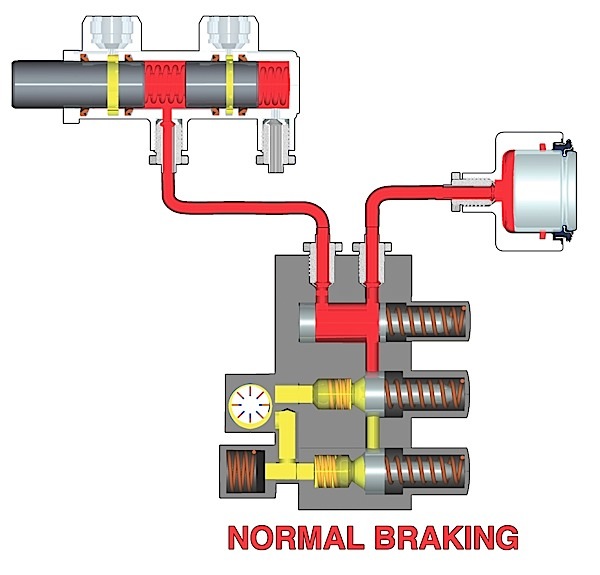
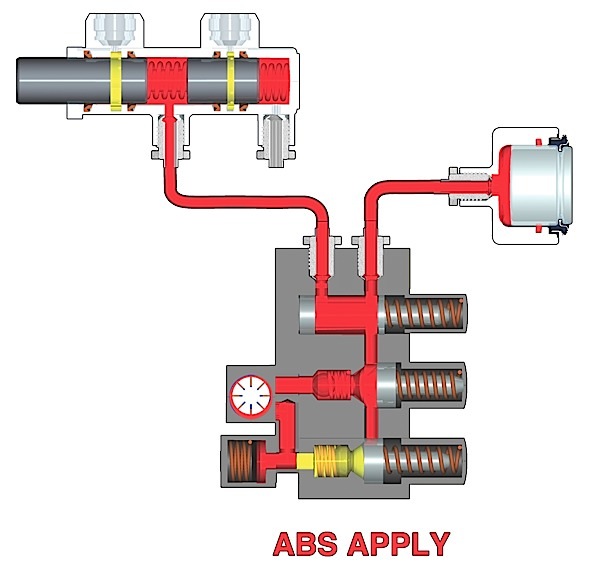
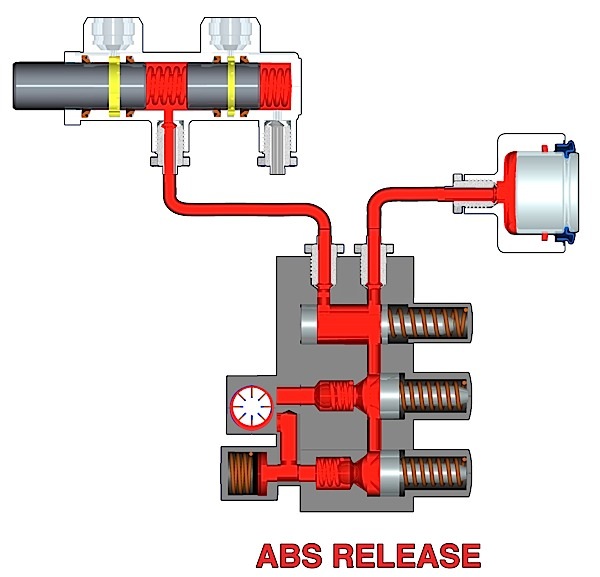
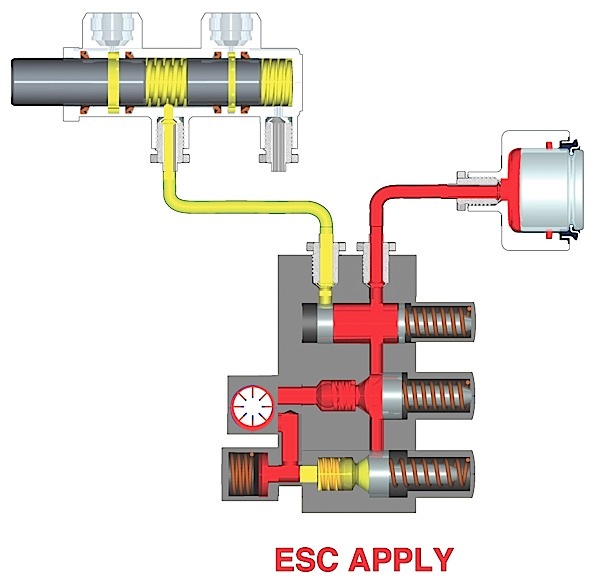
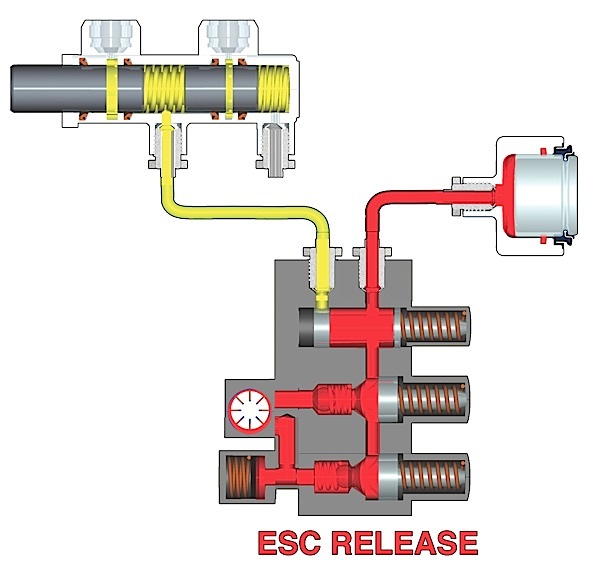
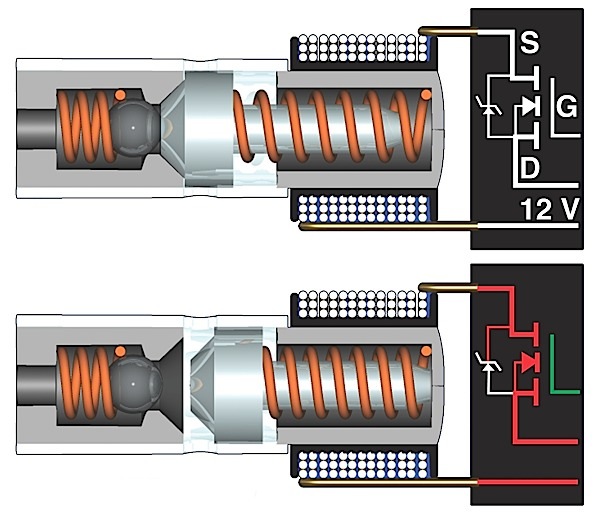






Passive types of wheel speed sensors are still used in many applications so understanding their operation is important.
As the metal tooth passed by the permanent magnet wrapped in copper wire, the magnetic field was altered and measured by a computer. This is not a sci-fi novel, but how a passive wheel speed sensor works.
A passive wheel speed sensor is often called a “variable reluctance sensor” by some engineers. The sensor is mounted at a specific gap from a toothed reluctor ring. As the teeth pass by the wheel speed sensor, it changes the magnetic field and produces alternating current or AC voltage. The AC voltage can be seen by a scope as a sine wave.
To get the most out of these “liquid” tools, you first need to know how they work.

Regenerative braking is a hybrid’s first choice for braking.
