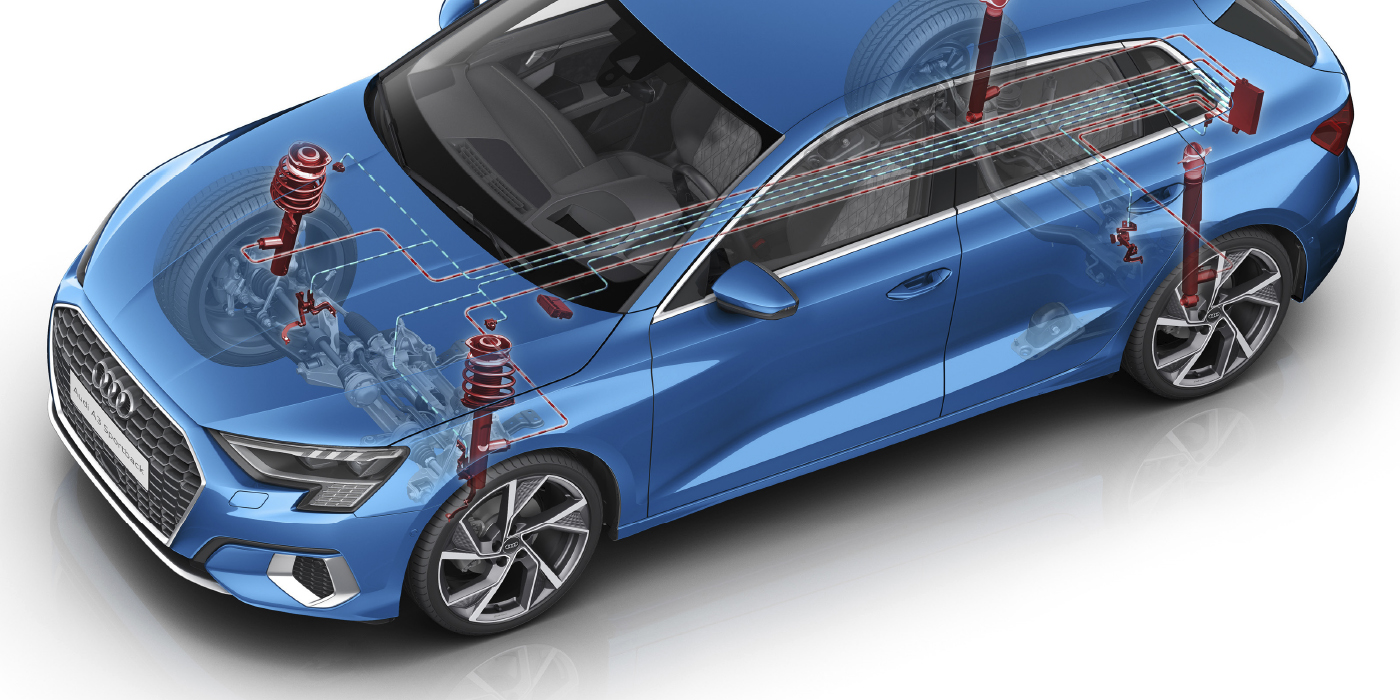
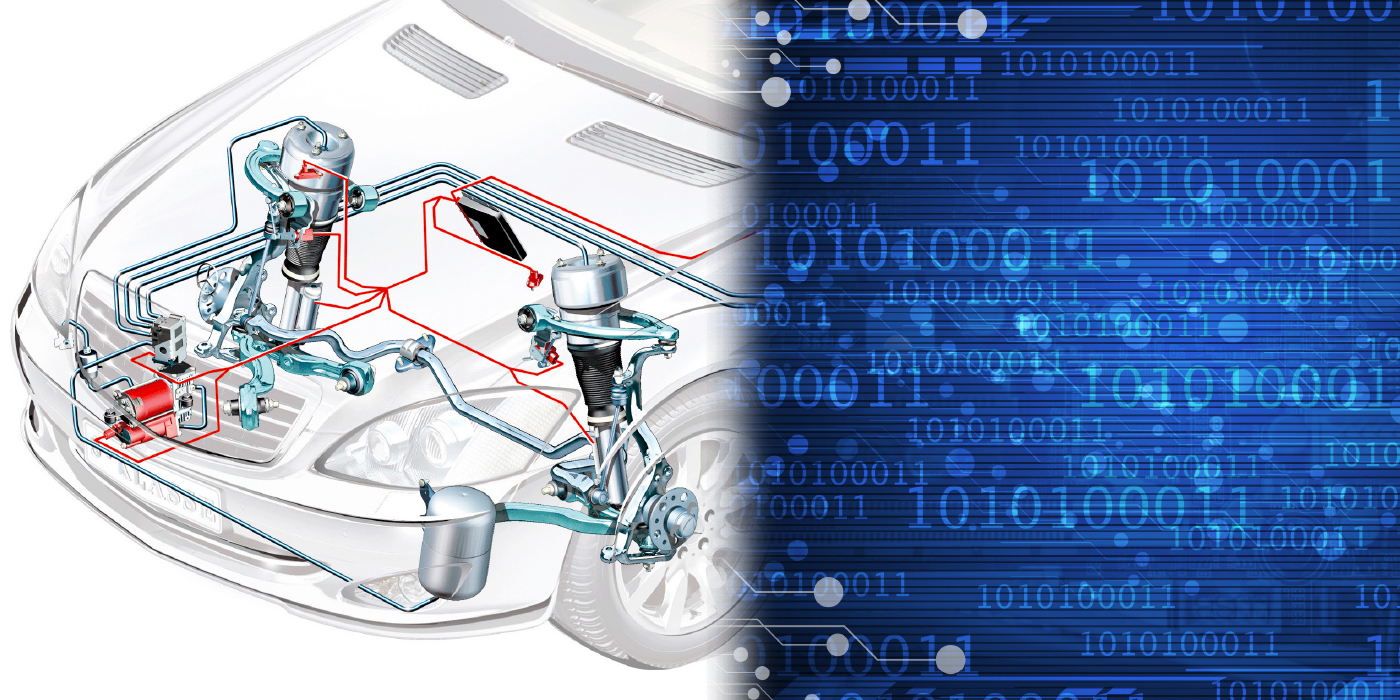
The third generation of the Toyota RAV4 shares all of the same infrastructure with the Corolla and many other Toyota vehicles. The front suspension is easy to adjust, while the rear needs a little more attention.
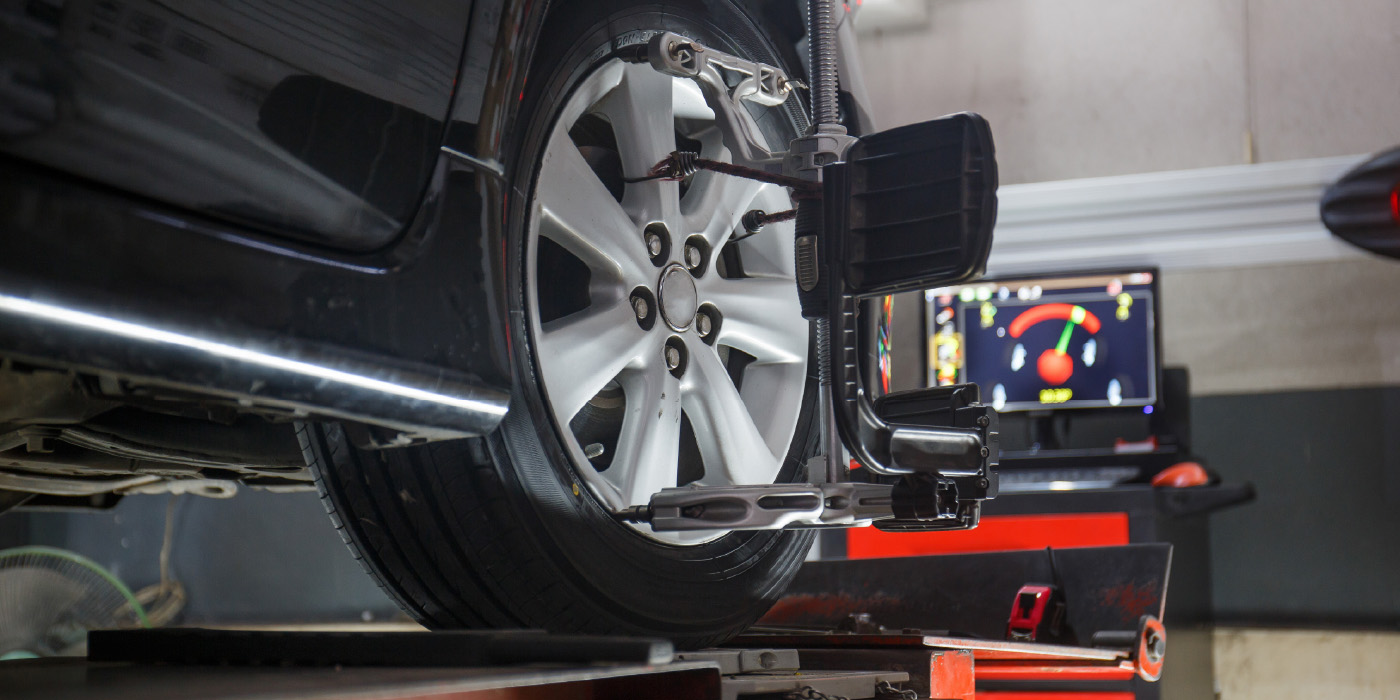
If you get one in your shop, it’s what you do after you adjust the angles that can make or break the alignment. The RAV4 has electric power steering and the stability control is a very common option. These systems need to know the correct steering angle to operate. If it is not reset, it could result in the customer coming back with the VSA or steering malfunction indicator light on.
