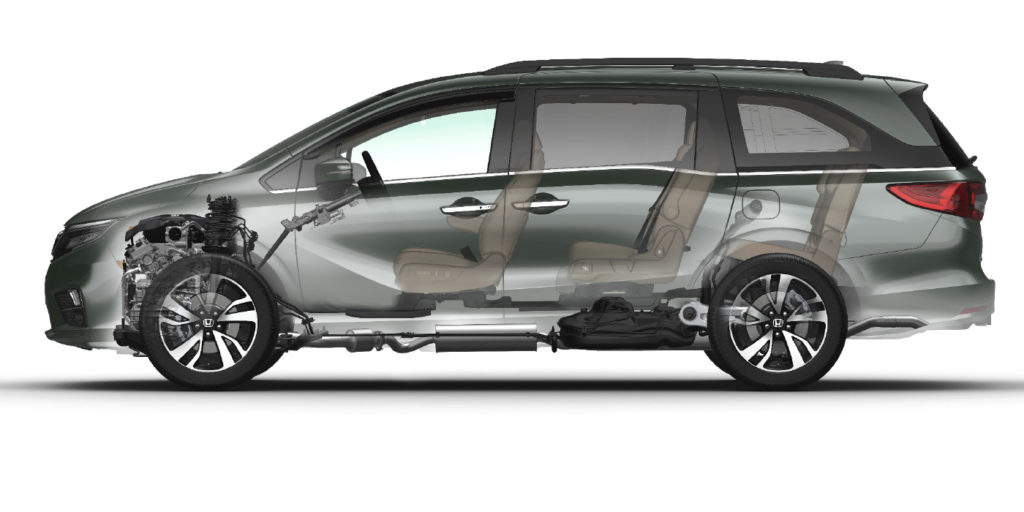
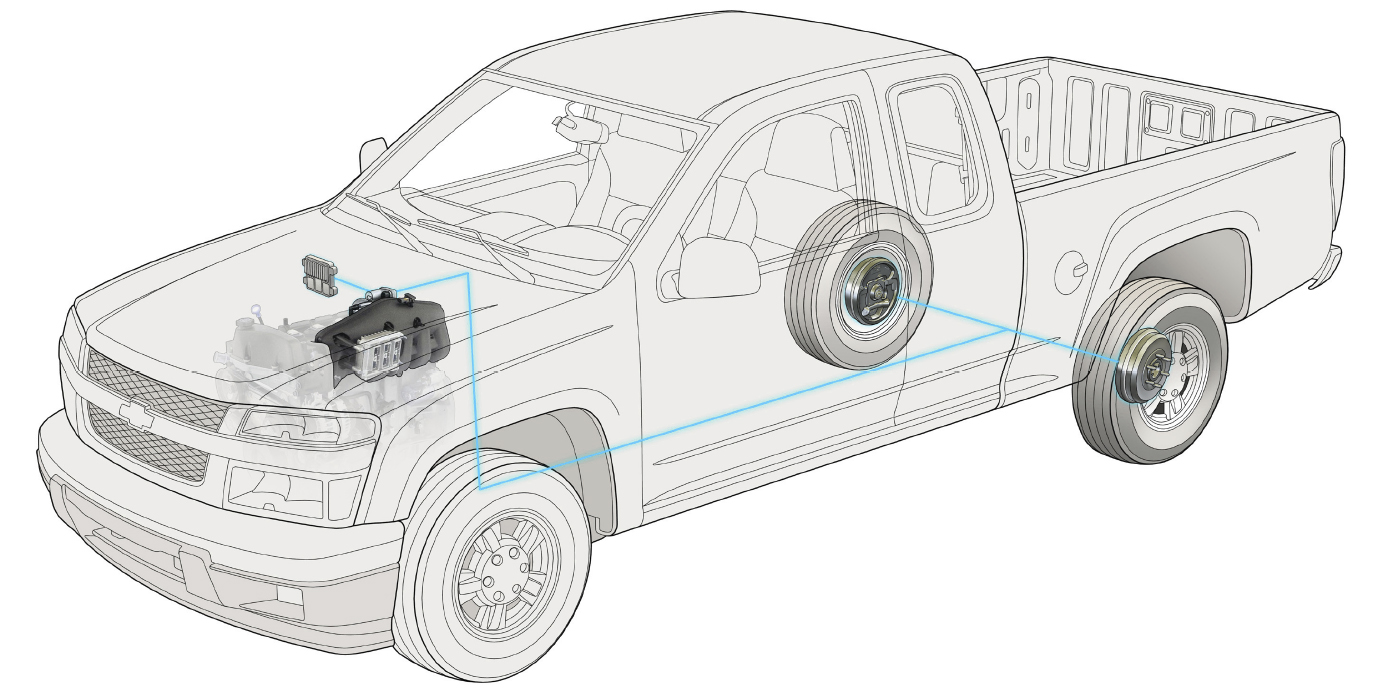
The brake system on the 2018 and newer Honda Odyssey is very conventional except for the rear brakes. The only recall has been for air trapped in the rear calipers.
The only difference between the previous Odyssey is the introduction of “Geomet” coating on the caliper guide pin bolts. Honda recommends the bolts be replaced if the pads are replaced. They claim the coating can be scraped away and lead to corrosion.
