The 2008-2017 Chevrolet Traverse, Saturn Outlook, GMC Acadia and Buick Enclave represent a large portion of GM. These vehicles can be front- or all-wheel drive. All models have the same rear disc brake setup with the parking brake in the hat of the rotor. All Lambda platform vehicles incorporate Tire Pressure Monitoring (TPM) ABS and Stabilitrak electronic stability control.
Front Pad Removal
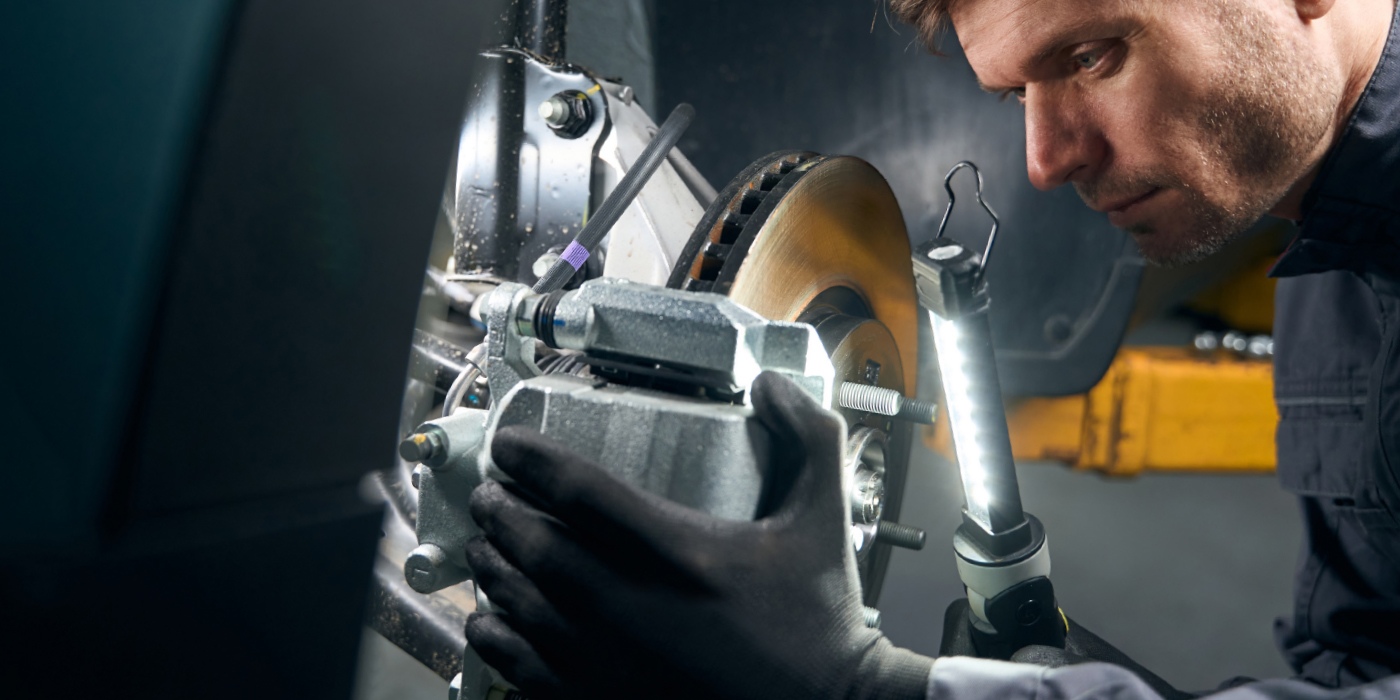
Before replacing the pads, inspect the master cylinder to ensure that it has not been topped off before retracting the pistons into the caliper bores. The front brakes are a floating dual-piston caliper type; the pistons are phenolic. The caliper bridge bolts have a guide pin and bolt that attach the caliper to the bracket. Removing the bottom bolt allows the caliper to be pivoted out of the bracket.
To release the pad from the clip, there are tabs at the ends of pad that are depressed to release the pad. The pads have noise dampening material attached to the back of the pads.
Front Pad Install
Inspect the dust boots for damage and replace if necessary.
Inspect the guide pins and replace and lubricate if necessary. The boot is to be seated in the grooves of the caliper bracket and guide pin.

Install new anti-rattle clips and pads, rotate the caliper and align the flats on the guide pin to the mounting ear of the caliper. Torque the guide pin bolts to 64 Nm (30 ft/lbs).
The caliper bracket bolts on this vehicle use high strength thread locker to hold it in place (it is the “red stuff”). Make sure to clean the old thread locker material off the threads with denatured alcohol before putting new thread locker on. The bolts should be tightened to a whopping 129 ft/lbs!
Rear Pads
Inspect the dust boots for damage and replace the caliper if necessary. Inspect the guide pins and replace and lubricate if necessary. The boot is to be seated in the grooves of the caliper bracket and guide pin. Install new anti-rattle clips and pads, rotate the caliper and align the flats on the guide pin to the mounting ear of the caliper. Torque the guide pin bolts to 64 Nm (30 ft/lbs).
Like in the front, the rear caliper brackets use thread locker. Make sure to clean threads. Then torque the bolts to 148 ft/lbs.
Rotor and Hub Inspection Specifications:
Front Brakes
• New thickness: 29.0 mm (1.14”)
• Min thickness: 27.5 mm (1.08”)
• Max allowable assembled lateral runout: 0.06 mm (0.002”)
• Max allowable scoring: 1.50 mm (0.059”)
• Max allowable thickness variation 0.025 mm (0.001”)
Rear Brakes
• Min thickness: 18.4 mm (0.72”)
• New thickness: 20 mm (0.79”)
• Max allowable assembled lateral runout: 0.06 mm (0.002”)
• Maximum allowable scoring: 1.50 mm (0.059”)
• Max allowable thickness variation: 0.025 mm (0.001”)
Rotor Lateral RunOut Inspection Procedure
The hub and rotor are matched with the rotor indexed to the hub and secured with a Torx setscrew. Three lugs should be used to ensure the rotor is secured to the hub.
Attach the dial indicator to the steering knuckle and position the indicator at 90º to the rotor surface approximately 12.7 mm (0.50”) from the rotor. Replace any rotor that is worn or machined below this specification.
Parking Brake
The parking brake is located in the hat section of the rear rotor. It is applied mechanically by a cable actuated cam and lever located in the bottom of the backing plate. The shoes are attached to the backing plate with a pin and leaf spring. The shoes are held against the cam and lever with a spring.
A spring is also used to hold the shoes against the adjusting screw. The shoes are adjusted by rotating the star wheel on an adjusting screw located at the top of the backing plate. There is an adjusting slot located in the hat section of the rotor. It will require an old fashioned adjusting spoon to reach the star wheel.
The method of adjustment is to turn the rotor and adjust the star wheel until the shoes drag on the drum. Then back off the adjusting star until the rotor turns free. The rotor should be secured with the retaining screw and three lug nuts when the parking brake shoes are adjusted.
Bleeding
Like most modern brake systems with ABS, the system has an automated bleed procedure that requires a scan tool. An automated bleed is required if a hydraulic component like the modulator unit is replaced. Even if you are performing a gravity, pressure or manual bleed, it is a good idea to run an automated bleed procedure as a way to ensure the there is not any air trapped in the brake modulator or proportioning valve assembly.
The bleeding sequence is left front, left rear, right front and right rear. If pressure bleeding, GM recommends between 25-30 psi.