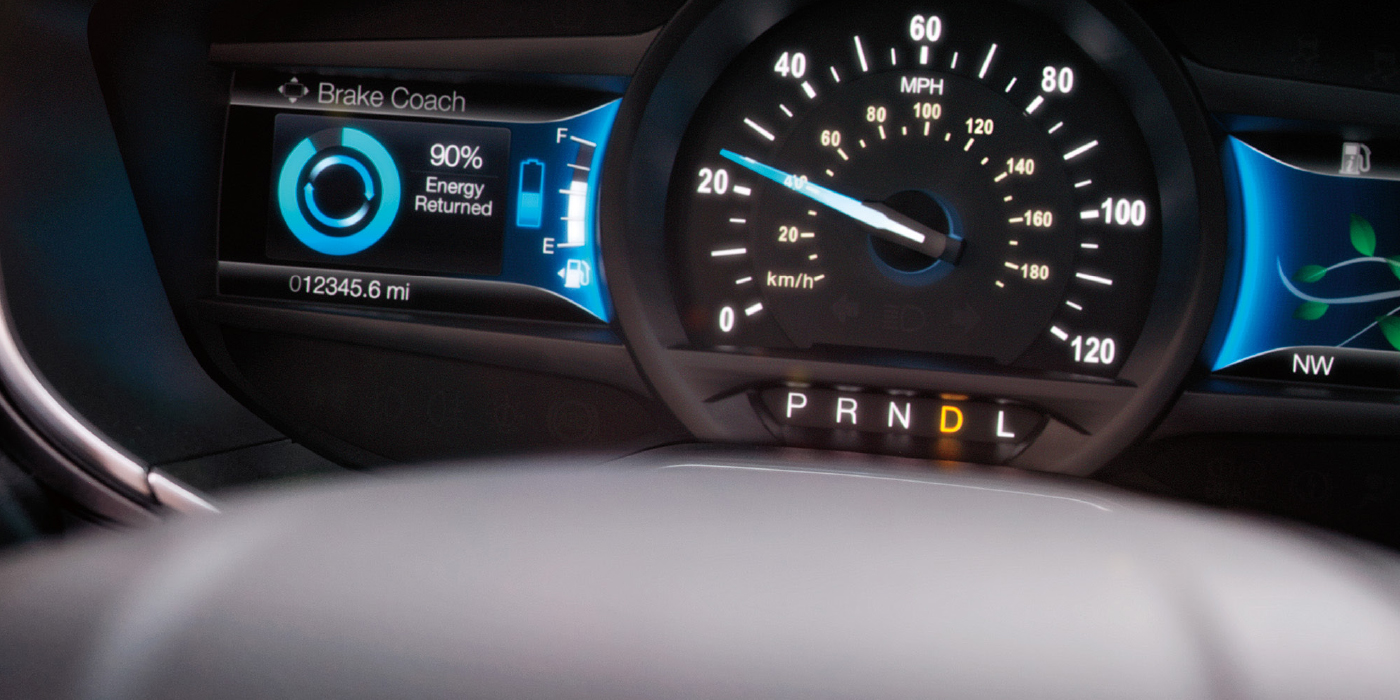

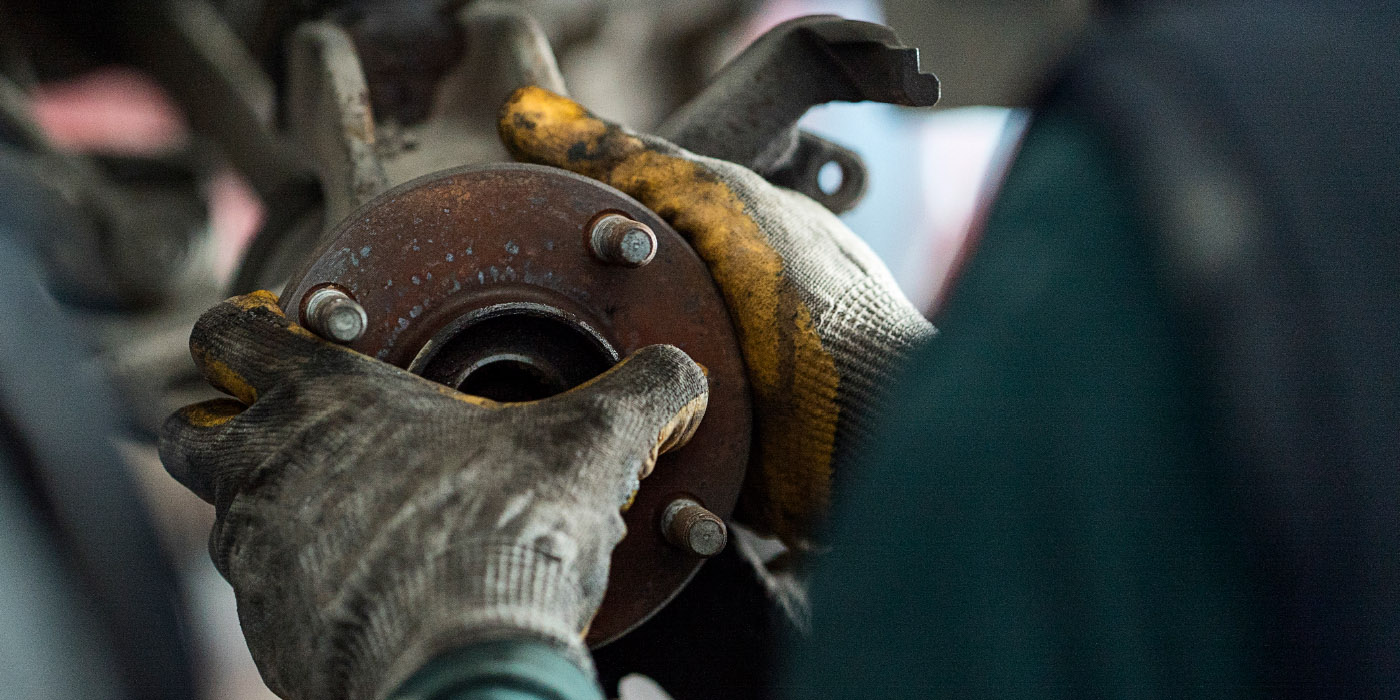
The process of replacing the hub unit on a Tesla is the same as many cars and light trucks.

