A “no brake pedal” condition can be encountered after a new master cylinder is installed, leading the technician to believe that the master cylinder is defective. This is likely not the case; the condition can be caused by the piston sticking in the bore of the master cylinder during the bleeding process when the brake system is manually bled. The brake pedal will go to the floor and subsequent efforts to get a satisfactory brake pedal will fail. A good indication of this condition is lack of fluid flow from the brake bleeders.
QUICK TIPS
1. Make sure the master cylinder is bench bled prior to installation.
2. Follow the vehicle’s manufacturer-specified bleeding procedure.
3. Some automotive manufacturers require a separate ABS bleeding procedure. Failure to follow manufacturer procedures may cause a “no pedal” condition after a new master cylinder installation.
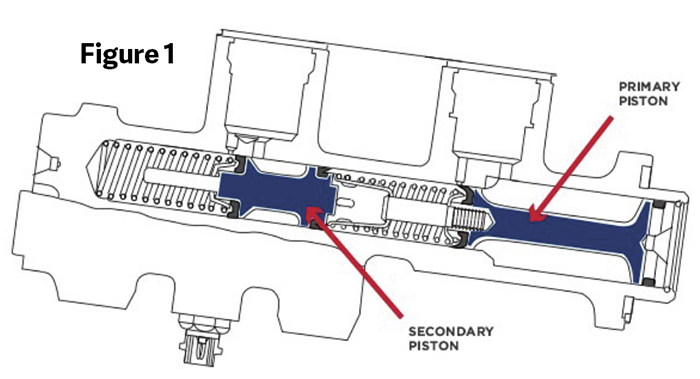
If you look at Figure 1, you can see the pistons are at the rest position. This allows fluid to flow from the fluid reservoir to the cylinder for normal operation.
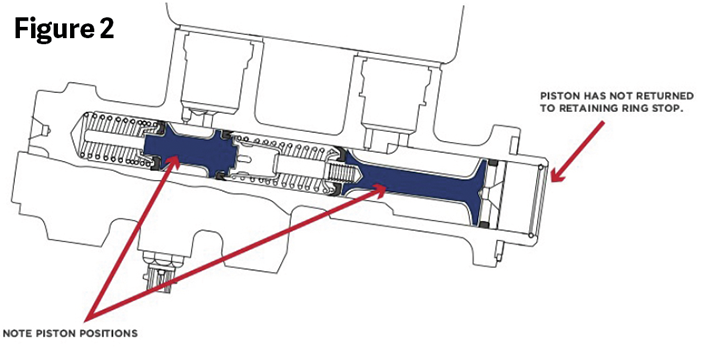
When the system is manually bled, the pedal is often depressed completely, moving the primary and secondary pistons to their extreme forward position (Figure 2). The primary piston can stick even though there are springs attempting to push it back in position. When a master cylinder is assembled, the seals and cylinder bore are lubricated for a positive seal. This combined with air trapped in the system can cause a vacuum lock in the cylinder, causing the pistons to stick. When the piston is stuck in the applied position, you can see the ports supplying fluid are blocked and will not fill the cylinder and operate properly.
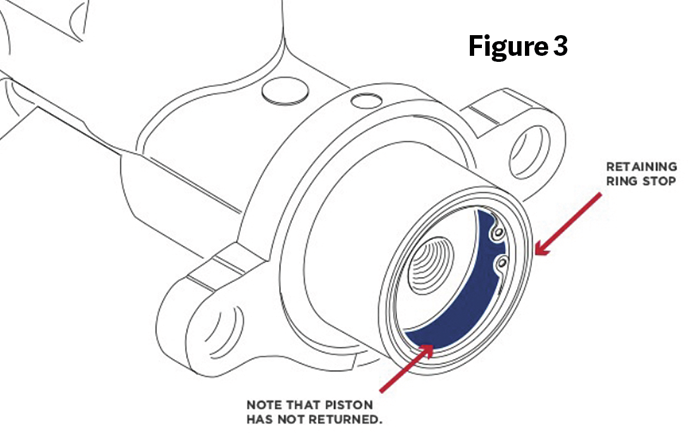
You can verify this condition by removing the master cylinder from the booster without disconnecting the brake lines. You will notice that the master cylinder piston is not resting against the snap ring, Figure 3.
Occasionally connecting a pressure bleeder and opening wheel bleeder screws will cause the piston to return. You can also tap lightly on the housing, with the bleeders open, to free the piston. After the piston has returned to its correct position and air is bled from the system, the problem should not recur.
Courtesy of Wagner Brakes