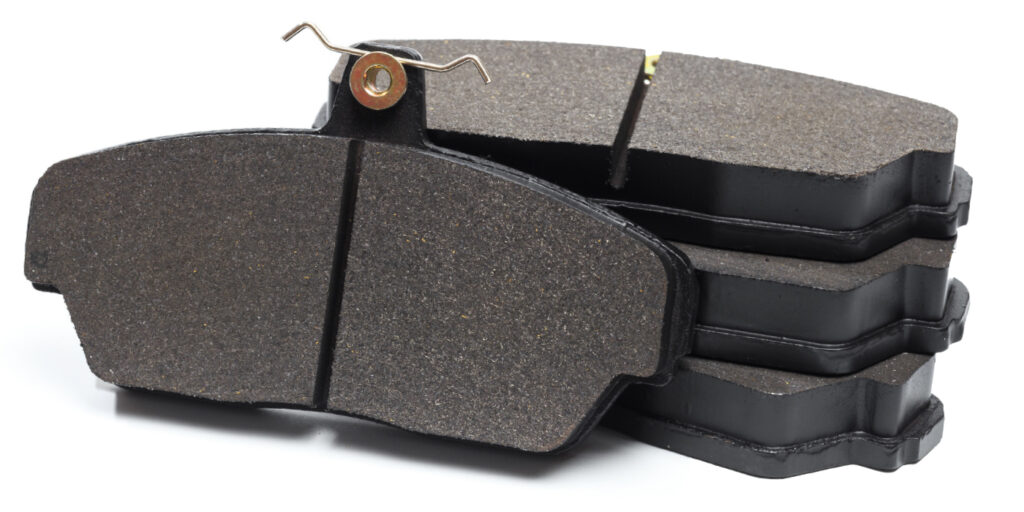
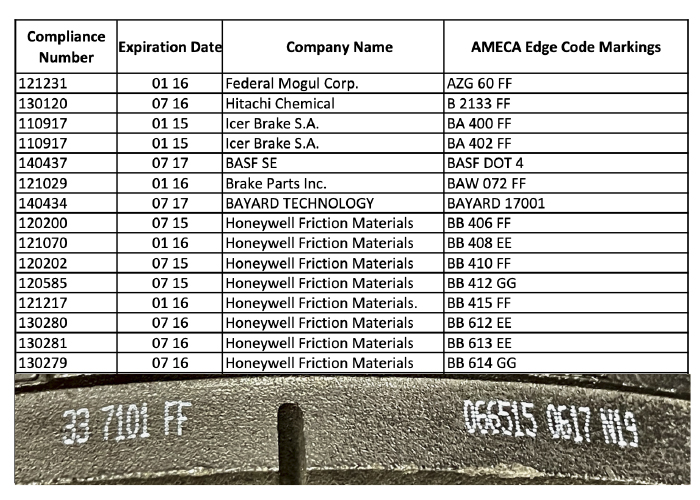
Just about every brake pad or shoe you install has a cryptic code printed on the side of the friction material or on the backing plate. As a technician, being able to read this code called the “Edge Code” is just as important as the Dewy Decimal system is to a librarian.
With the code you can tell who made the pad and friction material and if it meets certain environmental standards. Edge Code is a language written by engineers, federal entities and industry associations. Like any language, edge coding has its own “grammar.”
The first few letters usually indicate the manufacturer. Some companies use their full name or a two- or three-letter acronym. Deciphering the letters can be difficult and you might need a key. The Automotive Manufacturers Equipment Compliance Agency (AMECA), keeps a list of the manufacturer codes.
Using the “DB” edge code list, I can tell this brake pad was made by Roulunds Braking. But, it was in a box from Advance Auto Parts, which brings up another point. Many brake pad brands are not manufactured by the name that is on the box. Some of these products are sold under “private labels” like WearEver. But, these companies or retailers selling the pads usually make an effort to put their name somewhere on the pad. The same is true for some brake lines that source premium friction materials and specific pad sets for difficult applications. The next set of letters and numbers indicate the AMECA friction material composition compliance number, in most cases.
FF at the end of the top edge code number represents the hot and cold coefficients of friction. In the edge code, the first letter denotes the normal coefficient of friction (temperatures ranging from 200° F to 400° F) and the second letter indicates the hot coefficient of friction (ranging from 300° F to 650° F). You want to match the hot and cold friction levels with the original pads, if possible. If the friction levels don’t match, it could upset the braking balance of the vehicle.
Copper and Edge Codes
Brake friction formulations are now covered by new regulations in California and Washington, which require the phaseout of copper and other metals considered potentially harmful to the environment. As a result, these regulations, while currently limited to two states, are affecting all vehicle service providers across North America as the friction industry shifts to low- and zero-copper formulations in all regions. Additionally, millions of new vehicles equipped with low- or zero-copper brake pads are already being sold throughout the U.S. and Canada.
All brake pads and shoes manufactured after Jan. 1, 2014, for sale in California, are required to have new markings that indicate their compliance with these state regulations regarding friction formulations. On these pads in particular, the markings are a combination of letters and numbers tacked onto the end of an edge code.
Now, enter A, B and N — three new compliance designations from the Automotive Aftermarket Suppliers Association (AASA) that correlate with the various phases of the implementation timeline. These are the leaf codes on the box.
In California and Washington, all brake friction materials are restricted to no more than 0.1% by weight of asbestiform fibers, chromium, lead and mercury, and no more than 0.01% of cadmium by weight. By 2021, copper in all brake friction materials must be less than 5% by weight in both states. By 2025, California law requires that copper must be less than 0.5% by weight. Washington will adopt a date for 0.5% by weight copper following a feasibility assessment.
An N16 code indicates a brake pad has 0.5% copper by weight and was manufactured in 2016.
There is an X or WX compliance marking as well that indicates an exemption from the regulation. In the recommended edge code structure, the numbers that follow the A, B or N are for dating purposes. So, N17 would mean an “N” formulation, manufactured in 2017.
You might also see an optional set of four numbers, placed either before or after the new compliance markings. In addition to the edge codes, the Washington State regulation requires all brake pads and shoes manufactured after Jan. 1, 2015, have a leafmark icon printed on the packaging to show the level of compliance with the friction material regulation.
A=Designates compliance with requirements concerning cadmium, chromium, lead, mercury and asbestos.
B=Contains between 0.5% and 5% of copper by weight, as well as compliance levels for A certification.
N=Contains less than 0.5% of copper by weight as well as compliance levels for A certification.
Even if you don’t live in California or Washington State, you will see the leaf mark on brake pads.