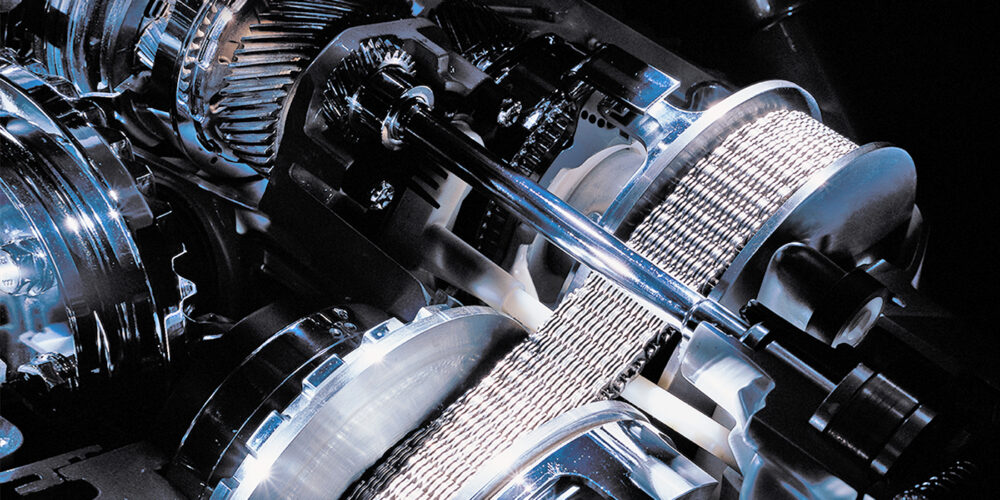
Transmissions – CVT
Knowing what the common issues are & understanding the options available to isolate & fix problems are the keys to success.
All transmission models have unique problems that are common to that model; JATCO CVT units are no exception. Technicians are facing an uphill battle when it comes to diagnosing and repairing CVTs