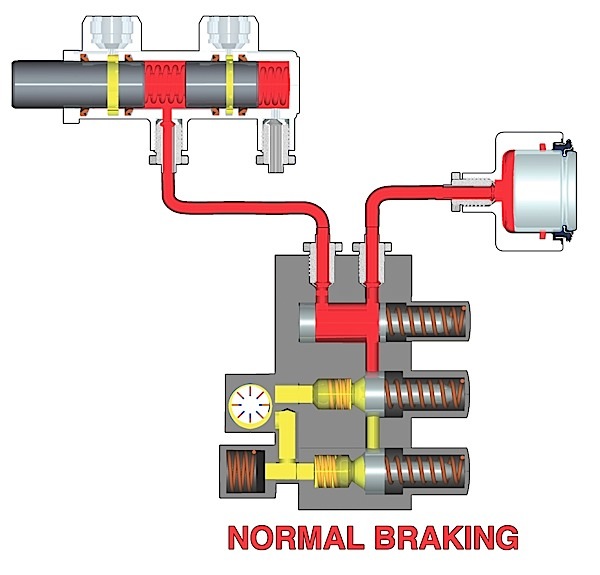
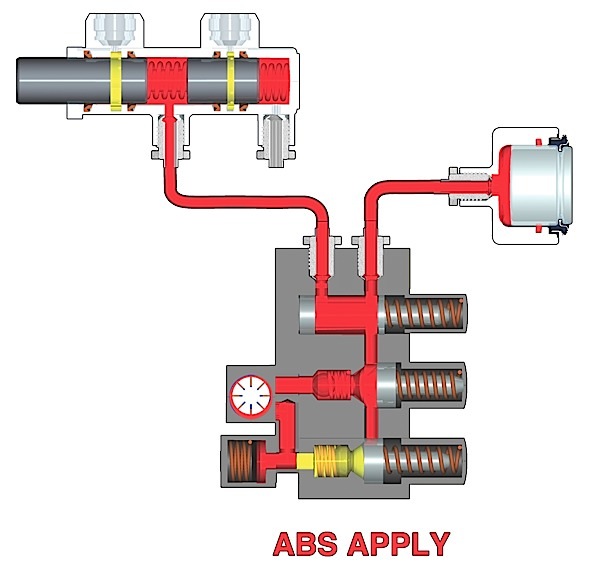
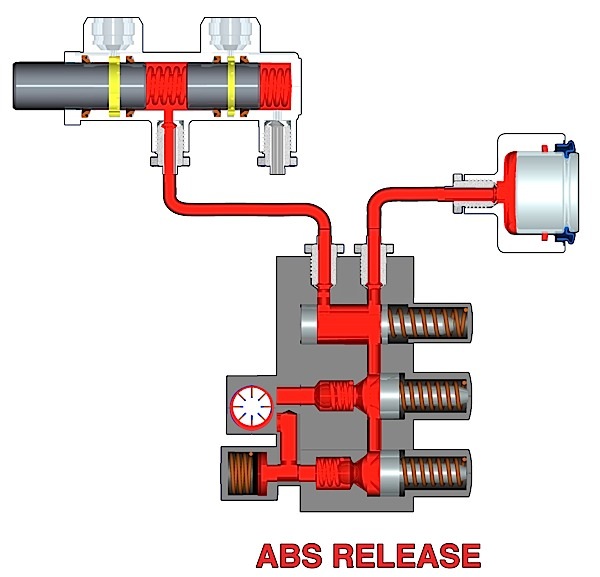
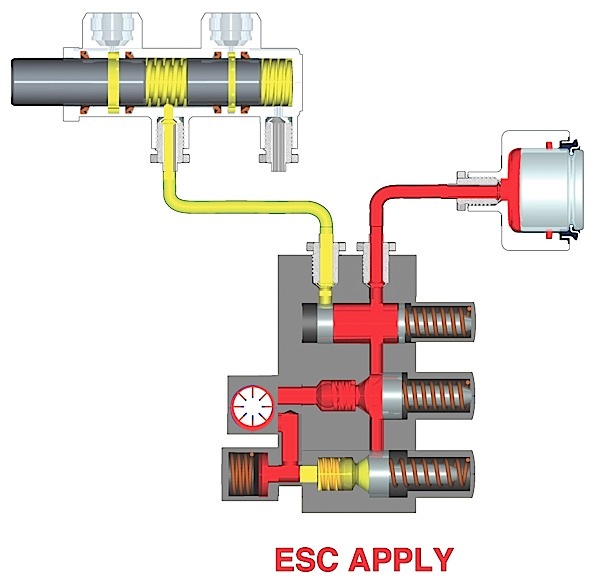