Always pay attention to the ride height. If the springs are weak, it can change the camber and caster in the front. In the rear, weak springs can change the camber and toe and cause the inner edges of the tires to wear prematurely. Often many of the alignment angles can be corrected with new springs or loaded struts.
Front Suspension
The front suspension on the RAV4 uses a MacPherson strut design. Caster is not adjustable from the factory. Camber can be adjusted using additional parts. Toyota uses coded bolts with dots on the heads that indicate a fixed range of camber. But, the aftermarket has a better solution, with cam bolts that can adjust ±1.75 degrees.
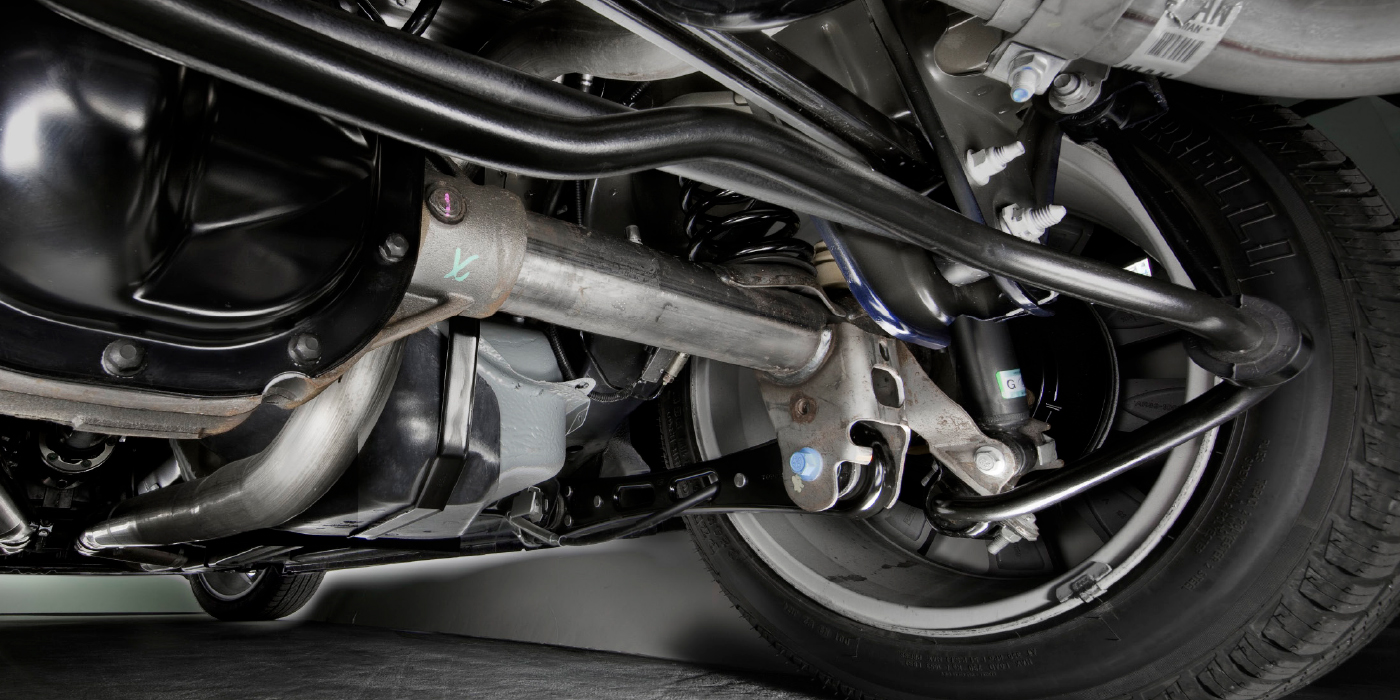
The most common wear points for the RAV4 are the lower control arms. The bushings on the arm can degrade and cause changes in the caster, camber and toe. Changing the control arm involves removing the lower crossmember.