if they don’t have the right information on hand. Knowing what the common issues are and understanding the options available to isolate and fix problems are the keys to a successful repair.
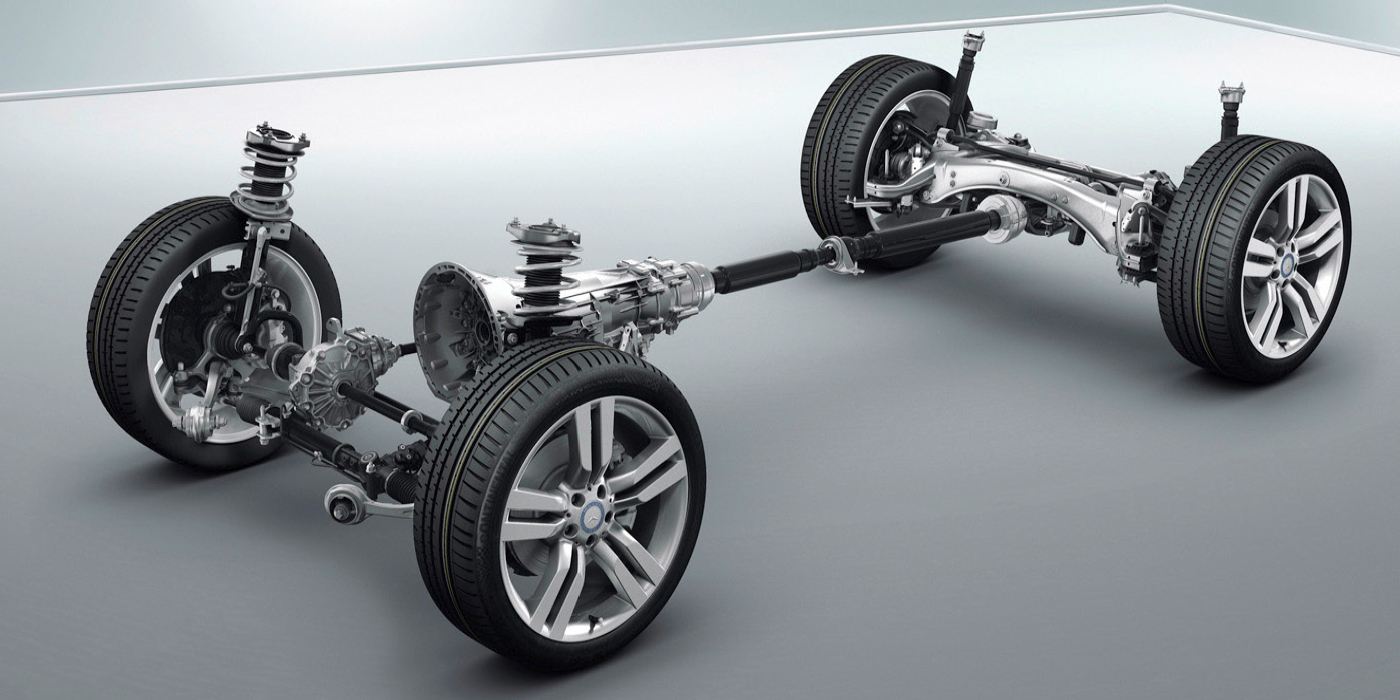
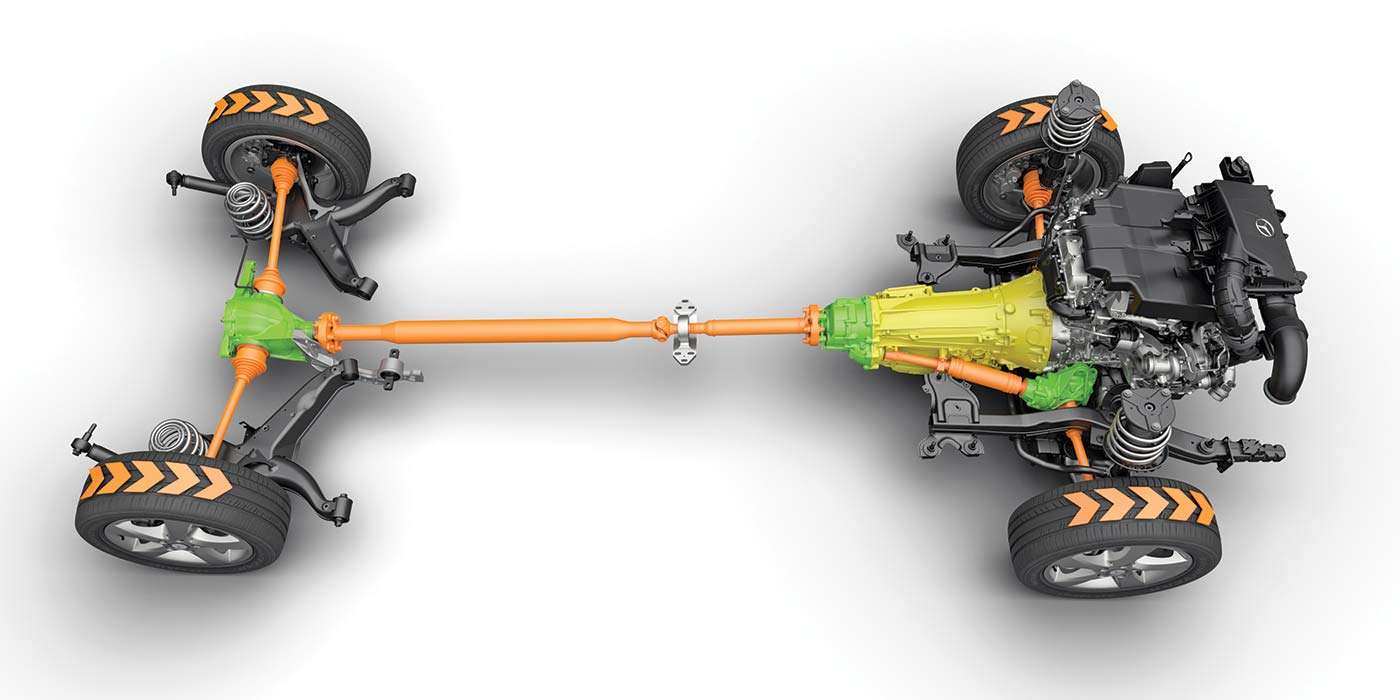
Simplifying AWD Systems
No matter the manufacturer, there is almost always an all-wheel drive (AWD) option.
