By Larry Carley
Technical Editor
The fuel pump is the heart of the fuel system. Most late-model vehicles have an electric pump mounted inside the fuel tank. If the fuel pump stops working for any reason, the flow of fuel to the engine stops and the engine dies. Fuel pump failures tend to be sudden and unpredictable, with few symptoms to warn the motorist that trouble is brewing. And the higher the mileage on the vehicle, the greater the risk of a fuel pump failure.
If an engine cranks normally, has spark and compression but won’t start because it is not getting any fuel – or it lacks adequate fuel pressure to start – the tendency is to blame the fuel pump for the no-start problem.
Unfortunately, replacing the fuel pump doesn’t always fix the problem. Why? Because many times, the problem is not the fuel pump, but something else.
Nearly 10 percent of all the fuel pumps that are sold by auto parts stores are returned because the pump did not work when it was installed or it failed to start the vehicle.
The Fuel Pump Manufacturer’s Council (FPMC) says that up to 80 percent or more of the fuel pumps that are returned for being “defective” work normally when tested by the manufacturer. The problem was not the fuel pump, but not diagnosing the no-start condition accurately.
Any number of things can prevent the engine from getting enough fuel to start and run:
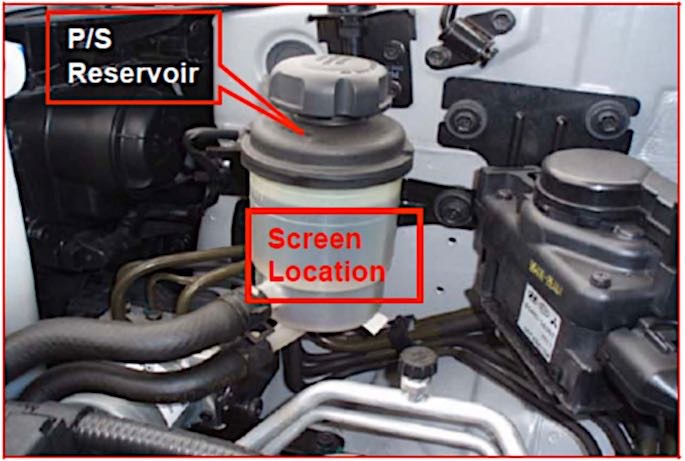
• The fuel strainer or inlet sock inside the fuel tank could be gummed up with dirt or rust;
• The fuel filter could be plugged;
• The fuel line could be pinched or blocked;
• The fuel pressure regulator could be leaking;
• The wiring connector or ground connection at the fuel pump could be loose or corroded;
• The fuel pump relay could be bad;
• The fuel pump fuse could be blown; or
• The fuel tank might be empty, or contain water, diesel fuel or other contaminants.
DIAGNOSING THE PROBLEM
Accurate diagnosis is important because it eliminates the replacement of good pumps, and the unnecessary return of new pumps. Warranty returns waste everybody’s time, especially the technician’s time because a tank-mounted pump often takes a couple of hours to replace. Warranty returns also mean extra paperwork for the parts store, warehouse distributor and pump manufacturer, not to mention the shipping costs.
To help your customers do a better job fixing fuel-related problems, FPMC will be launching a new website later this year. The website will include diagnostic information on how to test, replace and handle fuel pumps. The website will also have fuel pump technical service bulletins from fuel pump manufacturers, and links directly to the FPMC member’s own websites. The address is www.fuelpumpinfo.org.
Currently, the only way to test a fuel pump is on the vehicle. This requires a certain level of know-how and some special tools. If an engine does not seem to be getting any fuel (cranks and has spark, but won’t start), one of the easiest checks to make is to listen for the pump to run for a couple of seconds when the ignition is first turned on. No buzz from the pump means the fuel pump is not running. It may be a bad pump or it may be an electrical problem (no voltage to the pump).
NOT ENOUGH PRESSURE?
If an engine starts, but runs poorly (no power), it may not have enough fuel pressure. This can be checked by attaching a fuel pressure gauge to the service fitting on the engine fuel rail, or teeing the gauge into the fuel supply line. If fuel pressure is less than specifications, the next step would be to check the fuel pressure regulator, fuel lines and fuel filter for possible problems.
