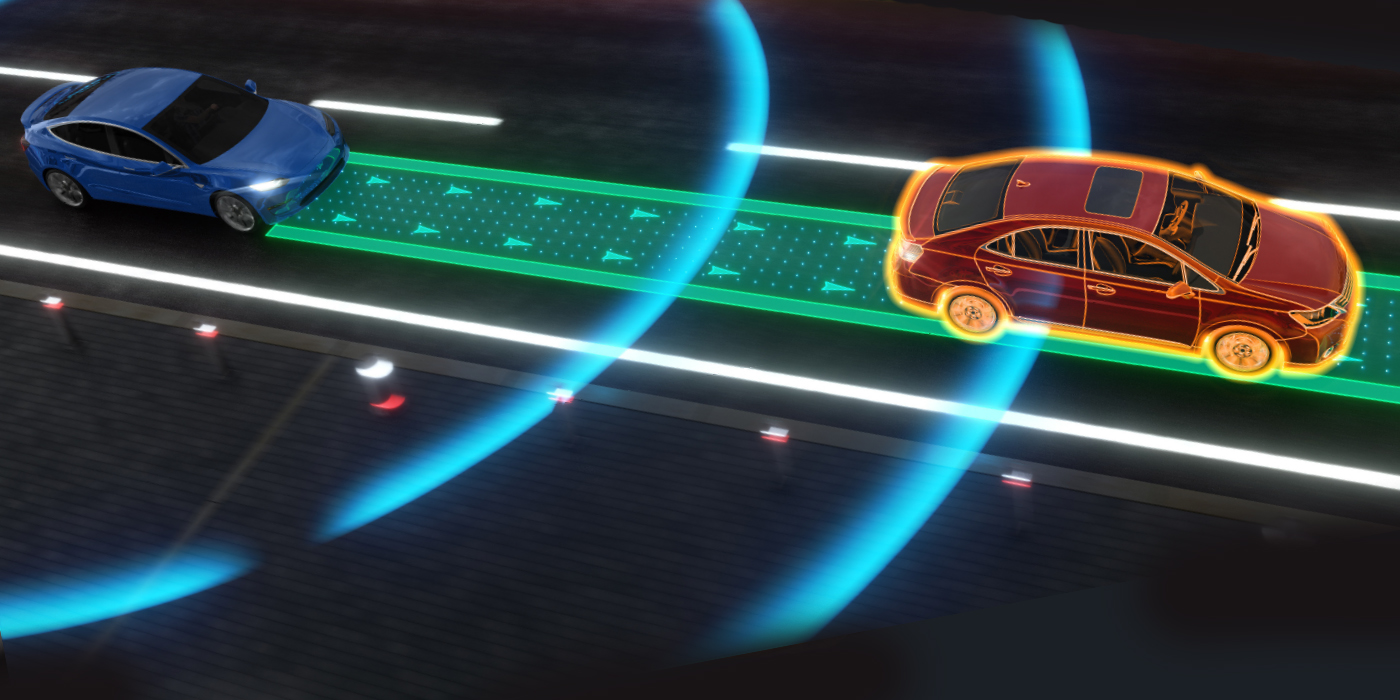
Most modern air ride systems can be a mystery to service if you do not have the right tools and information. One of the most misunderstood operations is when the car is started or “wakes up” without the key on.
Most air ride modules never go completely asleep. The system will wake up at set intervals to trim the vehicle since air pressure is dependent on air temperature. In some cases, the system wakes up when the doors are unlocked or the trunk is opened.
When the air ride system wakes up with the key in the ignition, the air ride module starts to talk to the other modules. These “handshakes” and exchanges occur in milliseconds. If the module cannot communicate with another module or access networked data through a gateway module, it will set a code or go into a safe mode. This sequence of events can be found in your service information system.
When diagnosing a communications issue, you might be required to go into a few modules other than the air ride module. In my experience, the main problems can be found on the CAN network and gateway modules. Information regarding ambient air temperature, door switches and security often comes from modules that are not on the same bus as the air ride module. Rather, this information has to go through a gateway module. Often, the information can go missing or become scrambled.
If the wake-up protocols go as written, they will perform a series of self-checks to make sure the system has pressure. This step typically involves opening the solenoids for the wheels for a set period, or with a set amount of pressure or amount of change in the ride-height sensors. Most vehicles will then trim the ride height starting in the rear before moving to the front. This can take less than a second. Some systems will perform a second check if the car is stopped and in gear.
During the operation of the system, the system is comparing compressor run times and reservoir pressure against the change in the ride-height sensor. Other information like barometric pressure, ambient air temperature and vehicle speed will be used to self-diagnose the system.
Air Ride Modes
The modern air ride vehicle could have several different modes depending on a few variables. As each mode is initiated, the computer will bleed off or add pressure to the corners to trim the vehicle. Each mode has a different way it filters sensor data from the ride-height sensors. In some cases, modes like small, fast suspension movements will be ignored while larger changes in ride height will be corrected.
Here are some examples of the modes that may be found on an air ride vehicle.
Preliminary/Wake: This mode is used when a door or a door/trunk is opened. This mode does some housekeeping with the sensors and valves. Only air from the reservoir is used to trim the vehicle.
Sleep Mode: This occurs when some vehicles sit for 30 minutes. In sleep mode, only lowering corrections that are permitted will balance the vehicle height to the lowest corner.
Post/Park Mode: This mode is used when the car is stationary with the key off. The ride height adjusts over time depending on the temperature.
Stance Mode: This mode is used when the vehicle is running and stationary. In this mode, the system will quickly react to changes in ride height.
Speed-Lowering Mode: This mode engages at higher speeds to improve handling as well as improve aerodynamics for fuel economy. Some vehicles will have different speed thresholds attached to this mode.
Jacking Mode: In this mode, the system monitors height changes at the corner that is being jacked up. If the system lowers the air suspension, but no reduction in height is achieved, it will cause the system to time-out quickly. If all four ride-height sensors change by preset values, the system will recognize the vehicle is being lifted on a hoist and stop adjusting the pressures. This mode typically will stop when the vehicle starts to move.
Additional modes exist depending on the vehicle. Some modes, like sleep and park, will work while the vehicle is off. When the key is off, an air ride system will periodically wake up to check the ride height and go back to sleep to conserve power. But, 99% of systems will not run the compressor when the engine is not running.
Compressor Management
There are two types of compressor arrangements — those with reservoirs and those without reservoirs. Most systems use the compressor to fill a reservoir. The air in the reservoir is then used to trim the pressure in the air ride units. When the reservoir is depleted or the parameters are right, the system turns on the compressor.