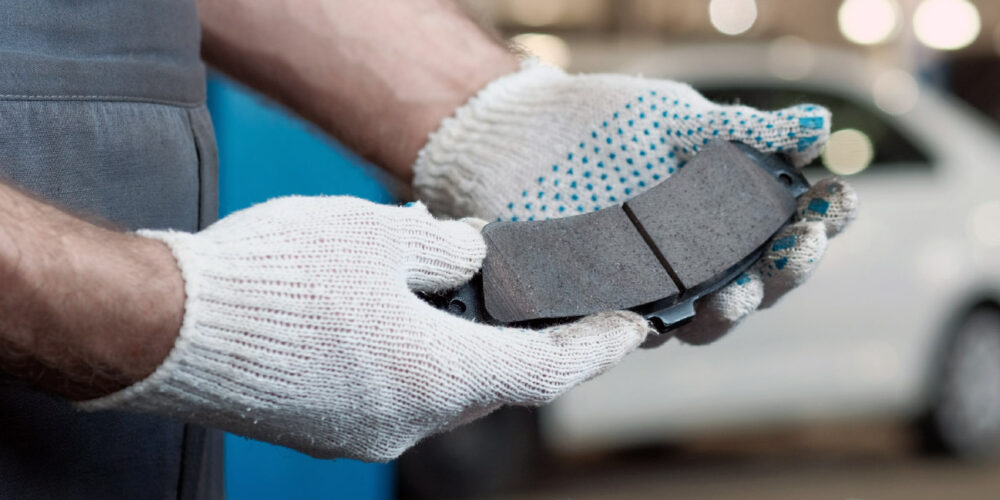
Brake Pad Edge Codes
The “Edge Code” can tell you information about a brake pad’s friction material.
When a brake pad is manufactured, one of the last steps involved is to print a series of letters and numbers on the edge of the friction material. This code has been on brake shoes and pads for more than 60 years, but what does it mean?
The “Edge Code” can tell you information about a brake pad’s friction material. These letters and numbers can help you to select the correct brake pads or shoes for a vehicle. But, the edge code can do only so much.
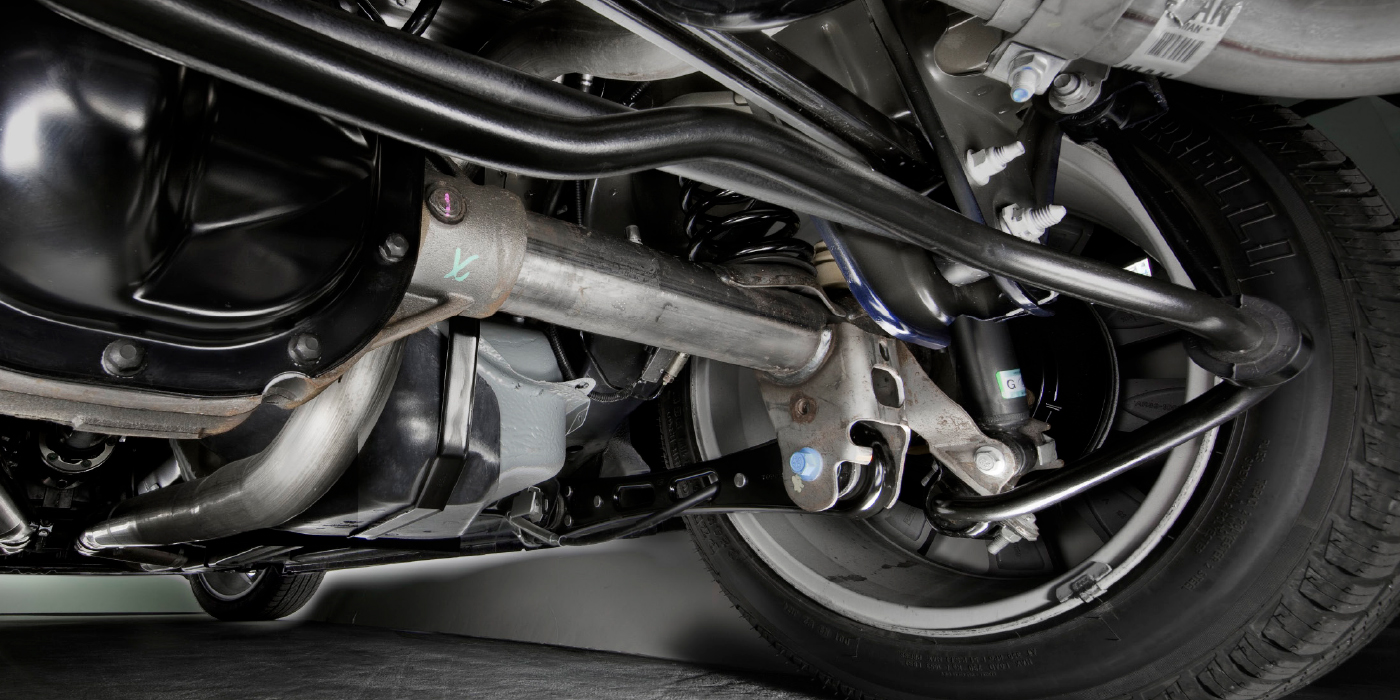
Chassis Parts and Alignment Angles
Knowing why the adjustment is required is critical to performing the total alignment.

