When replacing a press-type wheel bearing and hub flange, it’s important that all the wheel-end parts work together properly after reassembly. Damaged parts or improper torquing can cause premature hub failure and issues with overall vehicle performance.
A hub flange kit contains all the components needed to replace a worn out wheel bearing and flange. It’s best to use a kit that includes the hub flange, cartridge bearing, axle nut, seals and c-clip. Follow proper installation procedure and the steps below to ensure maximum service life for new components.
Note: the steps outlined below relate directly to a 2002 Mazda Protegé, but can generally be followed for other vehicles.
Disassembly
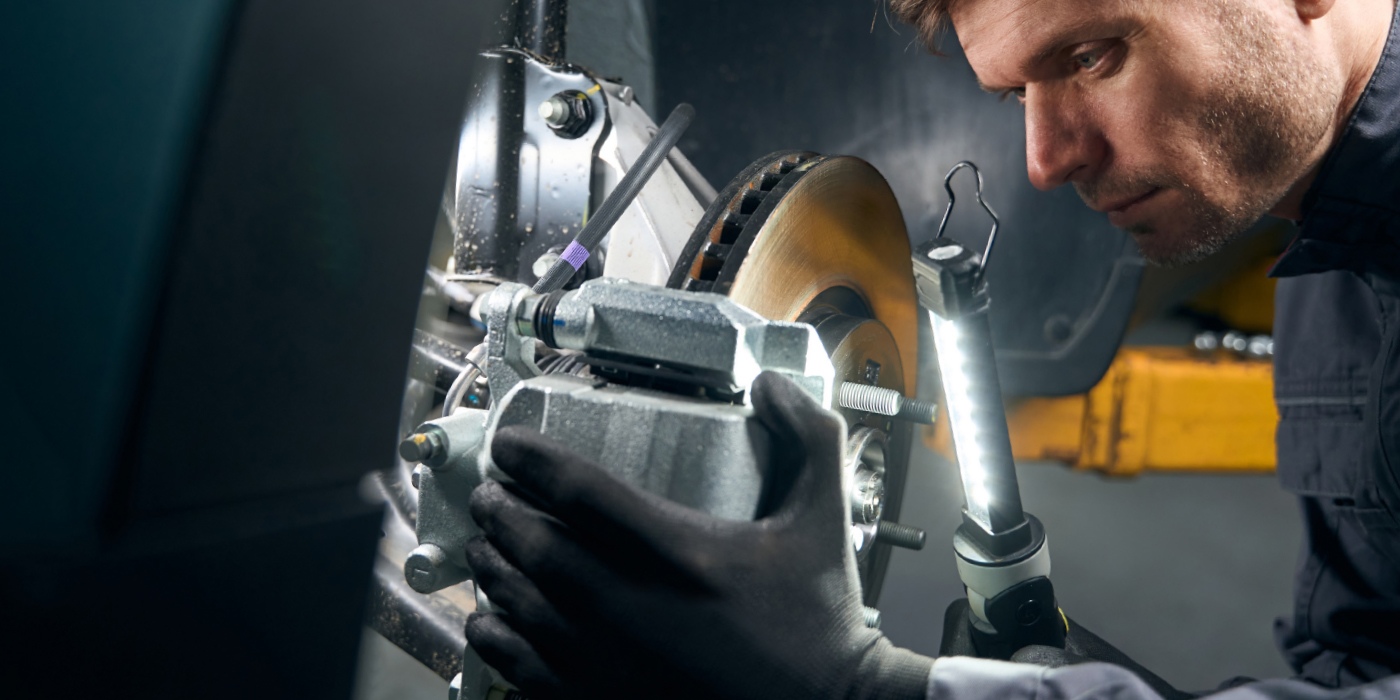
Once you have identified the proper hub flange kit for the vehicle you are ready to replace the wheel bearing and hub flange. Remove the tire, caliper and caliper bracket. Secure the caliper with a bungee cord to avoid damage to the brake line. Remove the rotor and axle nut and move the front half-shaft out of the way. Remove the lower ball joint and outer tie rod by removing the retaining nut and/or pinch bolt. Also remove the lower retaining bolt for the strut. Now remove the knuckle from the vehicle.