The process of replacing the hub unit on a Tesla is the same as many cars and light trucks.
The most common EVs on the road come from Tesla. The Model S, 3, X and Y share similar drivetrains and wheel-end components like the wheel-bearing hub units.
The process of replacing the hub unit on a Tesla is the same as many cars and light trucks. You do not need insulated tools or gloves to replace chassis parts. The only complications come with initial diagnostics and setting modes for service procedures.
The edge code is a language written by engineers, federal entities and industry associations.

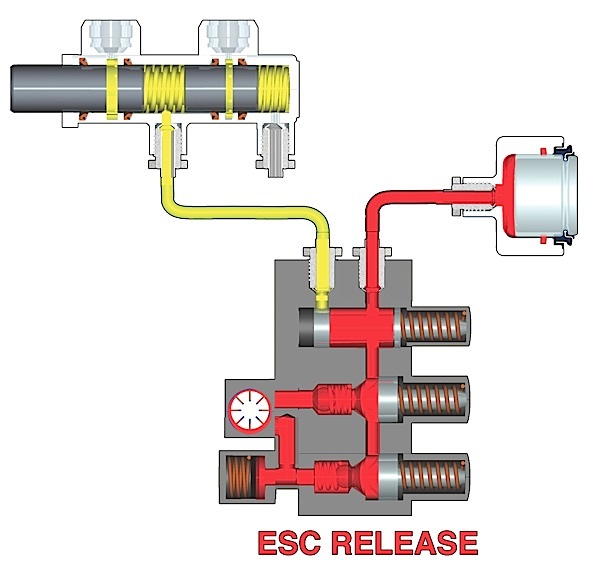
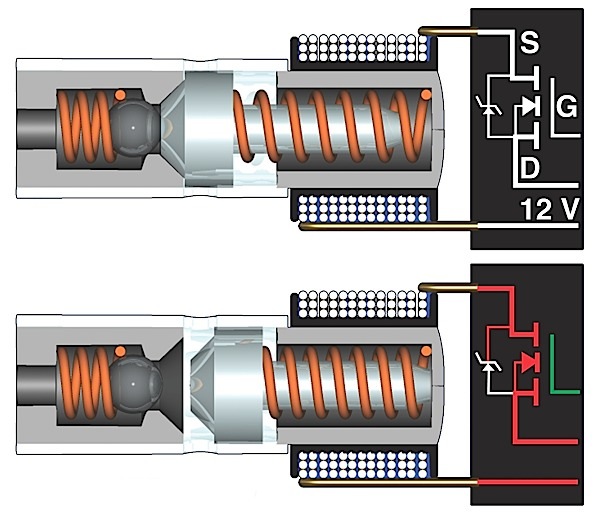
Reducing brake drag on late-model vehicles is not accomplished by a single component; it takes a system.

The brake repair market is starting to become dominated by a “good enough” mentality.

For a vacuum brake booster to work, it needs a source of vacuum.

With the right tools and service information, it is possible to resolve a customer’s complaint.

All wheel speed sensor codes are just the starting points of a diagnosis and not a reason to order a part.

Learn the latest about the salmon-inspired law.

Brake dust can indicate what could be wrong. This video is sponsored by Auto Value and Bumper to Bumper.
