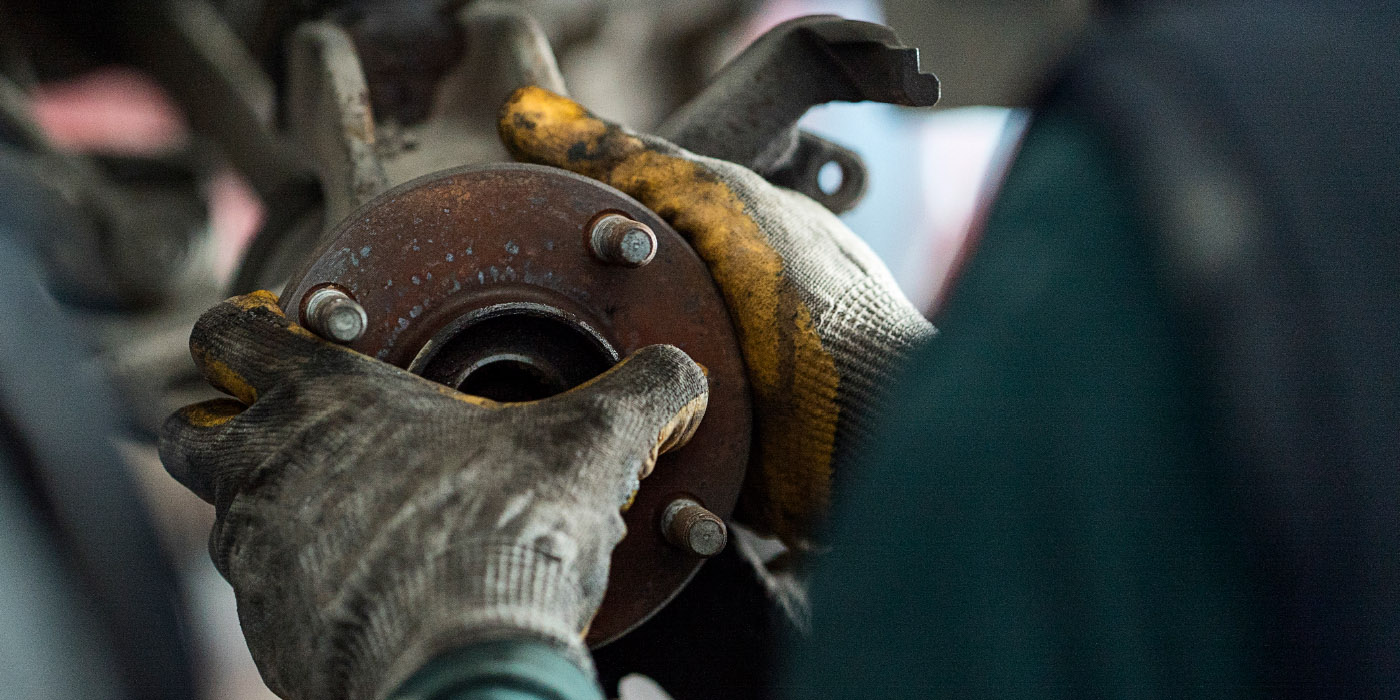
Under extreme braking conditions, some lubricants can’t stand the heat and melt off, evaporate, oxidize or burn. That’s why ordinary, general-purpose chassis grease should never be used for lubricating brake components. It simply won’t hold up. What’s needed is a specially formulated, high-temperature brake grease that can withstand the heat, but won’t harm rubber seals or plastic bushings. Petroleum-based lubricants should never be used for brake assembly work because mineral oils can cause seals to swell and fail.
What needs to be lubricated?