Suspension Upgrades – Selling Shocks and Struts
The question customers fail to ask is, what is “best” for their vehicle?

Air Ride Suspension Diagnostics
The key to understanding the logic of air ride systems is using service information.
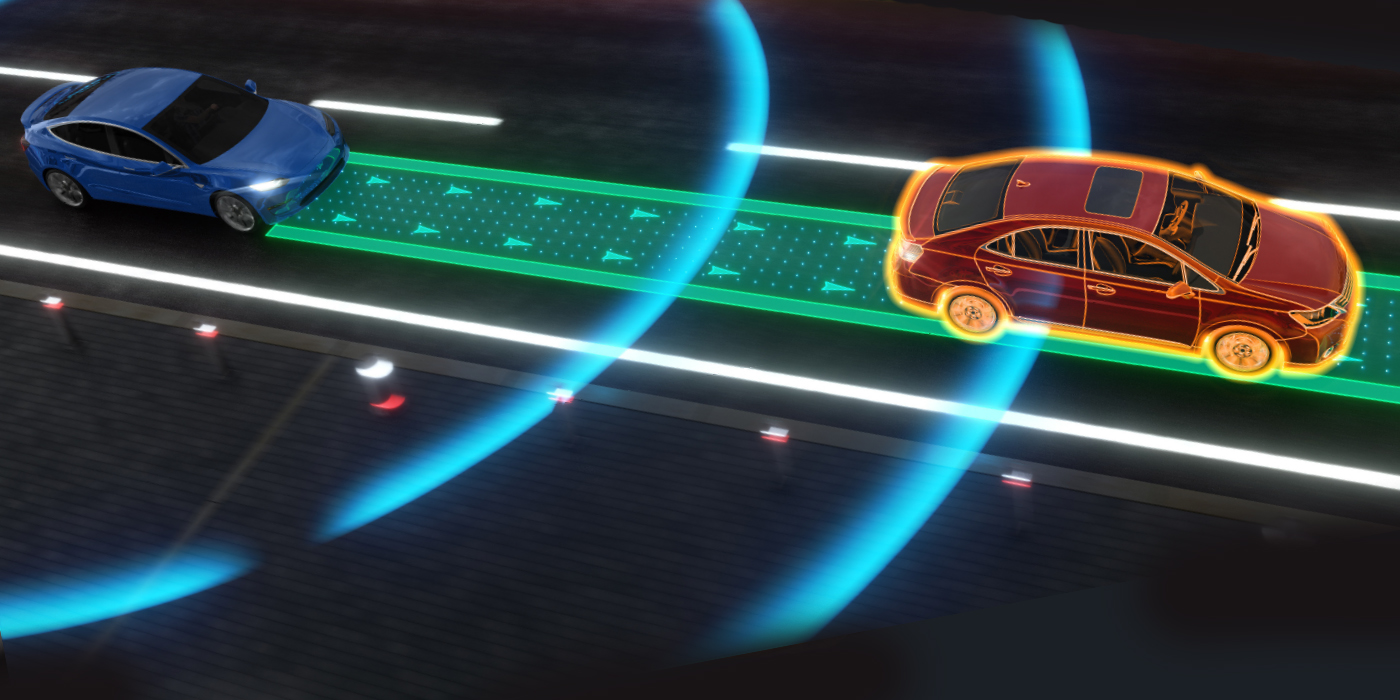
Steering Angle Sensor Operations
It is important for the ABS/ESC module to receive two signals to verify the steering wheel’s position.