Manual Transmission Service
Parts that wear out must be replaced.
Transmission Fluid Hydraulics
You need to know how transmission fluid flows inside an automatic transmission.

Advanced Wheel Bearing Diagnostics
Can a bump set a wheel speed sensor code?

Other Posts
How Well Do You Know Your Driveshaft?
There are three types of modern driveshafts with multiple configurations.
Transmission Service
The following is an example of a dishonest vehicle and how to go about catching it in its lie.

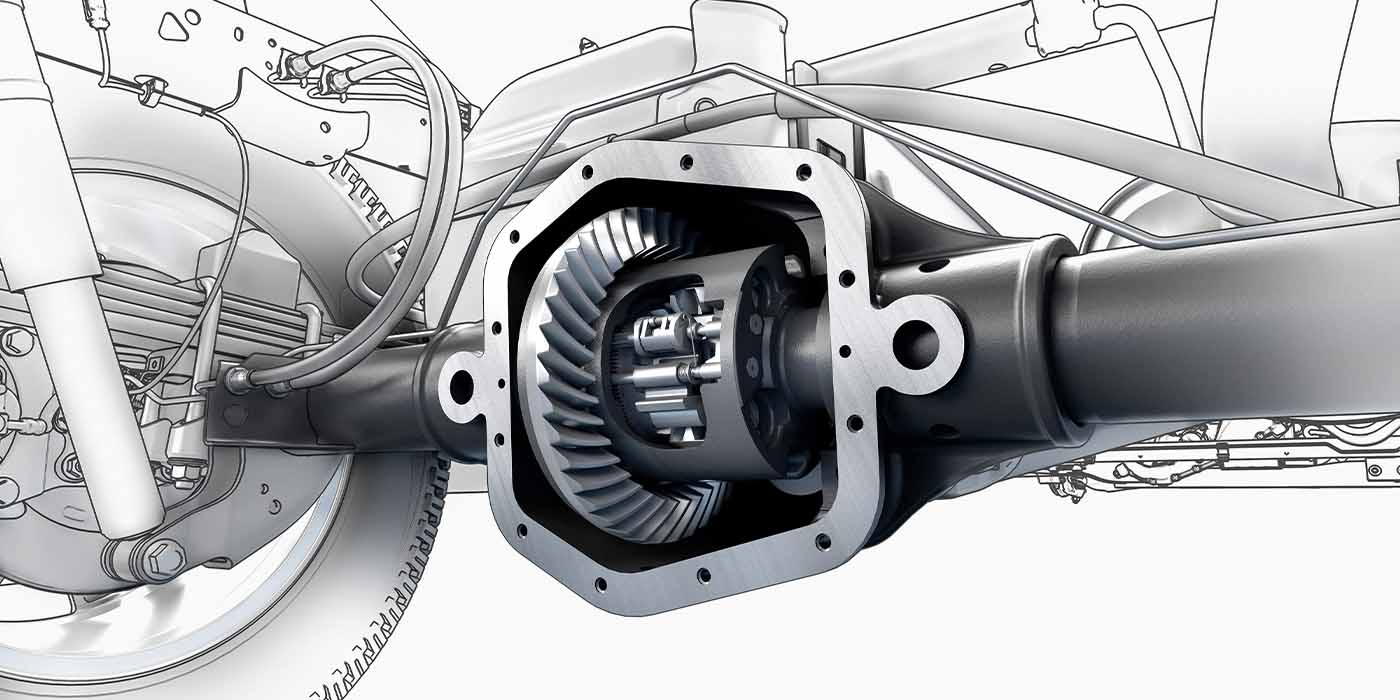
Limited-Slip Differentials And Diagnostics
A limited-slip differential helps to control the tangential forces.
