On V6 and DOHC models, it is normal to hear a valve noise (a “ticking” sound) during the first two minutes after engine start-up. However, vehicles that are overdue for an oil change or have not been started for a long period of time may experience the noise for longer than two minutes. The noise is caused by air in the high-pressure chamber inside the automatic valve lash adjusters.
Replacing valve lash adjusters will probably not eliminate valve noise. This bulletin contains procedures to bleed air out of the adjusters and to confirm that the adjusters do not require replacement.
Note: For Eclipse models with the 420A engine, refer to the “Lash Adjuster Check” on page 110-12 in the 1996 Eclipse service manual. Do not perform the procedures in this bulletin.
SERVICE PROCEDURE:
If the valve noise (a “ticking” sound) lasts more than two minutes after engine start-up, perform the following steps in order:
2. Warm the engine to normal operating temperature. Increase the idle speed gradually to 3,000 rpm, then back down to normal idle speed. Repeat this process several times (maximum of 10 times). If the valve noise continues, stop the engine. Inspect the automatic valve lash adjusters as described in Steps 3 and 4 below.
Caution: Wear protective gloves and use care to protect yourself from hot engine components.
 3. Remove the oil cap on the rocker cover and listen for the source of the noise. If it seems to be coming from the valve lash adjusters, proceed to Step 4. Otherwise, refer to section 11 of the appropriate service manual for further engine diagnosis to determine the cause of the noise.
3. Remove the oil cap on the rocker cover and listen for the source of the noise. If it seems to be coming from the valve lash adjusters, proceed to Step 4. Otherwise, refer to section 11 of the appropriate service manual for further engine diagnosis to determine the cause of the noise.
4. Remove the rocker cover.
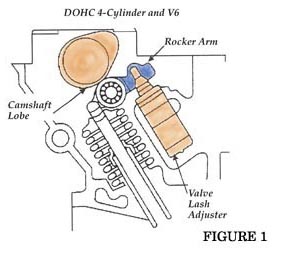
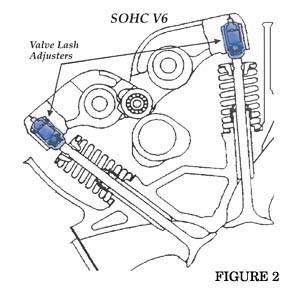
5. Using finger pressure, push down on the rocker arm over the head of each valve lash adjuster. See Fig. 1 and Fig. 2.
Note: Be sure that the camshaft lobe is on the flat side when performing this step.
 a. If the head of the adjuster sinks when finger pressure is applied, the adjuster must be replaced.
a. If the head of the adjuster sinks when finger pressure is applied, the adjuster must be replaced.b. If the head of the adjuster stays firm when finger pressure is applied, the adjuster is operating normally. Do not replace the adjuster. Refer to section 11 of the appropriate service manual for further engine diagnosis to determine the cause of the noise.
The above technical service bulletin is courtesy of Mitchell 1.
For additional information on Mitchell 1, visit www.mitchell1.com.