Other Posts
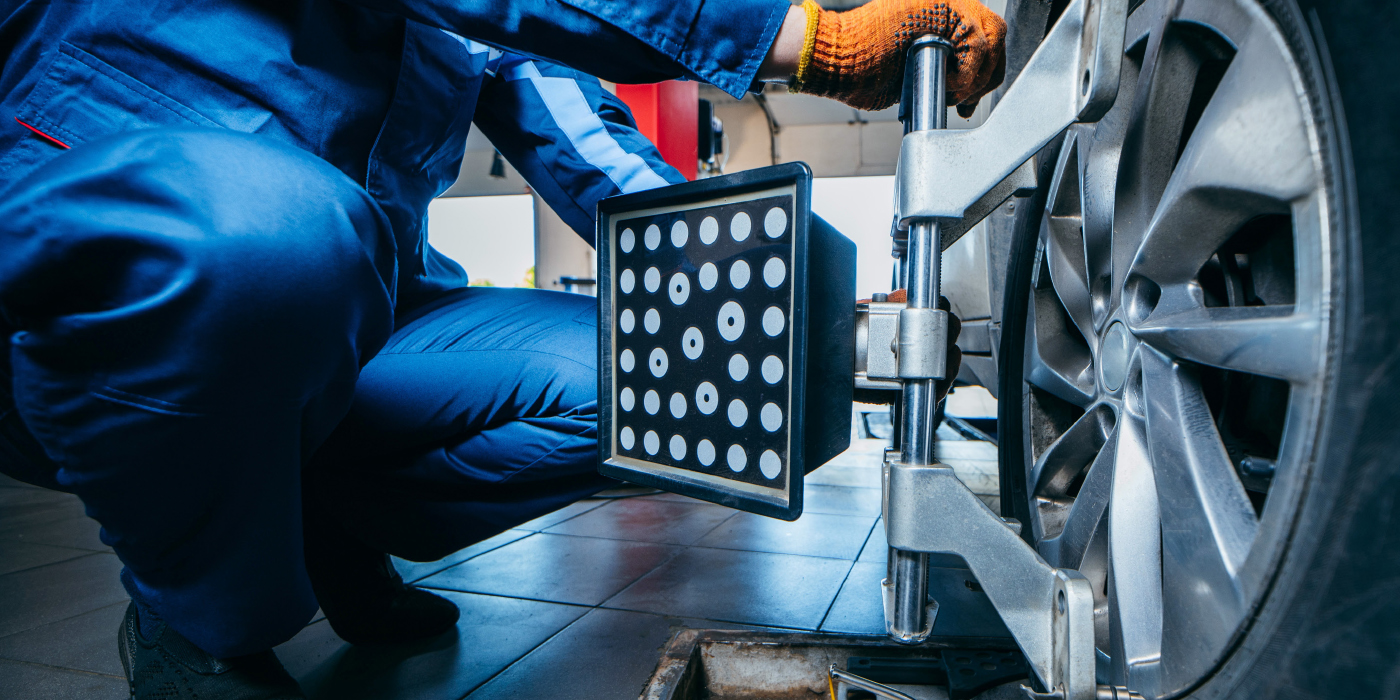
Chassis Alignment
The source of the complaint can be the angles, electronics or tires.

