Federal, state and local regulations govern proper procedures for recovering, recharging and recycling R-134a motor vehicle air conditioning (A/C) refrigerant.
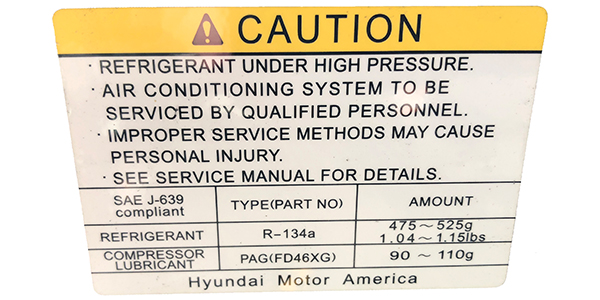
You can find relevant details specific to a vehicle’s refrigerant requirements on the sticker under a vehicle’s hood. The label shows refrigerant type and amount, and information about compressor lubricant. The location of this sticker varies by vehicle but is generally located somewhere up front. The sticker is governed by SAE Standard J639, which provides safety and design standards for automotive air conditioning refrigerant systems.
Technicians must check the vehicle’s sticker before servicing the vehicle. Failure to check the sticker could void the refrigerant recovery machine’s warranty and significantly increase the chances of using an incorrect amount of refrigerant or the wrong type or amount of PAG oil.
The relevant portions of this sticker are:
• Refrigerant Type: Make sure the refrigerant type is compatible with your A/C recovery machine.
• Refrigerant Amount: This is the amount of refrigerant you will tell the machine to put back into the vehicle during recharge (assuming all of it was removed in recovery, which is the normal method).
• Compressor Lubricant Type: This shows the type of PAG oil required by a vehicle’s compressor. Most vehicles are 46, 100 or 150. Use the correct viscosity for the vehicle being serviced. • Compressor Lubricant Amount: This is the full amount of PAG oil the compressor can use. You only need to replace the amount that was removed during service plus 15 mL or 3 to 4 percent of the full amount shown here.
For more information about air conditioning recovery processes and equipment, visit BendPak.