When a vehicle comes into a shop with a low or spongy brake pedal, what is your first thought? Chances are you think it is a problem in the hydraulic system. It could be a faulty master cylinder, a leak in the brake lines or a bad caliper.
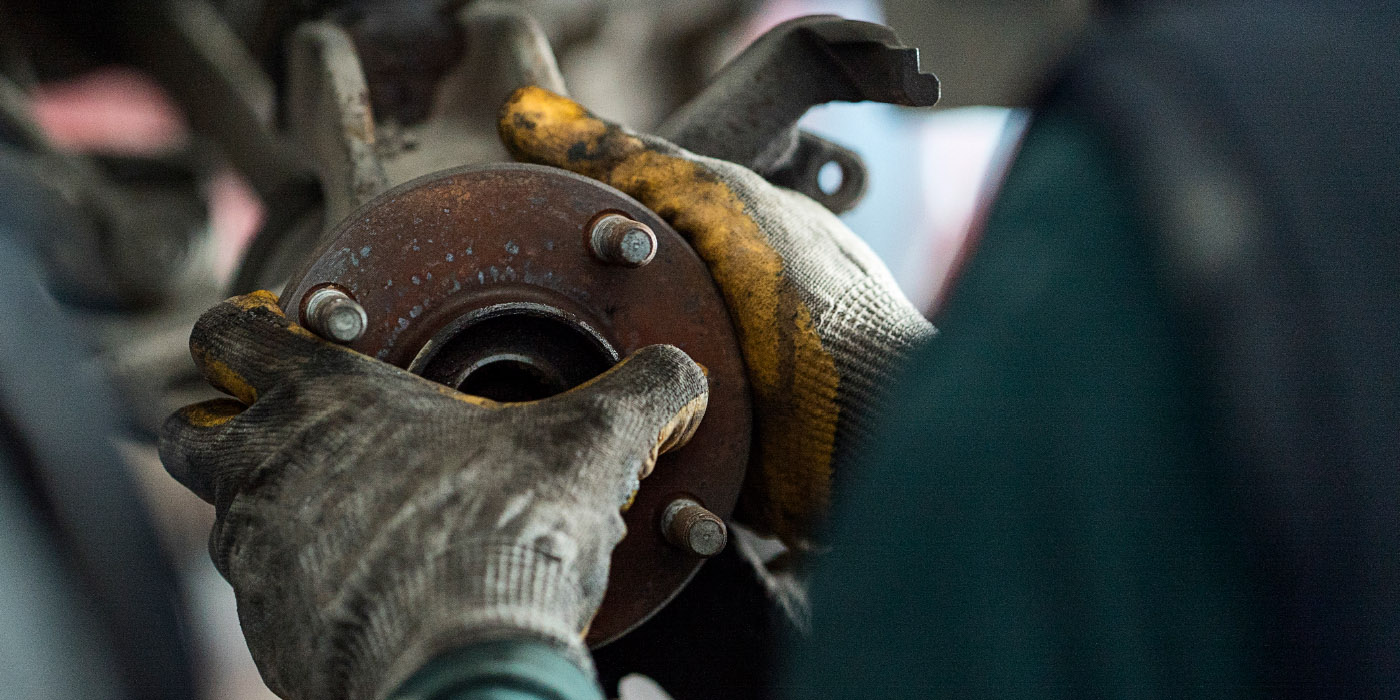
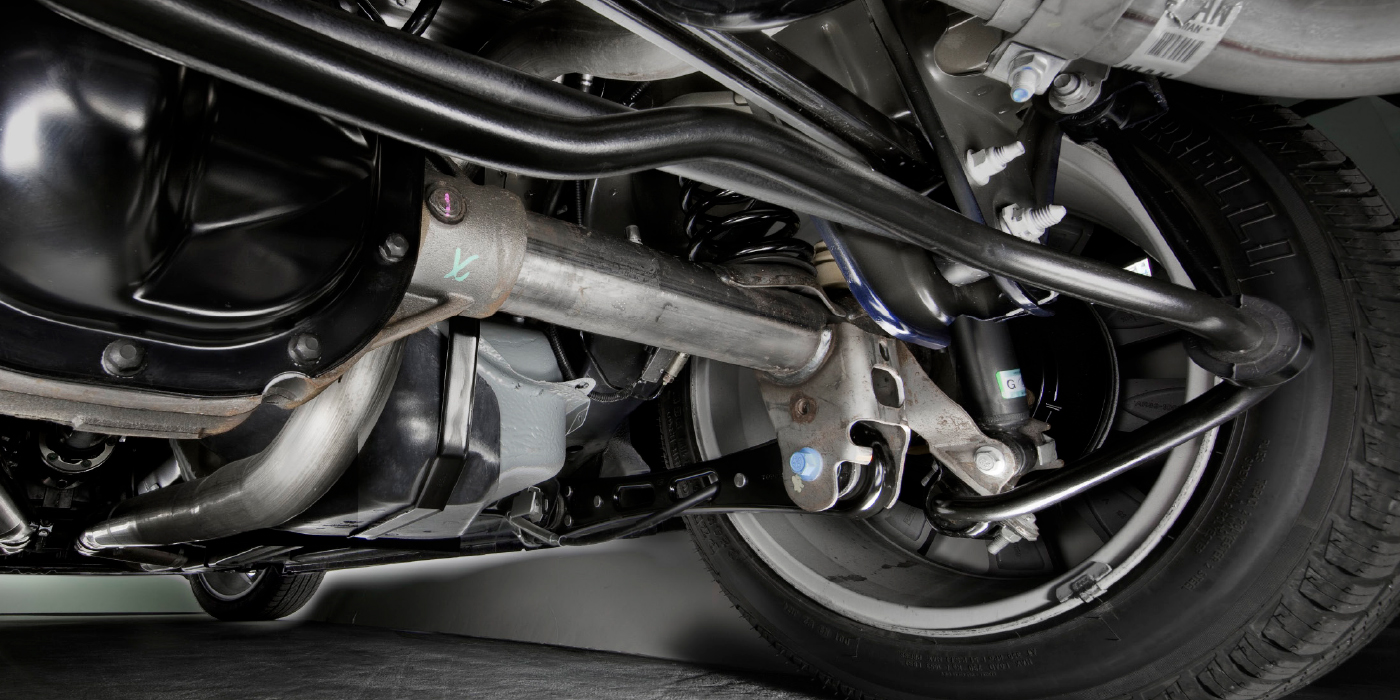
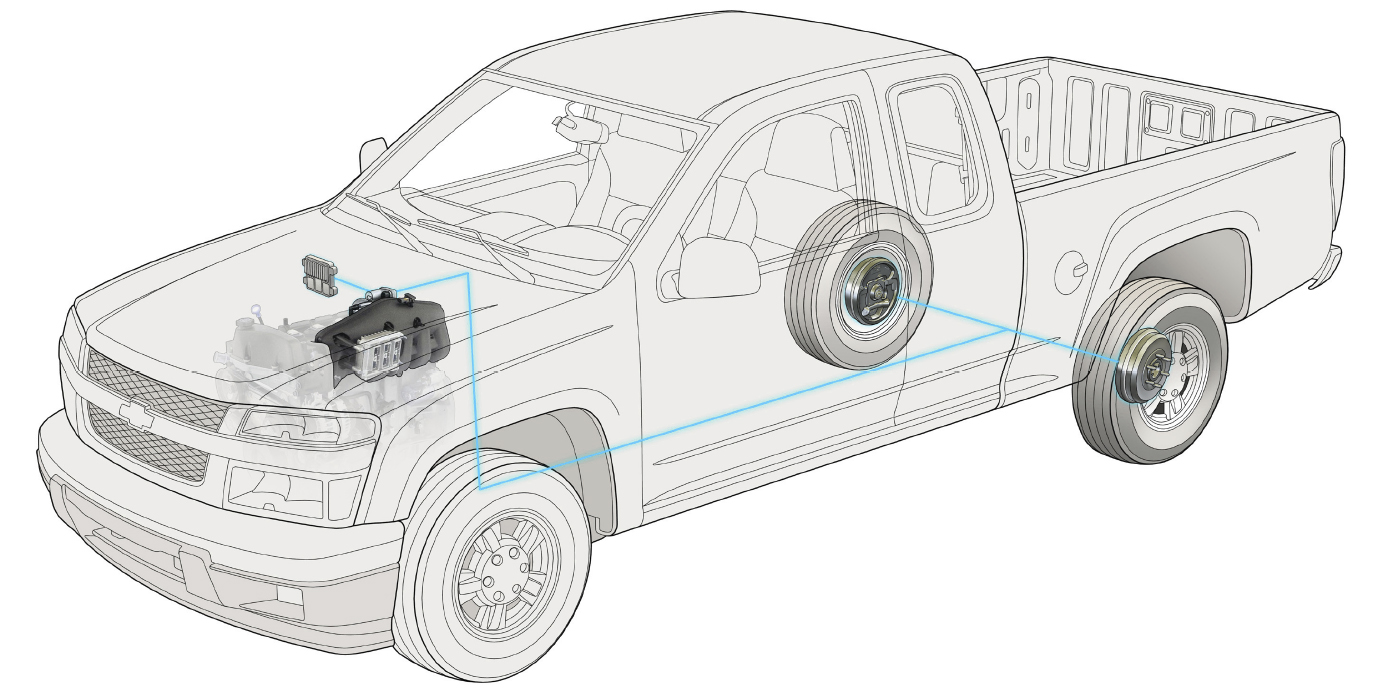
The cause of a low pedal doesn’t always lie in the hydraulic system. We recently had a car come into our shop with a low pedal. Another shop diagnosed the vehicle with a faulty master cylinder. However, after replacing the master cylinder, the low pedal remained. At first, we assumed that there was a problem in the hydraulic system somewhere. We got the car in the air and were preparing to perform an isolation/line lock test. But before we started the test, we wanted to run through our brake inspection checklist. As part of that checklist, we checked the play in the wheel bearing (See Image 1). We found significant play in the bearing.
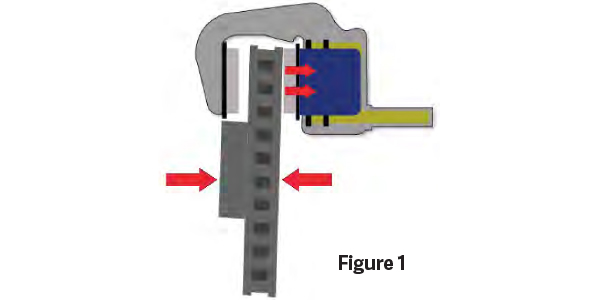
Brake rotors are held in alignment by wheel bearings. If you have a faulty or loose wheel bearing, the rotor will wobble on its axis. This wobble causes the rotor to push the piston into its bore. Now, when you hit the brake pedal, the piston has to travel farther to apply the brakes. This causes a low or spongy brake pedal. Figure 1 Repair Procedure: We determined the play in the wheel bearing was caused by a faulty bearing. We replaced the wheel bearing and a road test confirmed that this was the cause of the soft pedal. This was an important reminder to our shop that we can’t make assumptions.