Signs of a worn wheel hub bearing may be difficult to detect yet failure to identify and correct the problem can cause damage before a driver even knows there is a problem. When damage occurs can be attributed to driving conditions and/or installation procedures. Noise is a classic sign of a bad wheel bearing or wheel hub bearing but determining exactly why the damage happened may take some investigation.
To diagnose the cause of bearing damage, look closely at damaged hubs and compare customers’ hubs with the accompanying photos.
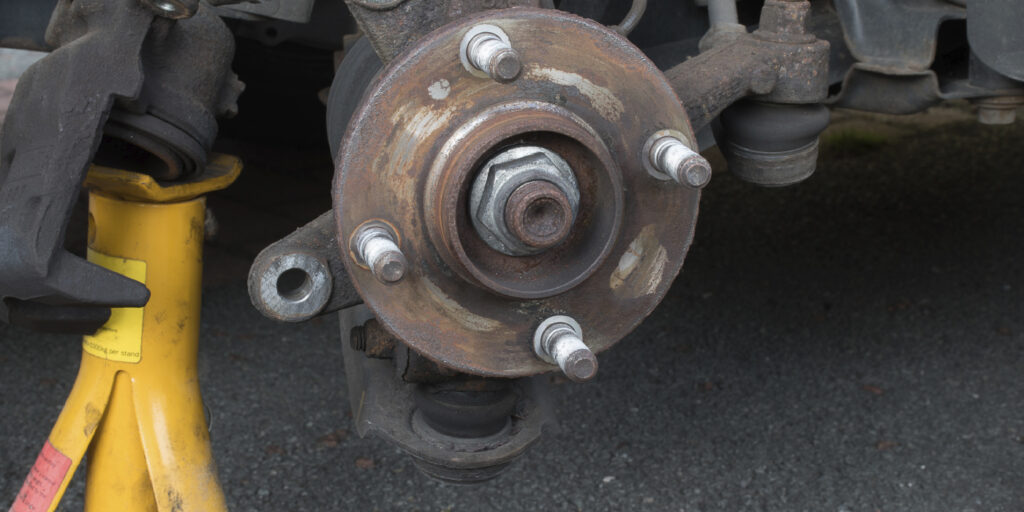
LOSS OF BEARING RETENTION (Figure 1)
Symptoms: Wheel vibration and/or excessive noise.
Diagnosis: Rough or worn axle retaining nuts indicate movement due to loss of bearing retention. Refer to the original equipment manufacturer’s instructions or visit timkeninfo.com to identify the proper torque for the axle retaining nut.
Cause: Loss of bearing retention is the leading cause of hub bearing damage, resulting in wheel vibration and/or noise. The axle retaining nut backs off when bearings demonstrate improper torque or have lost their self-retention features. This changes the setting of the bearings inside the hub, causing misalignment and accelerating wear.
Solution: Always use a new axle retaining nut and tighten it to the proper torque to avoid a rough and worn surface under the nut. Tighten axle lock nut to the proper torque to help avoid rough and worn surface under the nut.
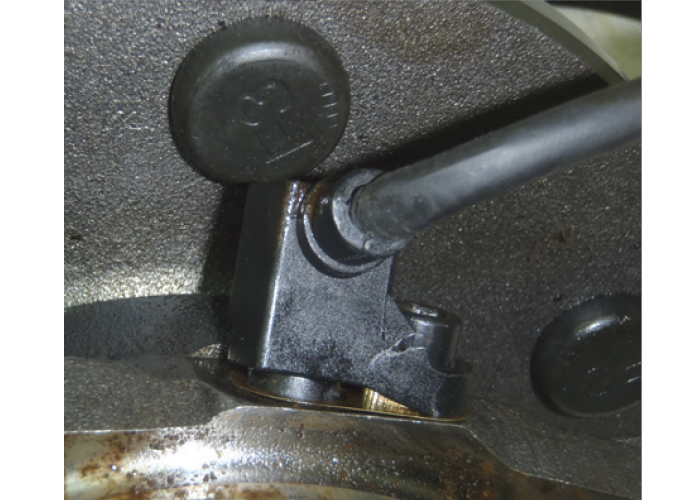
EXCESSIVE WEAR ON CONE BORE (Figure 2)
Symptoms: Accelerated bearing wear or multiple returns for the same wheel-end application.
Diagnosis: Inspect the hub barrel when replacing a wheel bearing with a separate hub. Check the hub barrel outer diameter (OD) for signs of damage. Look for ridges or discoloration on the barrel surface due to heat damage from cone turning. Replace the hub if you find any signs of damage.
Cause: Loss of axle retention or reinstalling a worn hub can allow the cone or inner race to spin on the hub, accelerating wear on the cone bore and hub barrel. This cone turning can indicate loss of bearing retention or improper fit between the cone bore and hub barrel diameter.
Solution: If you see damage to the hub barrel, replace it.