A fuel pump check should also include testing how much fuel the pump flows. A weak pump may develop adequate pressure at idle, but cannot keep up with the engine’s fuel demands at higher speeds, causing a loss of power. Fuel volume can be checked with a flow meter teed into the fuel supply line or return line, or the fuel supply line can be disconnected from the fuel rail and placed in a container to see how much fuel the pump delivers in 30 seconds. A good pump will usually deliver about a quart of fuel.
One of the FPMC members is currently developing a new fuel pump bench tester that will allow you to bench test a customer’s old fuel pump as well as a new pump before it leaves the store. The tester uses a safe, low flammable liquid to test both fuel pressure and flow volume. Such a tester would help resolve fuel pump warranty returns, and hopefully improve the accuracy of diagnosing questionable fuel pumps.
If a fuel pump has failed, several additional steps are necessary to prevent a repeat failure. If the old pump was contaminated with dirt or rust from inside the fuel tank, the fuel tank needs to be cleaned out or replaced. A new fuel pump inlet strainer or filter sock should also be installed when the pump is replaced, along with a new fuel filter. All the rubber fuel hoses in the fuel system should also be carefully inspected for cracks, leaks or damage, and hoses that are more than 10 years old should probably be replaced.
Additional items a fuel pump customer might need when replacing a fuel pump or filter include a quick-release tool set for disconnecting the fuel lines from the fuel filter, and possibly a bottle of fuel system cleaner.
FUEL PRESSURE TESTING TIPS:
Here are some tips you can pass along to your customers if they need help testing fuel pressure:
• Fuel pressure is critical on fuel injected engines. To run correctly, fuel pressure must be within specifications. There are no rules of thumb because requirements can vary from as little as 30 psi to as much as 90 psi depending on the application. The only rule is that KOEO (key on, engine off) fuel pressure is typically 6 to 10 psi higher than when the engine is running.
• If static fuel pressure is less than specifications, the fuel pump may not be running at normal speed due to low voltage (a loose or corroded wiring connection or ground) or high resistance in the relay.
• A hard starting problem may be due to a loss of residual fuel pressure in the system because the fuel pump has a faulty check valve, or the fuel pressure regulator is leaking. The fuel system should hold pressure for up to several hours after the engine has been shut off.
• Another check that should be made is dead head pressure. This is the maximum output pressure of the fuel pump. With the return line pinched shut, a good pump should produce two times (2x) its normal operating pressure at idle. If the pressure rating does not go up with the return line blocked, the pump may not be able to deliver enough fuel at higher engine speeds.
• The fuel pressure regulator should also be tested to see if it is working properly. With the engine running, disconnect the vacuum hose from the pressure regulator. Fuel pressure should increase 8 to 12 psi with the line disconnected. No change in pressure would indicate a faulty pressure regulator, or a leaky or plugged vacuum line. There should also be no fuel inside the vacuum line to the regulator. If the inside of the hose is wet, it means the regulator diaphragm is leaking and the regulator needs to be replaced.
• Another test that can help identify fuel system problems is a fuel pressure drop test. This test measures the drop in static system fuel pressure when each injector is energized. The amount of pressure drop for each injector can then be compared to see if the injectors are dirty and need to be cleaned or replaced. This test requires an “injector pulser” tool to energize the injectors.
An injector that is pulsed 100 times for five milliseconds should produce a minimum pressure drop of about 1 to 3 psi, and no more than 5 to 7 psi depending on the application. The difference in pressure drop between all the injectors should be 2 psi or less. A difference of more than 3 psi between injectors would indicate dirty injectors.
• Never run a dry electric fuel pump to test it. The fuel pump requires fuel for lubrication, and running it dry may damage it.
• When replacing an in-tank pump, always disconnect the battery to prevent any unwanted sparks. Then drain the tank before removing the tank straps and opening the pump’s retaining collar. When installing the new pump, always replace the filter sock and use a new O-ring for the sealing collar.