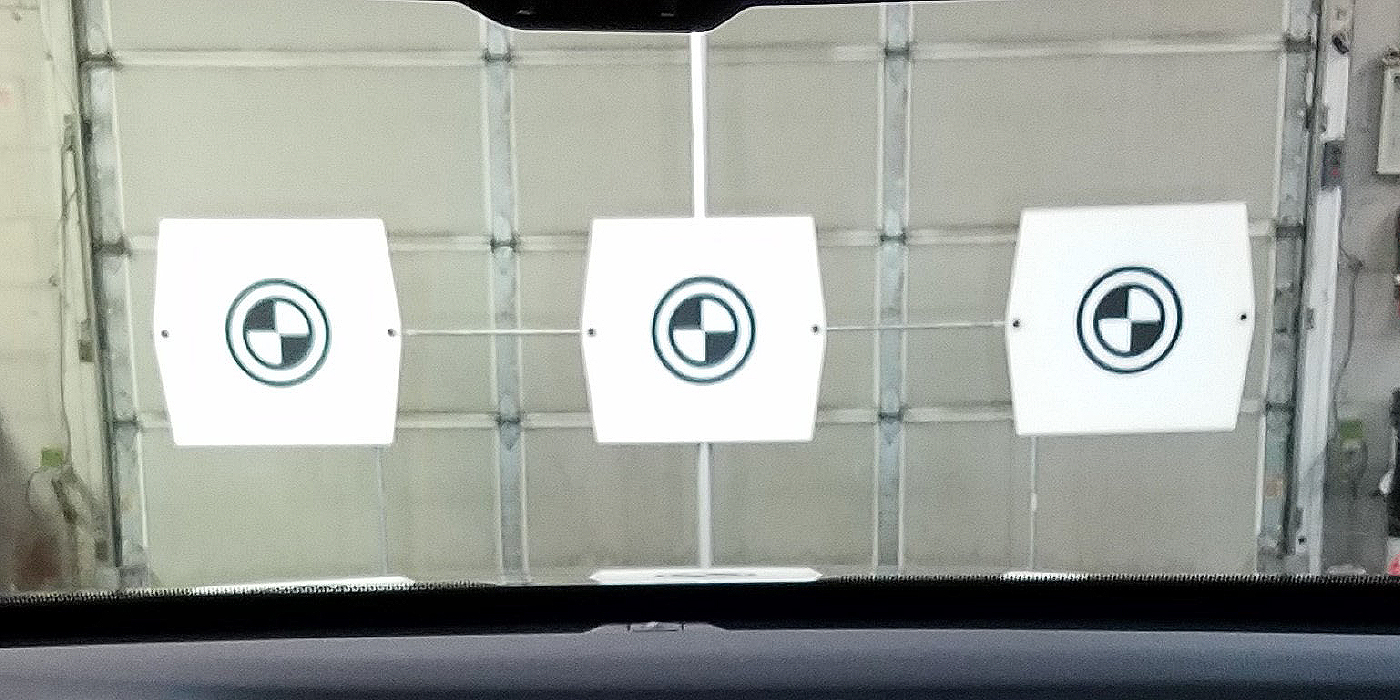
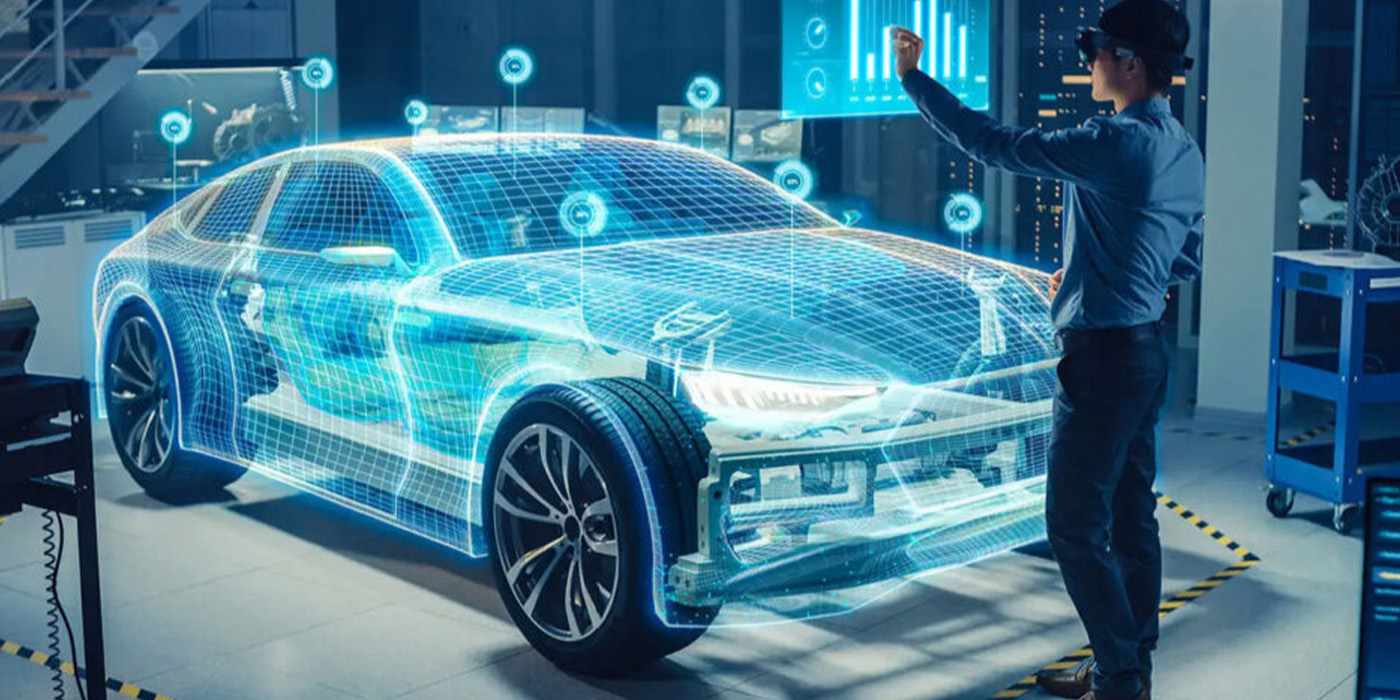
Laying Out Your Shop for ADAS/EV Repairs
With so many vehicles equipped with some form of ADAS, rethinking your electronics layout or plan might be in order.