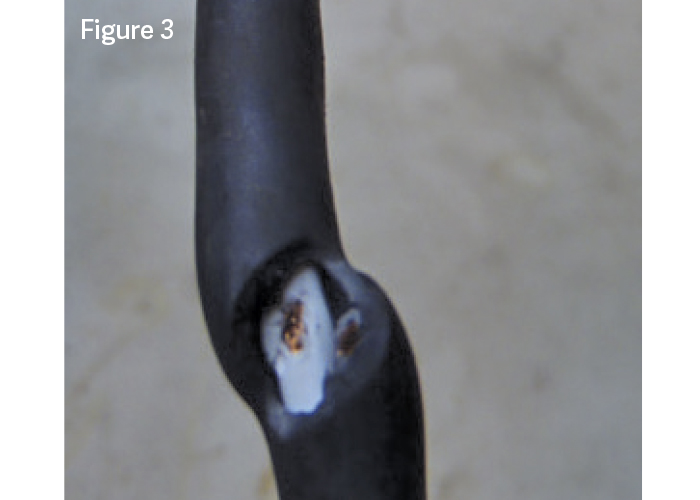
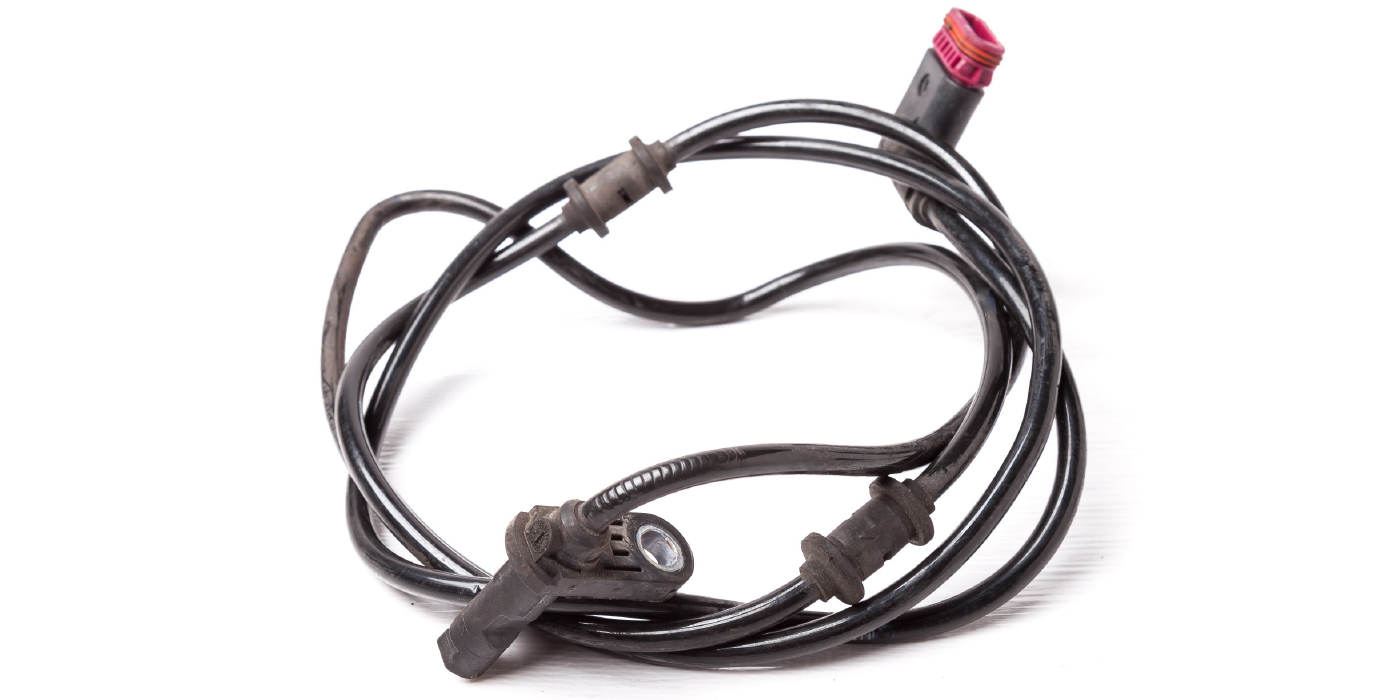
ABS MALFUNCTION (Figure 3)
Symptoms: A damaged sensor cable or a broken wheel speed sensor turned the anti-lock braking system (ABS) light on.
Diagnosis: Look for damage from sharp objects or evidence that the cable was caught in a pinch point. Ensure the cable is routed through the entire sensor cable retaining clip. If the sensor cable is not damaged, examine the external sensor for cracks in the sensor body or a loose cable in the sensor head.
Cause: Sharp objects may have damaged, pinched or bent the sensor cable. Sensor cable damage is a common cause of ABS malfunctions. Installation may have damaged the wheel speed sensor.
Solution: Route sensor cable through all retaining clips. Use hubs in good condition to reduce wear. Avoid pinched cables by using retainer clips.
Courtesy of Timken.