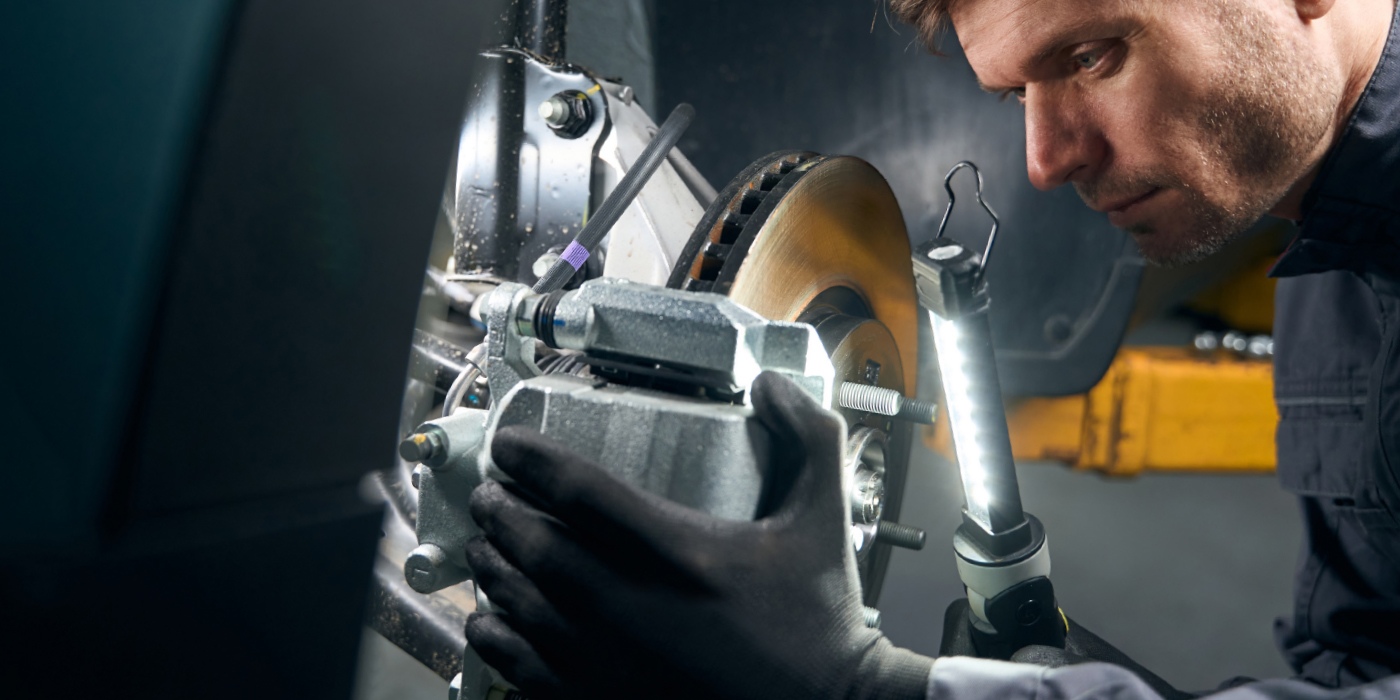
Lubricate any mechanical components in the brake system that slide, move, rotate or bear pressure. On disc brakes, lubrication points include the caliper slides and bushings, self-adjuster mechanisms on rear disc brakes with calipers, and the parking brake cables and linkage.
Why do lubricants work to reduce some brake noises?
When a caliper finger is lubricated at the point where it touches the brake pad, the lubricant creates a boundary layer that keeps the vibration of the brake pad from exciting the caliper finger and the caliper. This is one approach to solving NVH problems, but it can have limitations. Lubricants do not dampen forces by adding extra mass like a brake shim. Also, lubricants can not fill in pitting on brake slides, nor do they insulate against vibration. Plus, they are only effective for some frequencies.
What are the types of lubricants?
There are several basic types of brake lubricants: those that are designed for lubricating hardware and mechanical components and typically contain a high percentage of solids (dry-film lubricants), and those that are designed for lubricating seals, boots and other internal parts when assembling calipers, wheel cylinders and master cylinders. Lubricant for hardware is a special high-temperature grease designed to provide lasting protection. The lubricant may be a synthetic- or silicone-based product.
Moly
Synthetic-based, boundary-type lubricants that come in tube, paste or stick form have a high solids content and typically contain a variety of friction-reducing ingredients such as molybdenum disulfide (moly or MOS2) and graphite.
Moly and graphite are both dry-film lubricants that can handle high temperatures and pressures. Some of these products are rated to withstand intermittent temperatures as high as 2,400° F!
Moly won’t evaporate or burn off over time, and it won’t attract or hold dirt like ordinary “wet” greases can.
Silicone
Silicone-based brake grease is designed for caliper and wheel cylinder assembly work because silicone is an excellent lubricant for rubber and plastic. Silcone’s normal working range is -40° F to 400° F, but it does not have the high temperature staying power of a high-solids synthetic lubricant. Also, silicone is a “wet” lubricant that can attract and hold dirt, making it less suitable for lubricating external metal-to-metal contact points. This type of product is best suited for assembling calipers, wheel cylinders and master cylinders.
Regardless of what type of brake lubricant you choose, always follow the supplier’s recommendations as to how their product should be used.