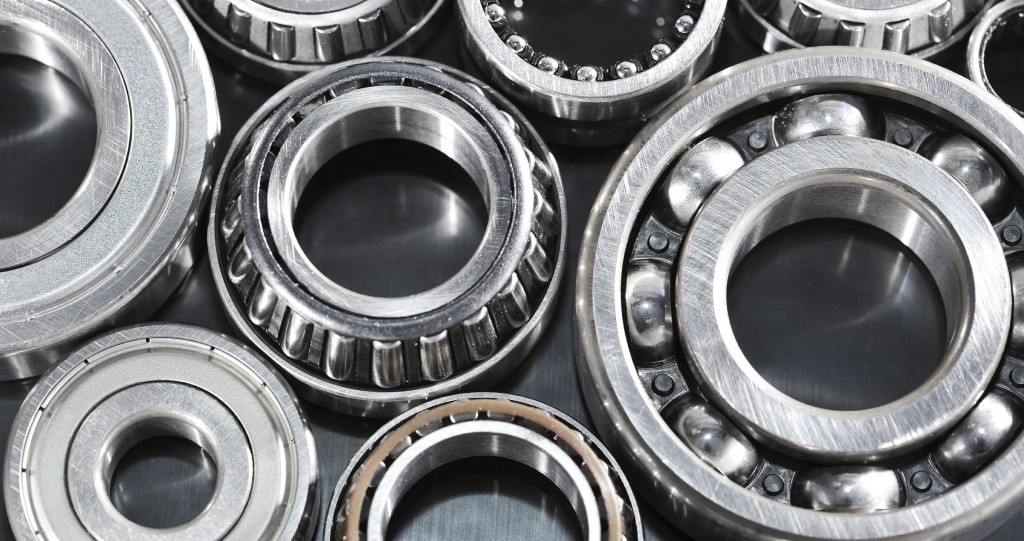
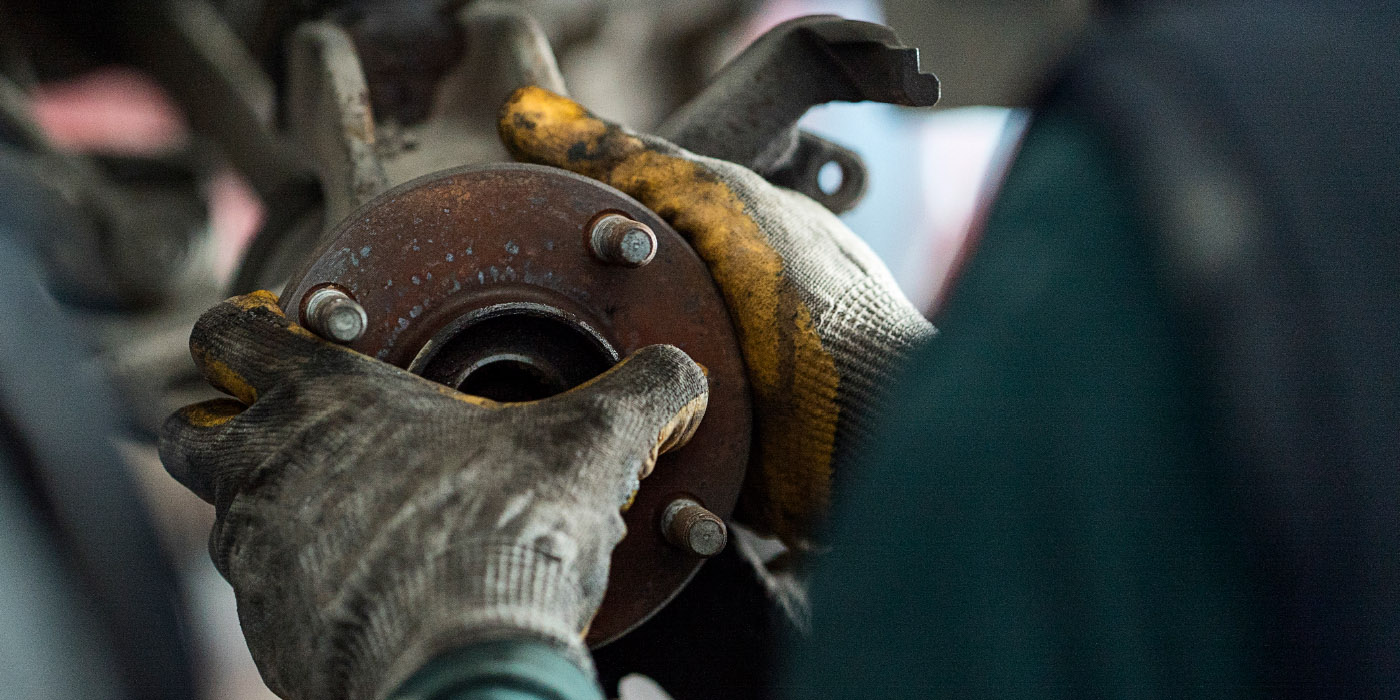
Wheel Bearing Damage Can Mean Inadequate Lubrication
A bearing’s lifespan depends largely on proper lubrication, with about half of all bearing damage attributable to inadequate lubrication, according to the bearing and seal experts at SKF.
Although inadequate lubrication can be classified into eight basic categories, two of those causes — water contamination and debris contamination — can be particularly attributed to bearing damage.
The main common type of bearing damage with moisture/water exposure is rusting, pitting and corrosion — a condition known as “etching.”
Fresh grease is smooth and buttery looking, while water-laden grease is milky white in appearance. Note that as little as 1% water contamination in grease can cause significant bearing damage.
An easy way to test for the presence of water in grease is known as the “crackle test.” It involves placing a sample of grease onto aluminum foil, then placing a flame under the foil. If the grease melts and lightly smokes, there is minimal or no water present. If the grease crackles, sizzles and/or pops, it contains a considerable amount of water.
Always wear safety glasses or goggles and other protective clothing when performing this test, and also ensure there is adequate ventilation.
Debris contamination results from dirt, sand and other environmental particles, with common causes of internal debris contamination resulting from wear to gears, splines, seals, clutches, brakes, joints and failed or spalled components.
These hard particles travel within the lubrication, through the bearing, and eventually bruise (dent) the internal surfaces and cause bearing damage. The dents form shoulders that act as surface-stress risers, causing premature surface damage and reduced bearing life.
Courtesy of SKF.