Rear Suspension
The rear suspension is a multilink design. On high-mileage vehicles, inspect the lower knuckle bushing for play and deflection. Another sign of a worn bushing is premature tire wear on the inside edge of the rear tires.
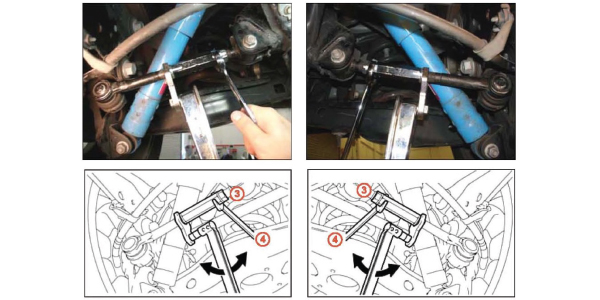
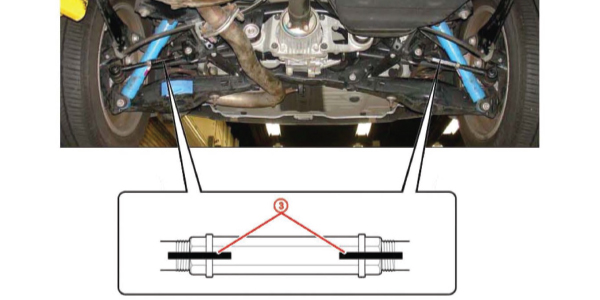
The rear toe links use a sleeve that connects the two portions of the rod. The sleeves are problematic. The sleeves and jam nuts can come loose if you don’t take your time using the correct procedures. Don’t try to tighten both jam nuts at the same time. Instead, grab the sleeve with a crow’s foot and torque wrench and put an open-end wrench on the jam nuts. Tighten the sleeve to 15 ft/lbs.
If you get a 2005-2011 Toyota RAV4 in your shop for an alignment with a complaint of either rear tire wear or a knocking noise, you need to be aware of a recall and inspection campaign Toyota issued in 2012. Toyota Safety Recall COJ involved inspecting the right and left toe links for looseness. Based upon this inspection, it may have been necessary to replace the arm(s).
Toyota received reports from dealers indicating that some vehicles experienced symptoms of the recalled condition after being inspected or repaired. Toyota discovered that some inspections were not up to standards.
If a lower toe link was inspected and has passed, it will have an epoxy and plastic covering indicating that it passed the inspection. The bad news is that if the cover is there, the toe can’t be adjusted and must be replaced. There are aftermarket toe links that utilize a better design than the original Toyota part.
Camber can be adjusted with an adjustable upper arm. These arms can give an additional three degrees of adjustment. These components can give adjustments for the rest of the life of the vehicle and allow for fine-tuning of the rear camber angles to maximize tire life.

Steering Angle
Sensor Reset
Most 2006-2013 RAV4 models are equipped with an optional Vehicle Stability Control (VSC) system that requires a scan tool and special procedures to perform a zero-point calibration of the steering angle sensor. It is highly recommended to do this through the OBD-II port with a scan tool. Yes, it is possible to reset the system by jumping two pins in the diagnostic connector and disconnecting the battery. But, there is no way to confirm or document the calibration was properly performed.
The steering position sensor’s basic function is to monitor the driver’s steering inputs. This includes the angle of the steering wheel and/or the rate at which the driver is turning the wheel. The steering position sensor on the RAV4 is located behind the steering wheel and is a high-resolution sensor.
The VSC system relies on accurate steering input from the steering angle sensor to analyze a situation and apply appropriate measures to help direct the vehicle on the intended path. If the system is not calibrated after a toe adjustment, the system will not operate properly and may illuminate the VSC malfunction light after the driver has picked up their RAV4.
The Toyota VSC system uses the information from the steering position sensor and compares the information to the yaw rate sensor to determine what the car is doing.
When a vehicle is aligned and the toe in the front or rear is altered, it changes the thrust angle of the vehicle. The thrust angle is directly connected with the slip angle and the measurements taken by the yaw position sensor. Even if you adjust only the rear toe, you are altering the thrust angle, and the steering position sensor must be recalibrated.
After the sensor is reset, it is necessary to drive the vehicle and turn the steering wheel to the right and left at the speed of 22 mph (35 km/h) for at least five seconds to calibrate the sensors and complete the reset. If this is not performed, the VSC may set a code and the sensor may read 1150 degrees. This is not an indication the sensor is faulty, only that it has not been properly reset.