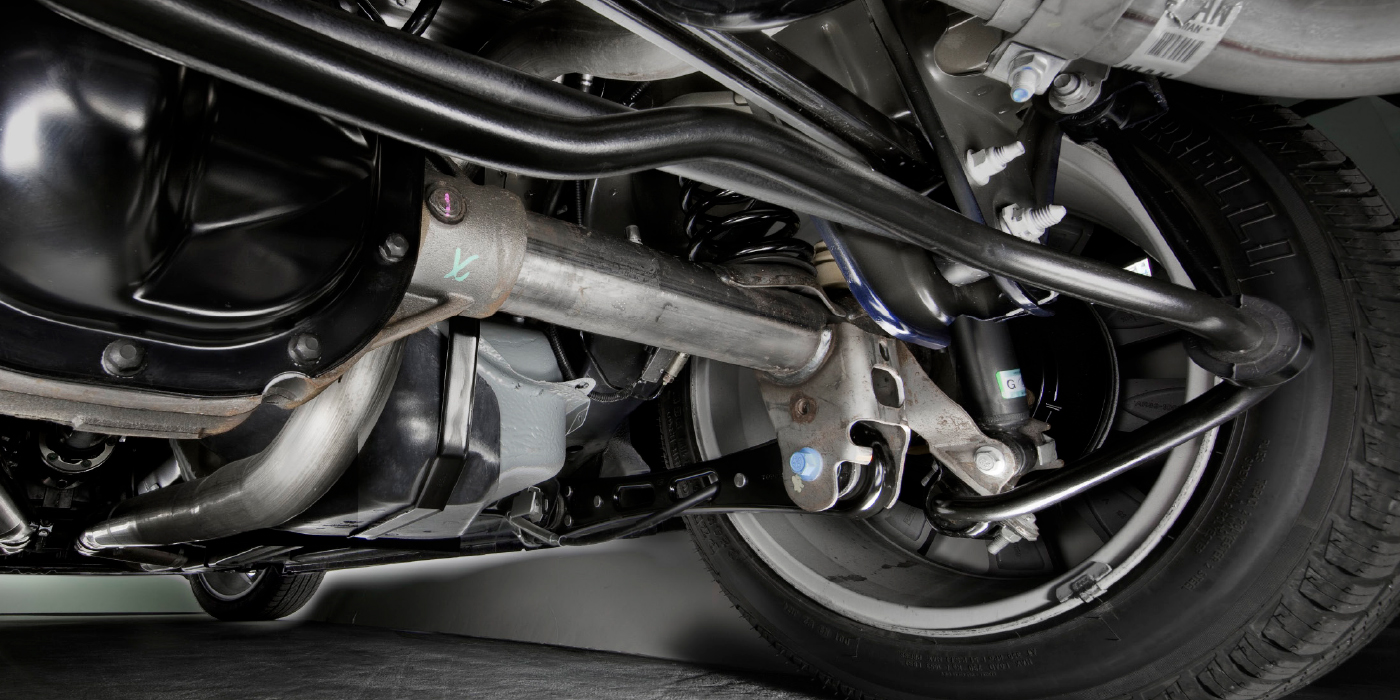
The original rack and pinion may have a check valve and retaining clip in the pressure port. See graphic below for a typical installation. The valve prevents fluid from backing up into the pump when the engine is shut off. Not all original units have a check valve, but if one is present, it should be transferred to the replacement rack. Note also that they don’t always have a retaining clip. The installation will be successful without the clip; it’s there to hold the valve in place during installation and to prevent the valve from falling out if the lines are serviced. If the clip is reused, be very careful not to damage port threads. The most important thing is to install the check valve in the pressure port, being careful to orient the valve as shown.
CAUTION: Pressure and Return ports are the same thread size. Refer to ProTech PT 22-0007 to determine which port is the pressure port.
Note:
This ProTech bulletin is supplied as technical information only and is not an authorization for repair.
Tech Tip courtesy of CARDONE Industries, Inc.