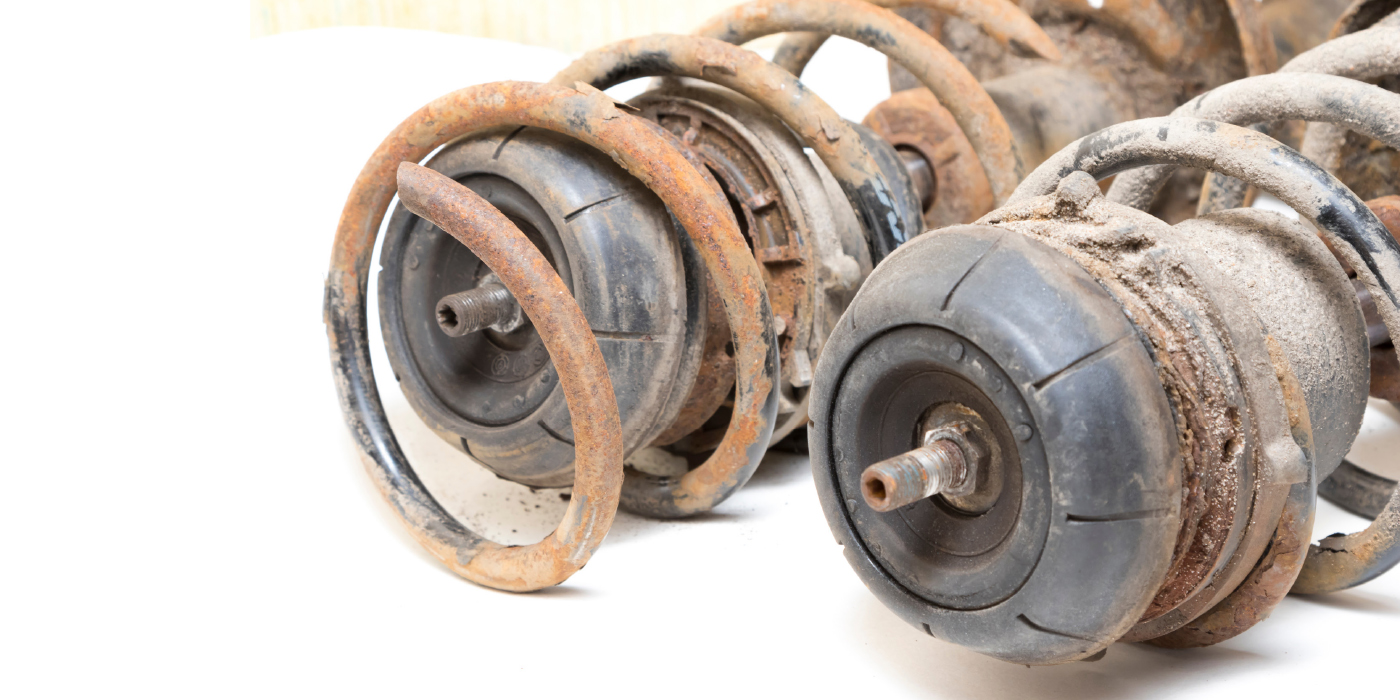
Broken Springs
What is the cause for the failure? Why does it occur with specific vehicles?

The Importance Of ADAS Calibrations
Following best practices and using appropriate equipment ensure customer satisfaction and safety.