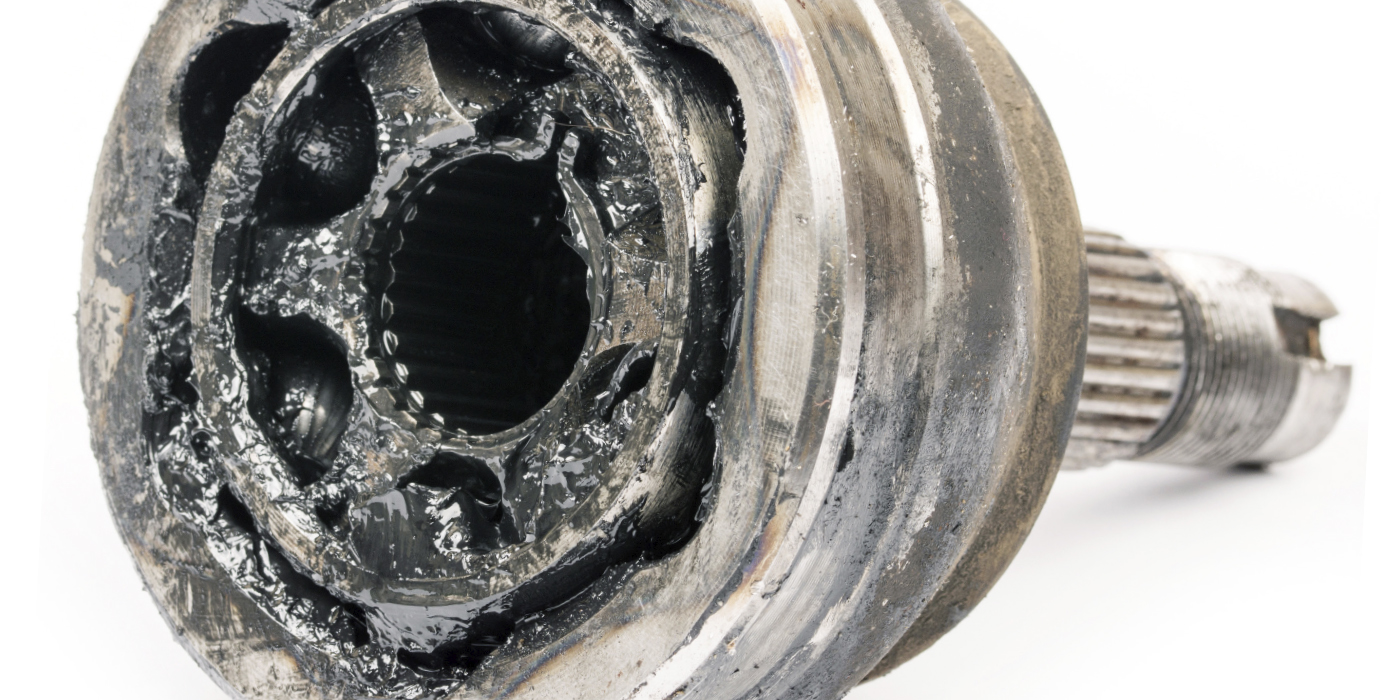
Seven CV Joint Mistakes You Shouldn’t Make
If a CV joint fails, it rarely fails on its own. Outside factors can damage a joint worse than cutting a boot with a knife.