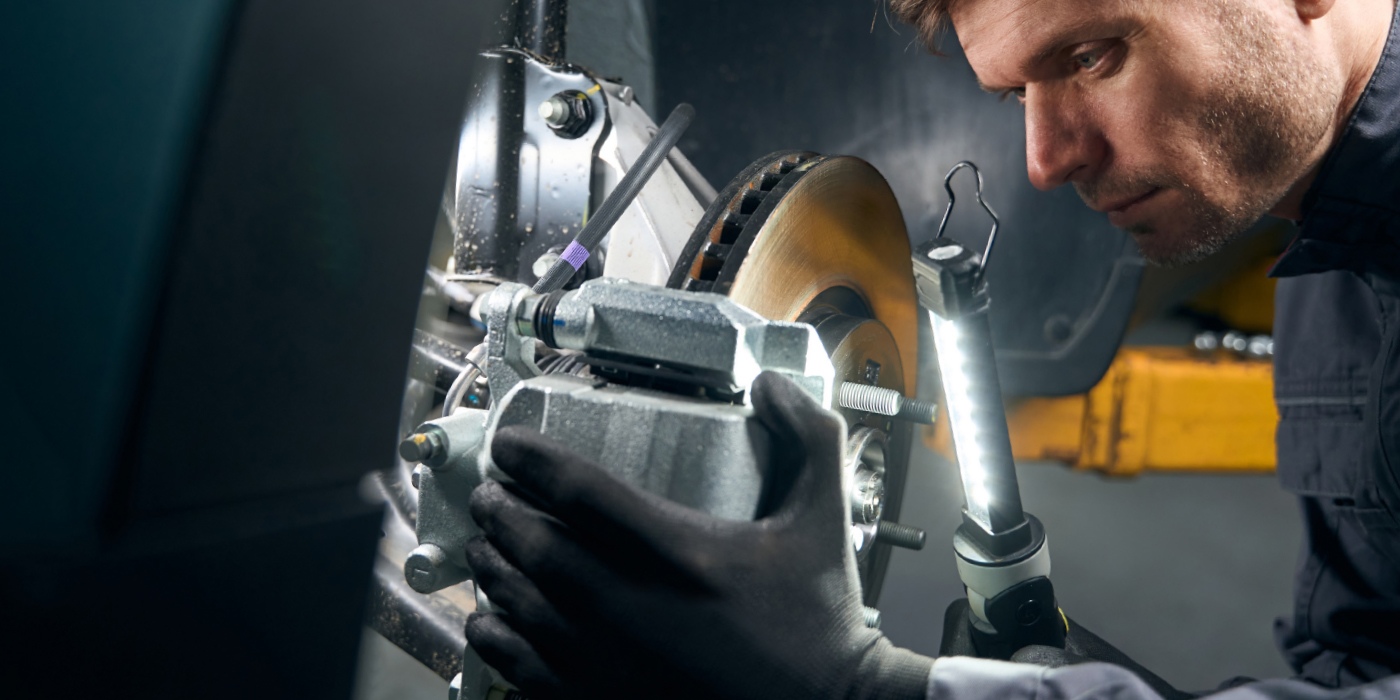
The rear brakes have an electric parking brake with electric actuator motors on the calipers. The actuators need to be removed to service the rear pads. First, the system must be put into maintenance or pad exchange mode. The final retraction of the piston can be performed with a T45 torx socket.
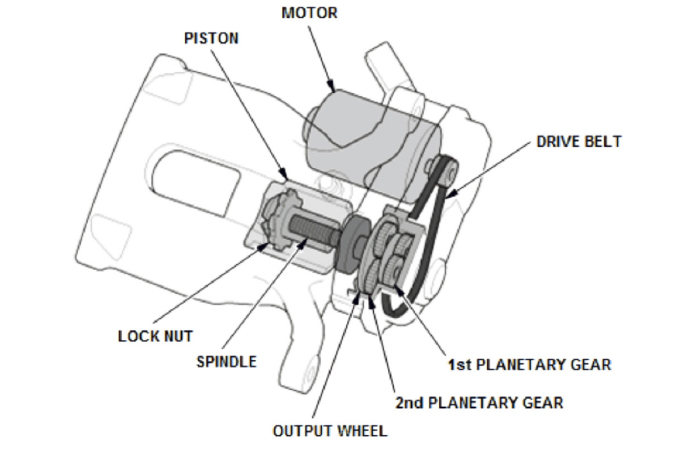
When you remove the actuators, an O-ring seals it to the caliper. Honda recommends using a new O-ring if the caliper is removed. The seal protects the expensive actuator against road spray and brake dust. These actuators use two planetary gear sets and a belt. Moisture and dirt can damage the mechanism.
After the new brake pads are installed, if you have a scan tool with the correct software, turn the vehicle to the ON mode.
Select ADJUSTMENT from the ABS/TCS/VSA menu with the scan tool, then enter the “BACK TO NORMAL MODE” from the maintenance mode, and follow the screen prompts.
The adjustment procedure can be performed without a scan tool. After installing the pads and caliper, turn the vehicle to ON mode. Apply the parking brake, then release the parking brake. Next, turn the vehicle to the OFF (LOCK) mode. Every 1,864 miles without applying the parking brake, the parking brake will perform an adjustment to compensate for brake pad wear when the vehicle is off.
This generation of Odyssey is like any other Honda when it comes to servicing the brakes. Using a low-quality brake pad or reusing the abutment clips can lead to a noise comeback.