The edge code is a language written by engineers, federal entities and industry associations.

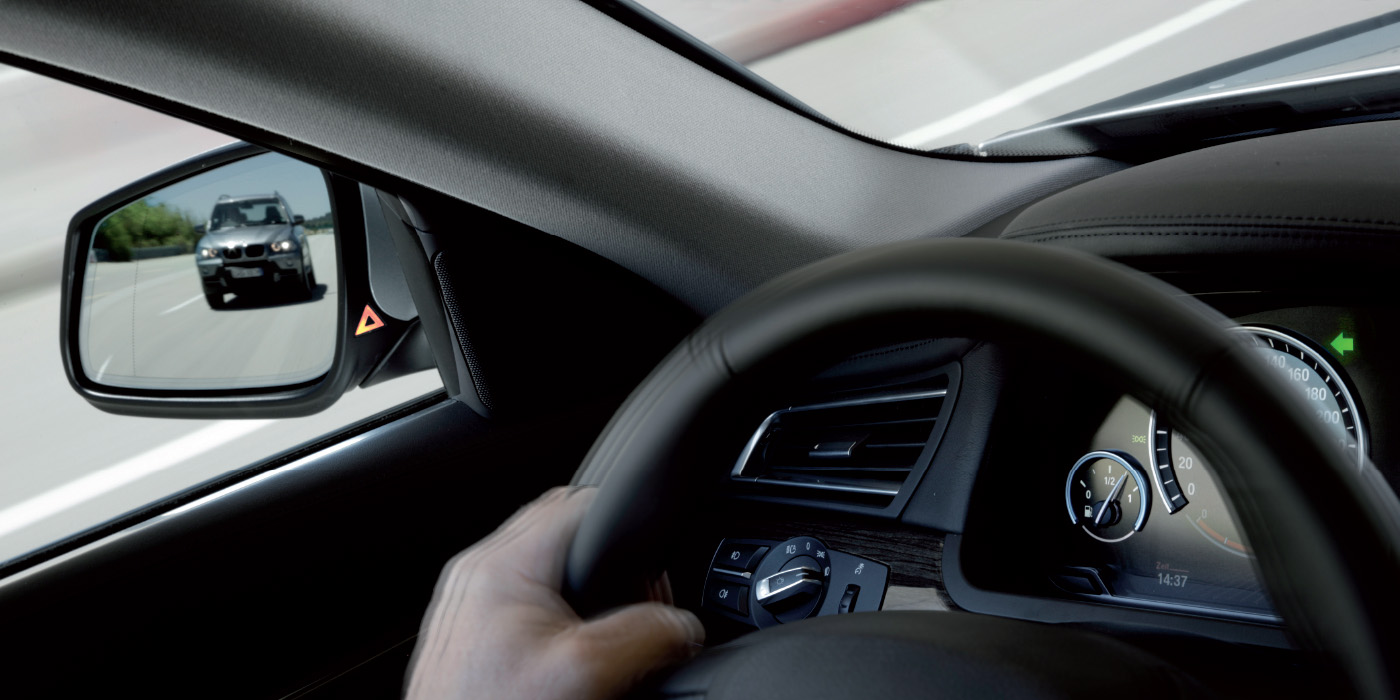
The logic behind most ADAS warnings or corrections is