Press-in Installation

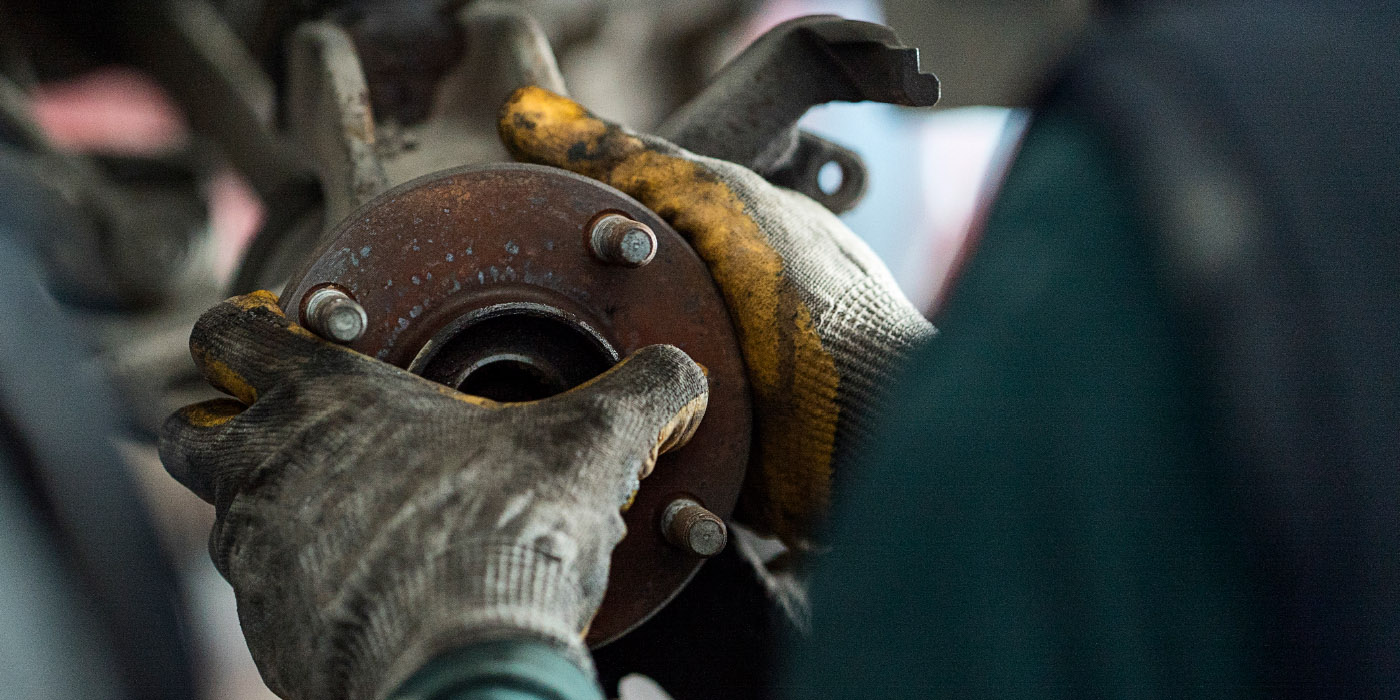
Set the knuckle on a flat surface on the press with the right adaptor and press the flange from the knuckle. Pull the c-clip off the knuckle and return to the press to remove the cartridge bearing.
Inspect the old bearing for signs of an out-of-round knuckle like uneven pressmarks. You can also use a bore gauge to check and see if the knuckle is out of round. Inspect and clean the interior of the knuckle to ensure that there are no high spots or deep grooving that can damage the new bearing.
Set the new bearing and knuckle on the press with the proper adaptor in place. Once pressed, install the c-clip. Return to the press and arrange the parts so that the adaptor supports the inner race of the bearing on a flat surface and the knuckle is centered atop the hub flange before pressing.
Reassembly
For reassembly, repeat the disassembly process in reverse order. Follow torque specification for the axle and lug nuts. Pump the brakes and test-drive the vehicle.
Courtesy of SKF. Please visit www.vsm.skf.com to learn more.