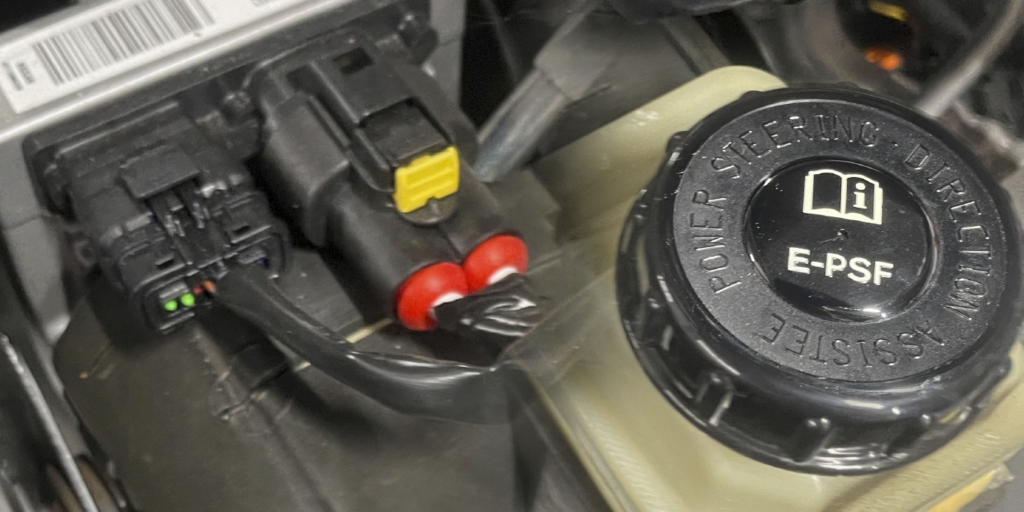
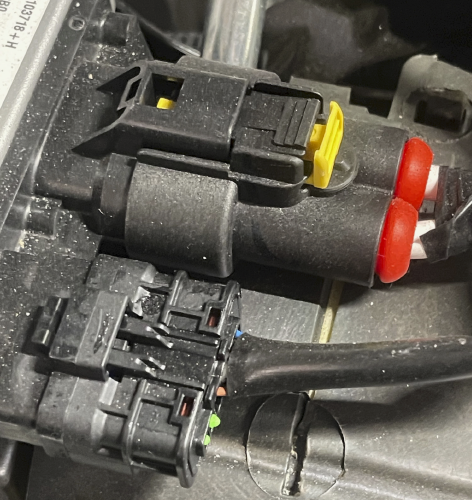
Nissan’s electro-hydraulic power steering system provides the same feel of a conventional hydraulic power steering system while improving fuel economy by using an electric motor to power the pump. The system is comprised of the electro-hydraulic pump assembly, control module and steering gear.
The power steering module is on top of the pump, and the motor controls the speed of the power steering pump according to vehicle speed and steering angle. By changing the pump speed, the module controls the steering assist force. The control module is connected to the hi-speed CAN bus that ties the engine control module (ECM) and ABS module. The ABS module provides vehicle speed and steering angle, and torque data to the power steering system. The connection to the ECM allows the alternator to provide enough power when the pump is running.
The control module monitors the hydraulic pressure output and temperature. After the engine started, the hydraulic pump electric power steering system performs a self-diagnostic test. If a malfunction occurs in the system, the fail-safe function stops the hydraulic pump or restricts operation.
When the hydraulic pump is operating and assist force is generated, the hydraulic pump electric power steering warning lamp is OFF. When the hydraulic pump electric power steering system is stopped by the fail-safe or protective functions and steering assist force is not being generated, the steering will go to a manual operation. The electric power steering warning lamp turns ON. The system is trying to prevent the pump from operating without fluid, which will damage the pump unit.
The control module also monitors the temperature of the motor and pump. During regular operation, the fluid temperature should not exceed 194º F. When the system sees temperatures more than the limit, the warning lamp turns ON and assist is limited or turned off completely.
There are several causes of excessive internal temperatures. For example, if the driver performs parking maneuvers for a long time with rapid movement of the steering wheel lock-to-lock, the pump can overheat. If the steering is held at full lock, the pump can overheat. When this happens, the system will store code C160A if an overheating condition has occurred.
If the alignment is out of specification and the driver is fighting a steering pull, it can cause the power steering pump to work harder and generate more heat. It can also happen if the tire inflation pressure is not equal. Why? The speed of the pump depends on the angle of the steering and the speed of the vehicle.
Common Codes
When this happens, the system will store code C160A if an overheating condition has occurred. When an event occurs, it will generate DTCs that can be read with a scan tool. A code for “certain steering assist force” means the operation of the pump was reduced to prevent overheating. A “manual steering state” indicates the pump was fully disabled.
C1143: Certain Steering Assist Force
C1601: Manual Steering State
C1606: Manual Steering State
C1607: Certain Steering Assist Force
C1608: Manual Steering State
• Most of the protective or fail-safe modes will stop if the engine is restarted. However, this is a continuous monitor, so chances are the code will return quickly.