to examine the plausibility of the situation.

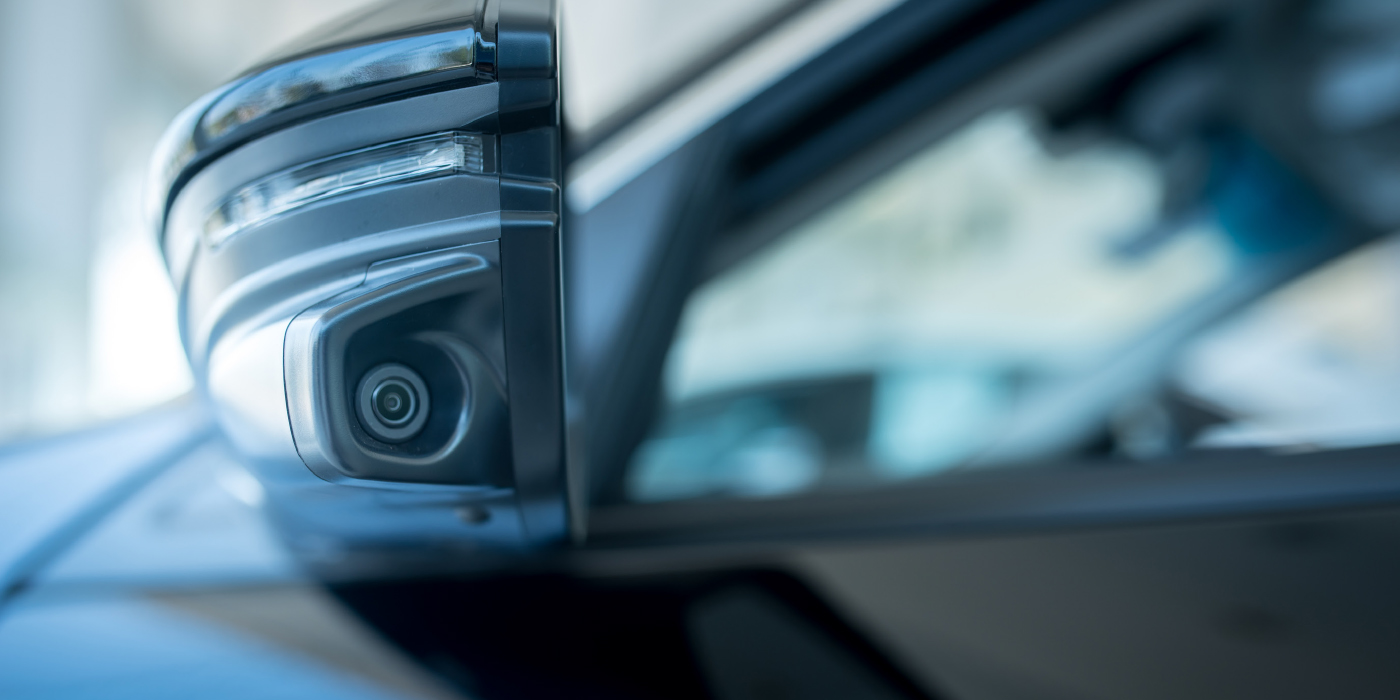
With the right tools and service information, it is possible to resolve a customer’s complaint.

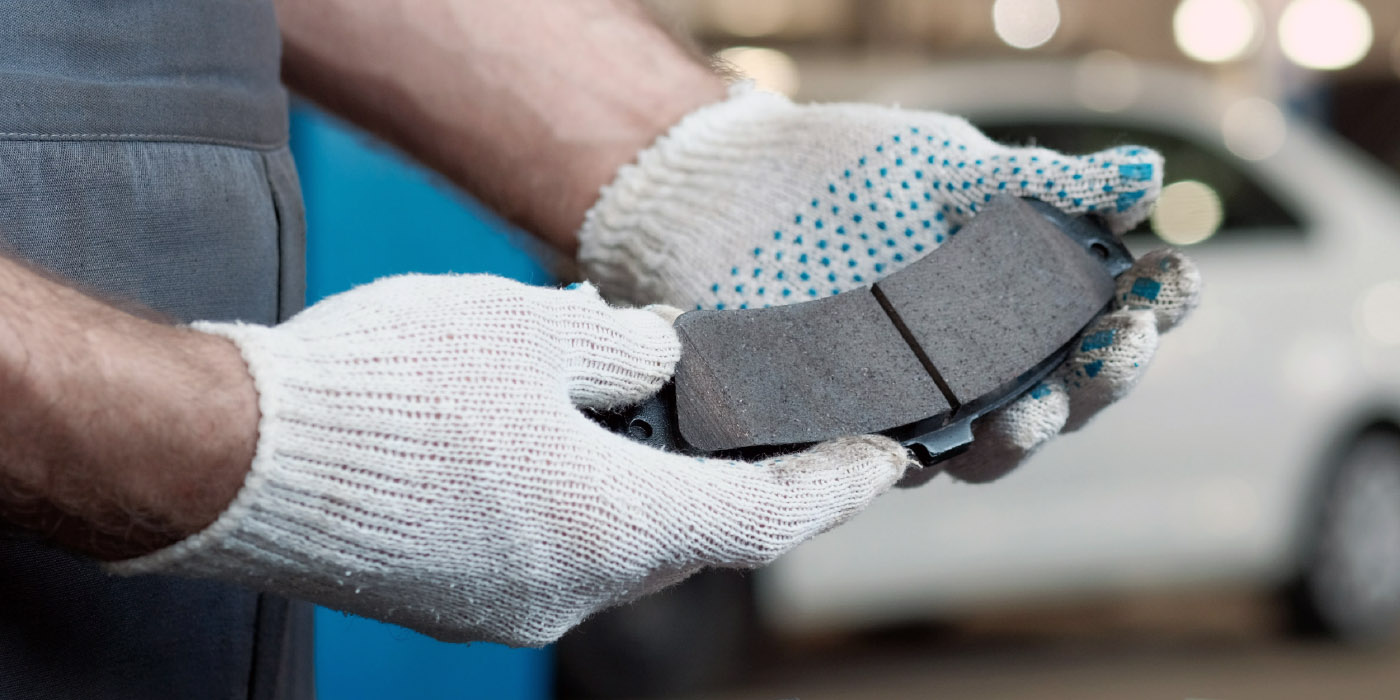
When replacing brake system components, it might seem like using compatible parts from any manufacturer – regardless of brand – should get the job done. However, for the safest brake job with the best performance, it’s always best to use parts from the same manufacturer, like ADVICS, where our brake pads, brake rotors, hydraulics, calipers

The brake repair market is starting to become dominated by a “good enough” mentality.
